Exogamy, the social practice of marrying outside one's social group or community, helps promote genetic diversity and strengthens alliances between distinct groups. This custom has been observed across various cultures, influencing social structure and inheritance patterns. Explore the rest of the article to understand how exogamy shapes relationships and cultural evolution.
Table of Comparison
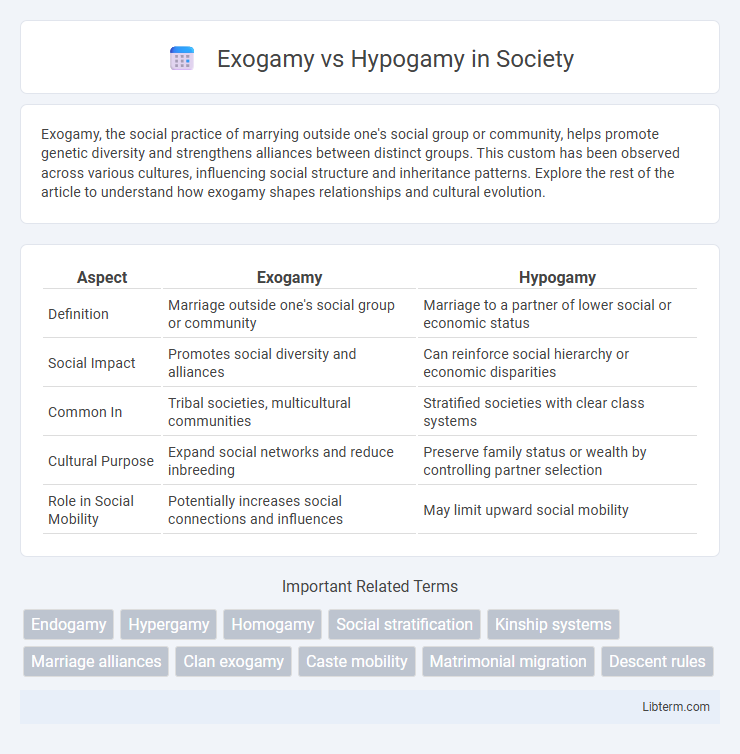
| Aspect | Exogamy | Hypogamy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Marriage outside one's social group or community | Marriage to a partner of lower social or economic status |
| Social Impact | Promotes social diversity and alliances | Can reinforce social hierarchy or economic disparities |
| Common In | Tribal societies, multicultural communities | Stratified societies with clear class systems |
| Cultural Purpose | Expand social networks and reduce inbreeding | Preserve family status or wealth by controlling partner selection |
| Role in Social Mobility | Potentially increases social connections and influences | May limit upward social mobility |
Understanding Exogamy: Definition and Examples
Exogamy refers to the social practice of marrying outside one's specific social group, clan, or community to promote genetic diversity and strengthen social ties. Common examples include tribes encouraging marriage with members of other tribes or ethnic groups, ensuring alliances and preventing inbreeding. This practice contrasts with endogamy, where individuals marry within their social group, highlighting exogamy's role in expanding social networks.
Hypogamy Explained: Key Concepts and Patterns
Hypogamy refers to the social pattern where an individual marries someone of lower socioeconomic status, contrasting with exogamy which emphasizes marriage outside one's social group. Key concepts in hypogamy include status descent and the aspiration for upward social mobility through marital unions, often linked to gender roles and cultural norms. Patterns of hypogamy vary across cultures but commonly reveal how economic, educational, and occupational disparities influence marital choices and social stratification.
Historical Roots of Exogamy and Hypogamy
Exogamy and hypogamy have distinct historical roots tied to social structure and marriage norms. Exogamy, rooted in ancient tribal societies, promoted genetic diversity and alliances by requiring marriage outside one's social or kin group. Hypogamy historically emerged in stratified societies, reflecting social mobility patterns where individuals marry into lower social strata, often influenced by economic and class dynamics.
Cultural Perspectives on Marriage Choices
Exogamy encourages marriage outside one's social or cultural group to promote genetic diversity and social alliances, prevalent in many tribal and traditional societies. Hypogamy involves marrying into a lower social or economic status, often influenced by cultural norms that prioritize familial stability or economic benefits. These marriage choices reflect deep-rooted cultural values shaping social hierarchies, kinship systems, and community cohesion.
Social and Economic Implications
Exogamy promotes social integration and expands economic networks by encouraging marriage outside one's social group, increasing access to diverse resources and cultural capital. Hypogamy, where individuals marry into a lower socioeconomic status, can lead to shifts in wealth distribution and social mobility, often challenging traditional class boundaries. Both practices influence social stratification, with exogamy fostering broader alliances and hypogamy potentially reducing inequality through downward social merging.
Psychological Factors Influencing Marital Preferences
Psychological factors influencing marital preferences in exogamy and hypogamy include individual values, social identity, and perceived social status. Exogamy often involves a preference for partners outside one's social group to increase genetic diversity and social alliances, while hypogamy reflects a psychological tendency to marry someone of lower socioeconomic status, potentially driven by security or traditional gender roles. These preferences are shaped by cognitive biases, emotional needs, and cultural conditioning that affect mate selection processes.
Exogamy vs Hypogamy: Comparative Analysis
Exogamy involves marrying outside one's social group or community, promoting genetic diversity and social alliances, while hypogamy refers to marrying into a lower social or economic class, often influenced by cultural or personal factors. Exogamous marriages tend to expand social networks and cultural exchange, whereas hypogamous unions may challenge traditional social hierarchies and impact family dynamics differently. Comparative analysis reveals exogamy emphasizes external social ties, whereas hypogamy highlights socioeconomic mobility or preferences within marital choices.
Changing Trends in Modern Societies
Exogamy, the practice of marrying outside one's social group, contrasts with hypogamy, where individuals marry into a lower social or economic status. Modern societies witness shifting trends as globalization and online dating platforms expand social networks, increasing exogamous unions across ethnic and cultural lines. Simultaneously, economic changes and evolving gender roles contribute to a decline in hypogamous marriages, reflecting greater social mobility and changing perceptions of status in partner selection.
Impact on Family Structure and Social Mobility
Exogamy promotes alliances between different social groups, expanding family networks and enhancing social mobility by integrating diverse cultural and economic resources. Hypogamy often consolidates family wealth and status within a lower or similar social stratum, potentially limiting upward social mobility but strengthening internal family cohesion. The choice between exogamy and hypogamy significantly shapes family structures, influencing patterns of inheritance, social capital, and intergenerational mobility.
Future Directions in Marital Patterns
Future directions in marital patterns emphasize the evolving dynamics between exogamy, marrying outside one's social group, and hypogamy, marrying into a socially lower status. Sociological trends indicate increasing acceptance of exogamous unions driven by globalization and multicultural integration, while hypogamy faces persistent challenges due to entrenched social hierarchies. Emerging research explores how digital matchmaking and shifting economic roles influence these patterns, potentially reshaping traditional marital choices.
Exogamy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com