Manifest function refers to the recognized and intended consequences of social activities or institutions that contribute positively to society, such as education providing knowledge and skills. Understanding how manifest functions operate can clarify the explicit purposes behind social structures and their roles in maintaining social order. Explore the rest of the article to see how manifest functions shape your social environment and influence everyday interactions.
Table of Comparison
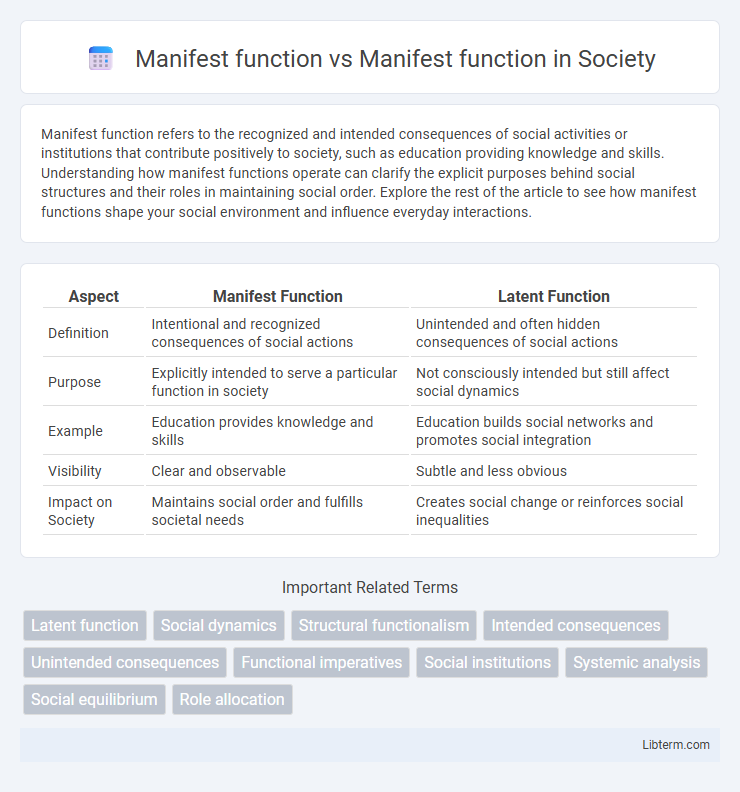
| Aspect | Manifest Function | Latent Function |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Intentional and recognized consequences of social actions | Unintended and often hidden consequences of social actions |
| Purpose | Explicitly intended to serve a particular function in society | Not consciously intended but still affect social dynamics |
| Example | Education provides knowledge and skills | Education builds social networks and promotes social integration |
| Visibility | Clear and observable | Subtle and less obvious |
| Impact on Society | Maintains social order and fulfills societal needs | Creates social change or reinforces social inequalities |
Introduction to Manifest Functions
Manifest functions refer to the intended and recognized consequences of social institutions or actions, designed to fulfill specific purposes within society. In sociological theory, these functions contrast with latent functions, which are unintended and often hidden outcomes. Understanding manifest functions helps clarify how social structures contribute to societal stability and collective goals.
Defining Manifest Functions in Sociology
Defining manifest functions in sociology involves identifying the explicit, intended, and recognized consequences of social institutions or actions that contribute to societal stability. Manifest functions are contrasted with latent functions, which are unintended and often hidden outcomes. Understanding manifest functions helps sociologists analyze how social structures fulfill specific roles and maintain social order.
Historical Background of Manifest Functions
Manifest functions, a concept introduced by sociologist Robert K. Merton, refer to the intended and recognized consequences of social institutions and actions. Emerging from structural functionalism in the mid-20th century, this concept contrasts with latent functions, which are unintended and hidden outcomes. The historical background of manifest functions is rooted in early sociological theories that sought to explain the purposeful roles institutions play in maintaining social stability.
Key Characteristics of Manifest Functions
Manifest functions refer to the explicit, intended, and recognized outcomes of social actions or institutions, characterized by their planned and easily observable nature. These functions produce consequences that participants expect and desire, such as education promoting knowledge and skills. Key characteristics include intentionality, clarity, and societal recognition, distinguishing manifest functions from latent functions, which are unintended and often hidden outcomes.
Manifest Functions in Social Institutions
Manifest functions in social institutions are the recognized and intended roles that contribute to the stability and functioning of society, such as education systems imparting knowledge and socializing individuals. These explicit functions facilitate social cohesion and the fulfillment of societal needs by establishing norms and roles within organizations like families, schools, and governments. Understanding manifest functions helps clarify how institutions maintain order and support the common good through their planned activities.
Real-World Examples of Manifest Functions
Manifest functions refer to the explicit, intended consequences of social institutions or actions, such as schools providing formal education to students. In contrast, latent functions are the hidden, unintended benefits like fostering social networks among peers within educational settings. For example, the manifest function of a hospital is to provide medical treatment, while a latent function includes offering employment opportunities to the community.
Manifest Function vs Latent Function
Manifest functions are the recognized and intended consequences of social institutions or actions, such as education providing knowledge and skills to students. Latent functions, on the other hand, are the unrecognized or unintended consequences, like schools fostering social networks or reinforcing social norms. Understanding the distinction between manifest functions and latent functions helps sociologists analyze both the explicit goals and subtle impacts of social phenomena.
Importance of Manifest Functions in Analysis
Manifest functions provide clear, intended consequences that help sociologists understand the explicit purposes of social institutions, behaviors, or policies. Their importance in analysis lies in revealing the overt roles these functions play in maintaining social stability and meeting societal needs, offering measurable outcomes for research. By focusing on manifest functions, analysts can distinguish between intended effects and latent functions, enabling a more precise evaluation of social phenomena.
Theoretical Perspectives on Manifest Functions
Manifest functions are the explicit, intended outcomes of social institutions or actions recognized in functionalist theory, highlighting their role in maintaining societal stability and order. Latent functions, by contrast, represent the unintended or hidden consequences that may reinforce or disrupt social systems. Structural functionalism emphasizes manifest functions as critical components for understanding how institutions contribute to social cohesion and the fulfillment of societal needs.
Conclusion: Role of Manifest Functions in Society
Manifest functions serve as the intended and recognized consequences of social institutions, providing stability and cohesion by fulfilling societal needs. They reinforce social norms and contribute to the smooth operation of society by clearly defining roles and expectations. Understanding the role of manifest functions highlights how explicit objectives of institutions promote social order and continuity.
Manifest function Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com