Government institutions serve as the backbone of public administration, ensuring the delivery of essential services and enforcement of laws within a society. They play a crucial role in policy implementation, maintaining order, and providing support for economic and social development. Explore the rest of the article to understand how these institutions directly impact Your daily life and contribute to overall governance.
Table of Comparison
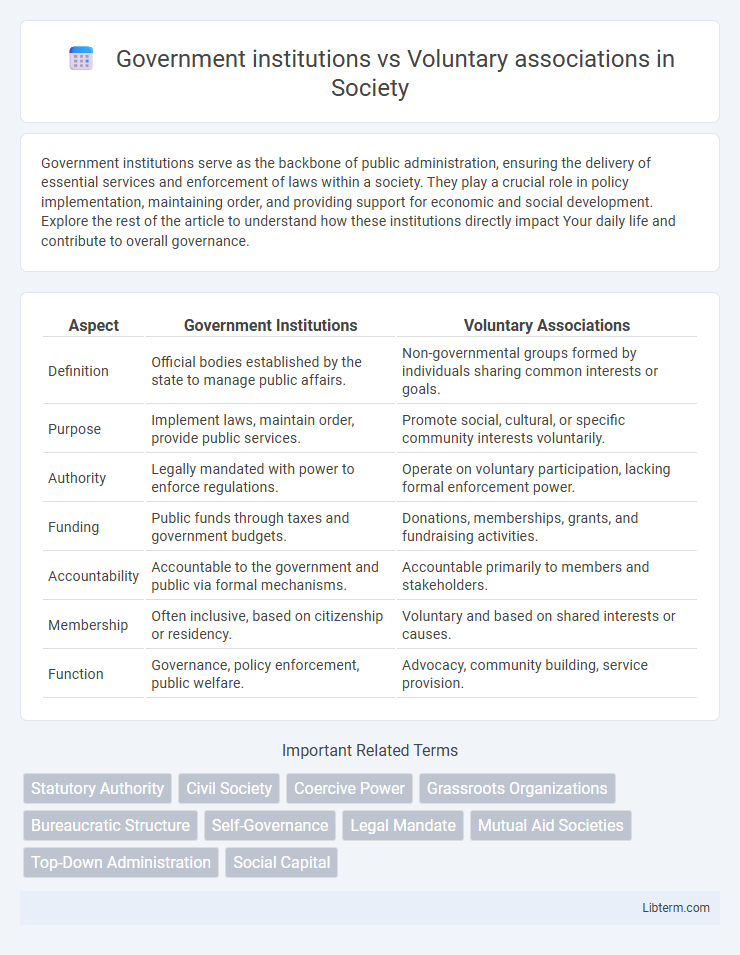
| Aspect | Government Institutions | Voluntary Associations |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Official bodies established by the state to manage public affairs. | Non-governmental groups formed by individuals sharing common interests or goals. |
| Purpose | Implement laws, maintain order, provide public services. | Promote social, cultural, or specific community interests voluntarily. |
| Authority | Legally mandated with power to enforce regulations. | Operate on voluntary participation, lacking formal enforcement power. |
| Funding | Public funds through taxes and government budgets. | Donations, memberships, grants, and fundraising activities. |
| Accountability | Accountable to the government and public via formal mechanisms. | Accountable primarily to members and stakeholders. |
| Membership | Often inclusive, based on citizenship or residency. | Voluntary and based on shared interests or causes. |
| Function | Governance, policy enforcement, public welfare. | Advocacy, community building, service provision. |
Defining Government Institutions
Government institutions are formal organizations established by legal authority to implement public policies, enforce laws, and provide services to the population. These entities operate under a structured hierarchy and are funded through taxation, ensuring accountability and legitimacy in governance. Unlike voluntary associations, government institutions possess regulatory power and the ability to compel compliance from citizens.
Understanding Voluntary Associations
Voluntary associations are organized groups formed by individuals who share common interests or goals, functioning independently from government control. These associations play a vital role in fostering community engagement, promoting social welfare, and advocating for specific causes without the regulatory authority vested in government institutions. Understanding their voluntary nature highlights the importance of collective action driven by shared values rather than formal legal mandates.
Historical Evolution of Governance Models
Government institutions have evolved from centralized monarchies to complex bureaucratic states, reflecting increasing administrative specialization and legal codification since the 18th century. Voluntary associations emerged prominently during the Enlightenment, fostering civil society by enabling collective action outside formal state control. The interplay between these entities shaped modern governance models, with governments institutionalizing authority while voluntary groups contributed to participatory democracy and social capital development.
Core Functions of Government Institutions
Government institutions primarily focus on core functions such as maintaining law and order, providing public goods, and ensuring national security. They also regulate economic activities, implement public policies, and manage social welfare programs to promote public well-being. These functions are backed by legal authority and funded through taxation, distinguishing them from voluntary associations that operate on membership and voluntary cooperation.
Key Roles of Voluntary Associations
Voluntary associations play a key role in fostering community engagement by providing platforms for collective action, social interaction, and advocacy outside government control. They often fill gaps in social services, promote civic responsibility, and support cultural or humanitarian causes through grassroots initiatives. Unlike government institutions, these associations operate on voluntary membership and flexibility, enhancing local empowerment and responsiveness to specific community needs.
Accountability and Transparency Comparisons
Government institutions operate under strict statutory frameworks ensuring high levels of accountability and transparency through public audits, legislative oversight, and mandatory disclosures. Voluntary associations, while often committed to transparency, rely on internal governance and donor reporting, resulting in varied accountability standards depending on their size, structure, and regulatory requirements. The disparity in formal oversight mechanisms makes government bodies more consistently accountable to the public compared to the fluctuating transparency levels found in voluntary associations.
Funding Sources and Resource Allocation
Government institutions primarily rely on public funding from taxes, grants, and government budgets, ensuring stable resource allocation to meet mandated public services and policy goals. Voluntary associations depend largely on private donations, membership fees, and fundraising activities, leading to more fluctuating resource availability shaped by donor priorities. Resource allocation in government institutions follows regulated processes aligned with public accountability, whereas voluntary associations exercise flexibility in distributing resources based on organizational mission and donor intent.
Decision-Making Processes
Government institutions employ hierarchical decision-making processes characterized by formal procedures, legal frameworks, and bureaucratic oversight to ensure accountability and uniform policy implementation. Voluntary associations utilize participatory and consensus-based decision-making, allowing members to influence outcomes through democratic voting or collective discussion, fostering inclusivity and flexibility. The contrast between these entities highlights a structured, rule-bound approach in government institutions versus the adaptive, member-driven strategies in voluntary associations.
Impact on Society and Individual Freedoms
Government institutions wield significant influence on societal structure by enacting laws and policies that regulate public behavior and allocate resources, shaping social order and collective welfare. Voluntary associations enhance individual freedoms by enabling personal choice and participation in diverse social, cultural, or political activities, fostering community engagement and social capital. The dynamic interplay between governmental authority and voluntary group autonomy critically affects the balance between societal control and individual liberty, impacting democratic governance and civil rights.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Government institutions face challenges like bureaucratic inefficiency, limited flexibility, and political influence that can hinder timely decision-making and innovation. Voluntary associations struggle with insufficient funding, volunteer retention, and limited authority, affecting their capacity to deliver sustained community impact. Future prospects emphasize increased collaboration between both sectors, leveraging government resources and voluntary associations' grassroots connections to enhance public service delivery and social innovation.
Government institutions Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com