Status inconsistency occurs when an individual holds different social positions with conflicting levels of prestige, wealth, or power, leading to tension and role strain. This phenomenon can affect social interactions, self-perception, and societal expectations, influencing both personal identity and group dynamics. Explore the full article to understand how status inconsistency impacts your social life and broader community relationships.
Table of Comparison
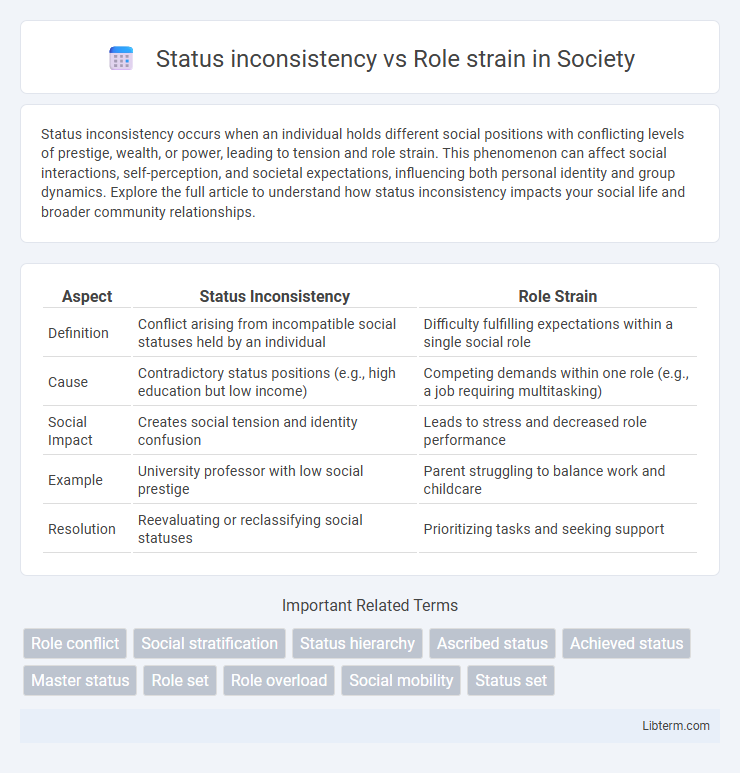
| Aspect | Status Inconsistency | Role Strain |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Conflict arising from incompatible social statuses held by an individual | Difficulty fulfilling expectations within a single social role |
| Cause | Contradictory status positions (e.g., high education but low income) | Competing demands within one role (e.g., a job requiring multitasking) |
| Social Impact | Creates social tension and identity confusion | Leads to stress and decreased role performance |
| Example | University professor with low social prestige | Parent struggling to balance work and childcare |
| Resolution | Reevaluating or reclassifying social statuses | Prioritizing tasks and seeking support |
Understanding Status Inconsistency
Status inconsistency occurs when an individual holds multiple social positions that conflict in terms of prestige or rank, creating tension and ambiguity about their social identity. This conflict differs from role strain, which involves difficulty meeting the demands within a single role rather than between roles. Understanding status inconsistency helps clarify how contradictory social statuses impact behavior, self-perception, and social interactions.
Defining Role Strain
Role strain occurs when an individual experiences difficulty fulfilling the expectations of a single social role due to conflicting demands or limited resources. It contrasts with status inconsistency, which arises from holding multiple social positions with conflicting prestige or expectations. Understanding role strain helps to analyze the stress caused by incompatible obligations within one role in sociology.
Key Differences Between Status Inconsistency and Role Strain
Status inconsistency occurs when an individual holds multiple social positions with conflicting levels of prestige or status, creating internal tension. Role strain arises when incompatible demands or expectations are placed on a single social role, causing stress in fulfilling responsibilities. The key difference lies in status inconsistency involving contradictory social standings across roles, whereas role strain involves difficulty within the expectations of a single role.
Sociological Theories on Status and Roles
Status inconsistency occurs when an individual's social positions hold contradictory prestige or power, creating tension due to conflicting social expectations, while role strain arises from difficulties in fulfilling the demands within a single social role. Sociological theories such as Symbolic Interactionism emphasize how individuals negotiate identity through status symbols, whereas Structural Functionalism views roles as part of a system maintaining social order but acknowledges strain when role expectations become incompatible. Understanding these concepts helps explain the complexities of social behavior and identity management in diverse social contexts.
Causes of Status Inconsistency
Status inconsistency arises when an individual holds multiple social positions with conflicting levels of prestige or power, such as a highly educated person working in a low-income job. This phenomenon is primarily caused by the mismatch between various social statuses, including occupation, education, and income, leading to confusion in social expectations and identity. Unlike role strain, which results from conflicting demands within a single social role, status inconsistency stems from the discordance across different social statuses held simultaneously.
Common Causes of Role Strain
Role strain commonly arises from conflicting demands within a single social role, such as work overload or ambiguous expectations, which hinder effective role performance. Status inconsistency involves tension when an individual's various social statuses hold differing levels of prestige or power, creating conflicting social expectations. Understanding these dynamics clarifies how competing pressures within one's roles lead to stress and affect social behavior.
Real-World Examples of Status Inconsistency
Status inconsistency occurs when an individual holds different social statuses that conflict, such as a highly educated person working in a low-paying job, leading to social tension and identity conflicts. Real-world examples include immigrant professionals working in lower-skilled occupations due to credential recognition issues or women with advanced qualifications facing workplace discrimination that limits their career advancement. These scenarios illustrate how status inconsistency impacts social interactions and individual well-being, contrasting with role strain, which involves stress from incompatible demands within a single social role.
Real-World Examples of Role Strain
Role strain occurs when conflicting demands arise within a single social role, such as a nurse managing heavy patient loads and administrative duties simultaneously. In contrast, status inconsistency involves conflicting expectations from multiple social statuses, like a female CEO facing gender stereotypes while leading a company. Real-world examples of role strain include teachers balancing classroom management, lesson planning, and parental communication, often leading to stress and reduced effectiveness.
Impacts on Individual Well-Being
Status inconsistency occurs when an individual holds conflicting social positions with incompatible expectations, often leading to confusion and lowered self-esteem. Role strain arises from the pressures within a single role, causing stress and reduced psychological well-being. Both phenomena negatively impact individual well-being by increasing anxiety, decreasing satisfaction, and impairing mental health.
Addressing Status Inconsistency and Role Strain in Society
Addressing status inconsistency and role strain in society requires recognizing the conflicts individuals face when their social positions or roles demand incompatible behaviors or expectations. Social policies should promote role clarity and flexibility, enabling individuals to manage competing demands across their statuses more effectively. Community support programs and workplace accommodations can mitigate stress by fostering environments that validate diverse role experiences and reduce conflicting pressures.
Status inconsistency Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com