Consumer society shapes modern lifestyles by encouraging constant acquisition of goods and services, often driven by advertising and social status. This culture impacts personal finances, environmental sustainability, and social values, influencing how you view success and happiness. Explore the rest of the article to understand how consumerism affects your daily life and global dynamics.
Table of Comparison
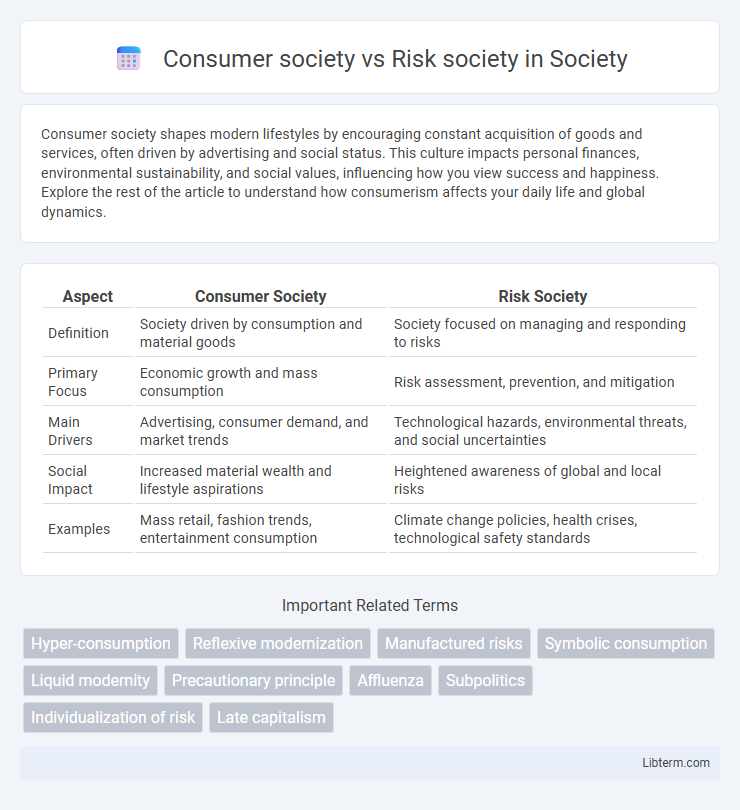
| Aspect | Consumer Society | Risk Society |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Society driven by consumption and material goods | Society focused on managing and responding to risks |
| Primary Focus | Economic growth and mass consumption | Risk assessment, prevention, and mitigation |
| Main Drivers | Advertising, consumer demand, and market trends | Technological hazards, environmental threats, and social uncertainties |
| Social Impact | Increased material wealth and lifestyle aspirations | Heightened awareness of global and local risks |
| Examples | Mass retail, fashion trends, entertainment consumption | Climate change policies, health crises, technological safety standards |
Understanding Consumer Society: Key Characteristics
Consumer society is characterized by high levels of consumption driven by mass production, advertising, and credit availability, fostering a culture of materialism and identity formation through goods. It features widespread access to goods and services, which shapes social status and personal satisfaction, often leading to environmental depletion and resource overuse. Understanding consumer society involves analyzing the economic, social, and psychological dimensions that promote continuous demand and consumption patterns.
Defining Risk Society: Origins and Concepts
The concept of Risk Society was introduced by sociologist Ulrich Beck in his 1986 work, highlighting a shift from industrial society to one preoccupied with managing risks generated by technological and economic progress. Risk Society emphasizes the systemic nature of modern risks such as environmental hazards, financial crises, and technological failures, which are often unpredictable and affect global populations. This contrasts with consumer society, where social behavior is primarily driven by consumption patterns and the pursuit of material goods.
Historical Evolution: From Consumerism to Risk Awareness
The historical evolution from consumer society to risk society reveals a shift from valuing mass consumption as a marker of economic success to recognizing the complex risks associated with technological advancement and environmental degradation. Consumer society, rooted in post-World War II industrial growth, prioritized material goods and economic expansion, but rising awareness of climate change, financial crises, and health emergencies has propelled the emergence of risk society. This transition underscores a growing emphasis on managing uncertainties and preventing global hazards that threaten social stability and sustainable development.
Drivers of Consumer Society: Materialism and Identity
The consumer society is primarily driven by materialism, where individuals seek to acquire goods as a means to express personal identity and social status. Consumption patterns reflect and reinforce social values, shaping lifestyles and self-perceptions through brand affiliation and product ownership. This focus on material wealth contrasts with risk society dynamics, which emphasize awareness and management of systemic risks over individual consumption behaviors.
Pillars of Risk Society: Uncertainty and Globalization
Risk society, a concept developed by sociologist Ulrich Beck, rests on the pillars of uncertainty and globalization, highlighting the pervasive and unpredictable nature of modern risks. Unlike the consumer society, which centers on consumption and material wealth, the risk society emphasizes how technological advancements and global interconnectedness create complex, transboundary risks such as climate change, pandemics, and financial crises. This shift underscores a collective awareness of vulnerabilities that transcend national borders, requiring new forms of governance and social cooperation to manage these uncertain global threats.
Impact on Social Structures: Comparing Values and Priorities
Consumer society prioritizes material wealth, consumption, and individualism, shaping social structures centered on economic growth and market-driven values. Risk society emphasizes awareness of global risks such as environmental hazards and technological threats, leading to social structures that prioritize collective safety, sustainability, and precautionary principles. The shift from consumption to risk awareness transforms social priorities from short-term gains to long-term resilience and social equity.
Environmental Consequences: Consumption vs. Risk Management
Consumer society drives environmental degradation through excessive resource extraction and waste generation, intensifying ecological footprints worldwide. Risk society emphasizes proactive risk management, addressing environmental hazards by implementing regulations and promoting sustainable practices to mitigate consequences. The tension between unchecked consumption and strategic risk governance shapes contemporary environmental policies and global sustainability efforts.
Economic Implications: Market Forces and Vulnerabilities
Consumer society drives economic growth through increased demand and consumption, stimulating market forces and innovation. Risk society highlights vulnerabilities by exposing how economic systems are susceptible to crises like financial collapses, environmental disasters, and health pandemics. These vulnerabilities challenge market stability, necessitating adaptive risk management strategies and regulatory interventions to mitigate systemic economic disruptions.
Cultural Shifts: Changing Attitudes Towards Safety and Consumption
Consumer society prioritizes material acquisition and instant gratification, with cultural values centered on consumption as a symbol of status and success. Risk society shifts the focus toward managing potential hazards associated with consumption, fostering heightened awareness of safety, environmental impact, and health consequences. This cultural transformation emphasizes precaution, sustainability, and informed decision-making in everyday consumer behavior.
Navigating the Future: Integrating Consumer and Risk Perspectives
Navigating the future requires balancing consumer society's emphasis on material acquisition with risk society's focus on managing uncertainties such as environmental hazards and technological threats. Integrating these perspectives highlights the need for sustainable consumption patterns that mitigate risks while promoting economic growth and social well-being. Understanding this dynamic enables policymakers and businesses to develop strategies that address both consumer demands and emerging global risks.
Consumer society Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com