Industrial society revolutionized the way humans produce goods, shifting from agrarian economies to mechanized manufacturing and mass production. This transformation brought rapid urbanization, technological advancements, and significant social changes that shaped modern economies and lifestyles. Discover how industrial society continues to influence Your world and the future by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
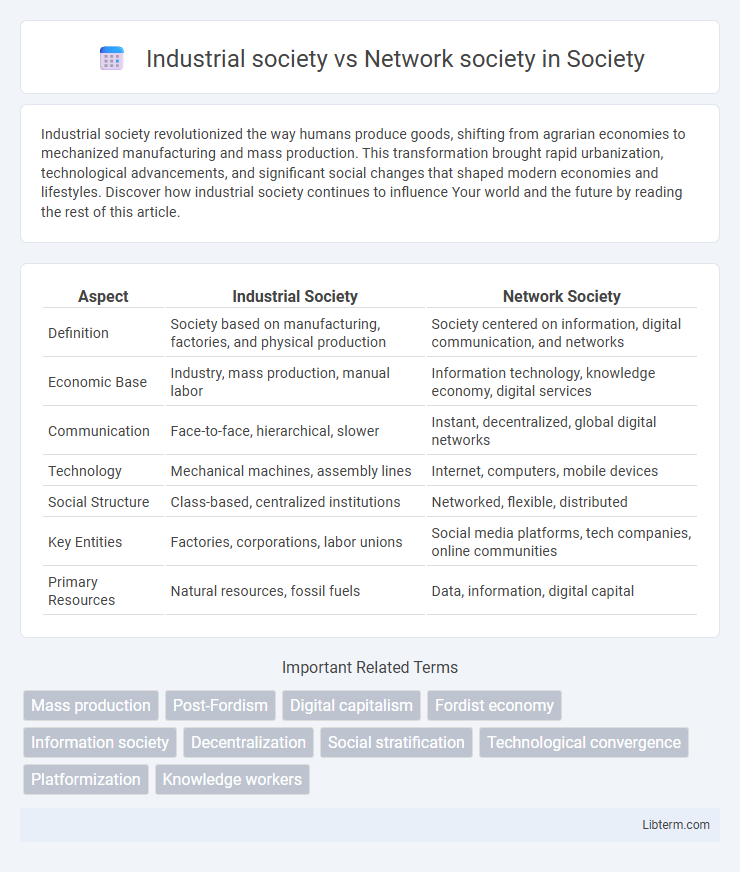
| Aspect | Industrial Society | Network Society |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Society based on manufacturing, factories, and physical production | Society centered on information, digital communication, and networks |
| Economic Base | Industry, mass production, manual labor | Information technology, knowledge economy, digital services |
| Communication | Face-to-face, hierarchical, slower | Instant, decentralized, global digital networks |
| Technology | Mechanical machines, assembly lines | Internet, computers, mobile devices |
| Social Structure | Class-based, centralized institutions | Networked, flexible, distributed |
| Key Entities | Factories, corporations, labor unions | Social media platforms, tech companies, online communities |
| Primary Resources | Natural resources, fossil fuels | Data, information, digital capital |
Defining Industrial Society
Industrial society is characterized by mass production, mechanized manufacturing, and centralized labor within factories, driving economic growth through physical goods and infrastructure development. It relies heavily on hierarchical organizational structures, standardized processes, and fossil fuel energy sources to power machinery and transportation networks. The shift from agrarian to industrial modes transformed social relations, urbanization rates, and labor specialization, underpinning the rise of capitalism and modern economic systems.
Understanding Network Society
The Network Society is characterized by the pervasive use of digital communication technologies that organize social, economic, and political activities through interconnected networks, unlike the Industrial Society, which relies on mass production and hierarchical structures. Information flows in real-time within the Network Society, enabling decentralized decision-making and fostering innovation through global connectivity. Key elements such as the Internet, social media platforms, and Big Data analytics drive the transformation from traditional industrial frameworks to dynamic, flexible, and knowledge-based economies.
Historical Evolution: From Industry to Networks
The historical evolution from industrial society to network society marks a transition from centralized manufacturing and mass production to decentralized digital communication and information sharing. Industrial society was defined by factories, hierarchical organizations, and standardized labor, whereas network society thrives on interconnectedness facilitated by the internet, social media, and real-time data exchange. This shift underscores the move from material-based economies toward knowledge-based economies driven by digital networks and information technology.
Key Characteristics of Industrial Society
Industrial society is characterized by large-scale manufacturing based on mechanized production, centralized factories, and a strong emphasis on physical labor and mass production. It relies heavily on hierarchical organizational structures, standardized processes, and extensive use of fossil fuels for energy. Economic activities are predominantly focused on tangible goods, with social organization centered around formal institutions and urbanization.
Core Features of Network Society
Network society is characterized by decentralized information flow, reliance on digital communication technologies, and global interconnectedness, contrasting with the hierarchical, production-based structure of industrial society. Core features include real-time data exchange, the dominance of knowledge work, and social organization through networks rather than institutions. This transformation fosters innovation, flexibility, and a shift from material goods to information as the primary economic resource.
Economic Structures: Factories vs Digital Platforms
Industrial society's economic structure is centered around factories that rely on mass production, standardized processes, and centralized labor to create goods efficiently. Network society shifts economic power to digital platforms that facilitate value creation through decentralized, user-driven interactions, and data exchange. This transition enables flexible, scalable business models leveraging global connectivity and real-time information flows.
Social Organization and Power Dynamics
Industrial society is characterized by hierarchical social organization and centralized power structures dominated by large bureaucracies and mass production systems. Network society features decentralized, flexible social organization enabled by digital communication technologies, facilitating dispersed power dynamics across interconnected nodes. The shift from industrial to network society transforms power from rigid institutional control to dynamic, network-based influence.
Communication Patterns and Information Flow
Industrial society relies on centralized communication patterns with hierarchical information flow, where messages follow structured channels controlled by specific institutions. Network society features decentralized communication networks that enable real-time, multidirectional information exchange across global digital platforms. This shift enhances the speed, accessibility, and interactivity of information flow, transforming social, economic, and cultural dynamics.
Impacts on Work, Education, and Lifestyle
Industrial society centralized work in factories with routine tasks, while network society promotes remote, flexible jobs driven by digital connectivity. Education shifted from standardized, classroom-based learning to personalized, online platforms emphasizing continuous skill development. Lifestyle transformations in network society include increased reliance on digital communication, blurred boundaries between work and leisure, and greater access to global information and resources.
Future Trends and Societal Transformation
The transition from industrial society to network society is marked by a shift from centralized manufacturing and hierarchical organization to decentralized digital networks enabling real-time communication and collaboration. Future trends emphasize the rise of artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things, and blockchain technologies, driving greater personalization, automation, and interconnectedness in social, economic, and political structures. This societal transformation fosters knowledge-based economies and redefines power dynamics, prioritizing information flow, innovation, and digital inclusivity over traditional industrial production frameworks.
Industrial society Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com