Identification plays a crucial role in verifying your identity across various platforms and services, ensuring security and personalized experiences. Accurate identification methods, such as biometric data or multi-factor authentication, reduce fraud and enhance trust in digital interactions. Explore the rest of the article to understand the latest identification technologies and how they protect your information.
Table of Comparison
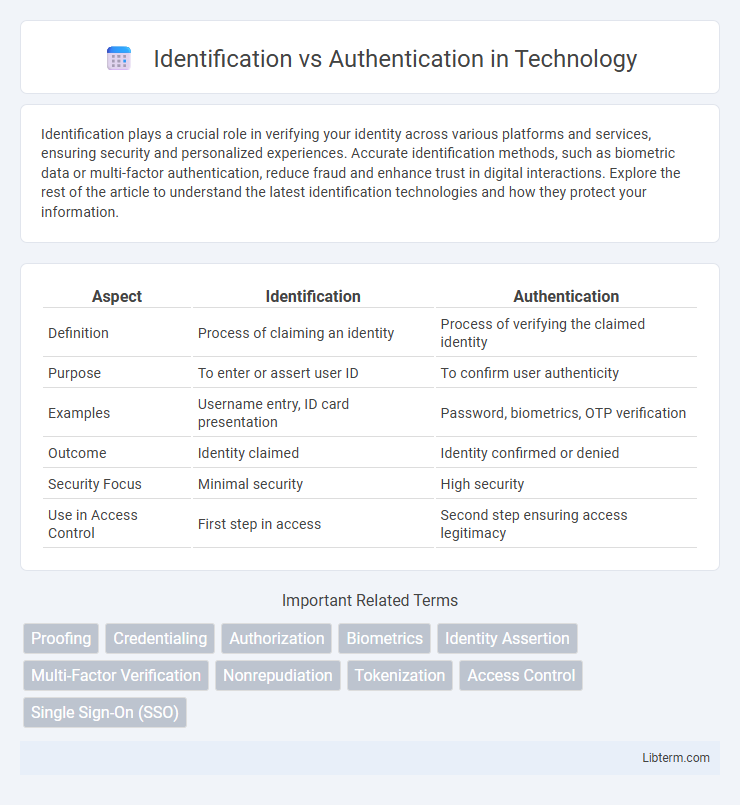
| Aspect | Identification | Authentication |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of claiming an identity | Process of verifying the claimed identity |
| Purpose | To enter or assert user ID | To confirm user authenticity |
| Examples | Username entry, ID card presentation | Password, biometrics, OTP verification |
| Outcome | Identity claimed | Identity confirmed or denied |
| Security Focus | Minimal security | High security |
| Use in Access Control | First step in access | Second step ensuring access legitimacy |
Understanding Identification and Authentication
Identification involves presenting a unique identifier, such as a username or ID number, to claim an identity within a system. Authentication verifies this claim by validating credentials like passwords, biometrics, or security tokens to ensure the individual is who they assert to be. Effective security systems rely on both processes to protect access and maintain data integrity.
Key Differences Between Identification and Authentication
Identification involves determining a user's identity by requesting an identifier such as a username or ID number, whereas authentication verifies the validity of the claimed identity through methods like passwords, biometrics, or tokens. Identification is the initial step in access control, establishing who the user claims to be, while authentication ensures that the claim is genuine and the user has the right to access the system. Key differences include their purpose--identification is about recognition, authentication about validation--and the types of data used, with identification relying on identifiers and authentication depending on proof of identity.
The Role of Identification in Security Systems
Identification serves as the crucial first step in security systems by establishing a user's claimed identity through unique identifiers such as usernames, biometric data, or tokens. It enables the system to distinguish one user from another, forming the foundation for subsequent security measures like authentication and authorization. Accurate identification reduces risks of unauthorized access by ensuring that the authentication process targets the correct identity profile within the security framework.
Authentication: Verifying User Claims
Authentication verifies user claims by confirming that the individual attempting access is truly who they assert to be, typically through methods like passwords, biometrics, or multi-factor authentication. This process depends on validating credentials against stored data to ensure accuracy and security. Effective authentication protects sensitive information and prevents unauthorized access within digital systems.
Methods of Identification
Methods of identification include biometric systems such as fingerprint and facial recognition, smart cards embedded with unique data, and traditional username or ID number entry. These techniques establish a user's claimed identity by leveraging unique physical traits or assigned credentials. Effective identification methods must ensure distinctiveness and reliability to serve as the foundation for subsequent authentication processes.
Common Authentication Techniques
Identification involves claiming an identity, while authentication verifies that claim using techniques such as passwords, biometrics, and security tokens. Common authentication methods include multi-factor authentication (MFA), which combines something the user knows (password), something the user has (token or smart card), and something the user is (fingerprint or facial recognition). These techniques enhance security by ensuring only authorized individuals gain access to systems and data.
Why Identification Alone Is Not Enough
Identification alone is insufficient because it only reveals who a user claims to be without verifying their identity, leaving systems vulnerable to unauthorized access. Authentication provides a crucial second step by validating credentials such as passwords, biometrics, or tokens to confirm the user's legitimacy. This two-step process ensures stronger security and reduces the risk of identity theft and fraud in digital systems.
Combining Identification and Authentication for Enhanced Security
Combining identification and authentication significantly strengthens security by first establishing a user's claimed identity through identification and then verifying that identity via authentication methods such as passwords, biometrics, or multi-factor authentication. This dual-step process reduces the risk of unauthorized access by ensuring that users are both recognized and verified before gaining entry to sensitive systems or data. Integrating these mechanisms creates a robust defense against identity theft, fraud, and cyber threats in digital environments.
Real-World Examples of Identification vs Authentication
Identification involves presenting an identity claim, such as entering a username or showing an ID card, while authentication verifies that claim through methods like passwords, biometric scans, or security tokens. For instance, when accessing a smartphone, unlocking the device requires authentication via fingerprint or facial recognition after the user identifies themselves by selecting their profile. In airports, passengers identify themselves with a passport, and authentication is performed by matching their photo to the traveler, ensuring secure verification.
Best Practices for Implementing Identification and Authentication
Implement secure identification by uniquely associating users with legal identities through robust identifiers such as usernames or biometric data. Strengthen authentication with multi-factor methods combining passwords, biometric scans, and hardware tokens to mitigate risks of unauthorized access. Implement continuous authentication and regular credential updates to maintain system integrity and prevent identity theft or account compromise.
Identification Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com