Paper wallets provide a secure way to store cryptocurrency offline by printing your private and public keys on a physical sheet, reducing risks from hacking and malware. They offer a cost-effective and user-friendly method to keep your digital assets safe, especially for long-term storage. Discover how to create and safely use a paper wallet in the detailed guide ahead.
Table of Comparison
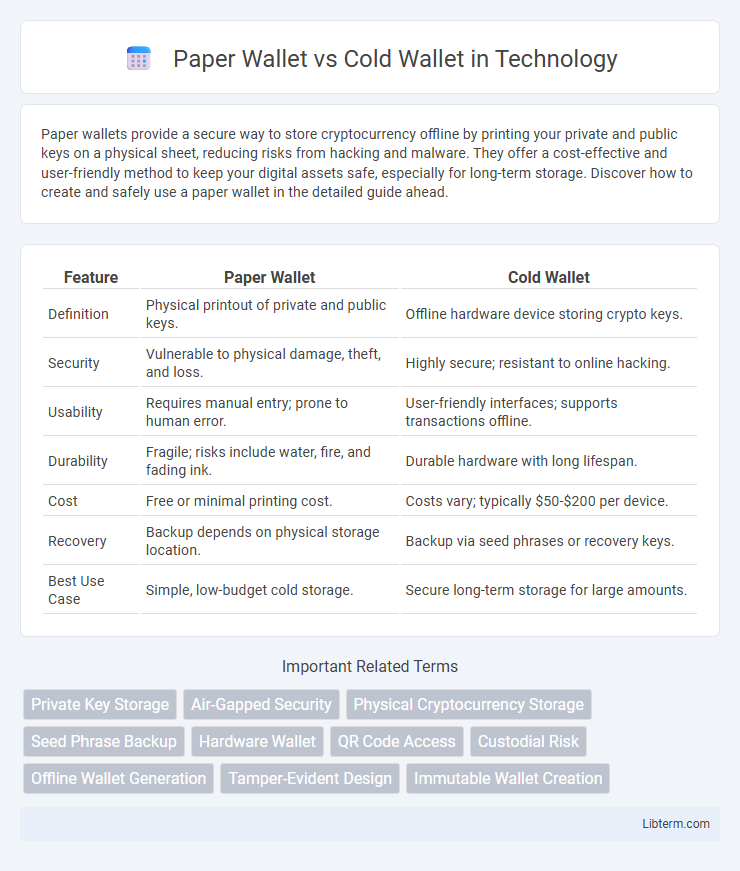
| Feature | Paper Wallet | Cold Wallet |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Physical printout of private and public keys. | Offline hardware device storing crypto keys. |
| Security | Vulnerable to physical damage, theft, and loss. | Highly secure; resistant to online hacking. |
| Usability | Requires manual entry; prone to human error. | User-friendly interfaces; supports transactions offline. |
| Durability | Fragile; risks include water, fire, and fading ink. | Durable hardware with long lifespan. |
| Cost | Free or minimal printing cost. | Costs vary; typically $50-$200 per device. |
| Recovery | Backup depends on physical storage location. | Backup via seed phrases or recovery keys. |
| Best Use Case | Simple, low-budget cold storage. | Secure long-term storage for large amounts. |
Introduction to Cryptocurrency Wallets
Cryptocurrency wallets serve as digital tools for securely storing private keys essential for accessing and managing digital assets across blockchain networks. Paper wallets are physical printouts containing public and private keys, offering a low-tech, offline storage solution that minimizes hacking risks but requires careful handling to avoid damage or loss. Cold wallets encompass offline storage methods, including hardware devices and paper wallets, designed to keep private keys isolated from internet threats and enhance security for long-term cryptocurrency holdings.
What is a Paper Wallet?
A paper wallet is a physical document that contains a cryptocurrency private key and public address printed as QR codes and alphanumeric characters, providing a form of cold storage by keeping keys offline. It offers heightened security against online hacking and malware, as the keys are never exposed to internet-connected devices. Compared to other cold wallets like hardware devices, paper wallets are a low-cost, straightforward solution but require careful handling to prevent physical damage or loss.
What is a Cold Wallet?
A cold wallet is a cryptocurrency storage method that keeps private keys completely offline to prevent hacking and unauthorized access. Unlike paper wallets, which store keys on physical paper, cold wallets can include hardware devices or air-gapped computers providing enhanced security and ease of use. Cold wallets are essential for long-term storage as they offer robust protection against cyber threats and malware.
Security Features Compared
Paper wallets provide offline storage by printing private keys and public addresses on physical paper, eliminating exposure to digital hacking risks but are vulnerable to physical damage and loss. Cold wallets, including hardware devices like Ledger and Trezor, store private keys securely offline with advanced encryption and PIN protection, offering enhanced resistance to malware and phishing attacks. While paper wallets lack dynamic security updates, cold wallets benefit from firmware upgrades and multi-factor authentication, improving long-term asset protection.
Ease of Use and Accessibility
Paper wallets provide a simple, offline method to store cryptocurrency by printing private keys on physical paper, which requires careful handling and secure storage to avoid loss or damage. Cold wallets, including hardware devices, offer enhanced security through encrypted private key storage while maintaining user-friendly interfaces with PIN protection and backup options. Despite paper wallets being cost-free and accessible for beginners, cold wallets balance ease of use with robust security features preferred by frequent users managing significant crypto assets.
Risks and Vulnerabilities
Paper wallets are vulnerable to physical damage, loss, and theft since private keys are printed on a tangible medium that can deteriorate or be misplaced. Cold wallets, often hardware devices, reduce exposure to hacking by storing keys offline but are susceptible to manufacturing defects, firmware vulnerabilities, and user mishandling such as improper pin protection. Both methods demand strict security practices to mitigate risks like unauthorized access and irreversible asset loss.
Backup and Recovery Options
Paper wallets provide a physical backup by printing private keys offline, minimizing digital exposure but requiring careful storage to prevent loss or damage. Cold wallets, such as hardware devices, offer secure offline storage with built-in recovery options like seed phrases that facilitate easy restoration of funds if the device is lost or damaged. Choosing between these depends on the user's preference for tangible backup versus more user-friendly recovery mechanisms integrated into cold wallet solutions.
Cost and Affordability
Paper wallets offer a highly cost-effective solution for storing cryptocurrency, as they require only paper and a printer with zero ongoing fees, making them ideal for users on a tight budget. Cold wallets, such as hardware devices, typically come with an upfront cost ranging from $50 to $200 but provide enhanced security features and durability that justify the investment for long-term holders. The affordability of paper wallets is offset by increased vulnerability to physical damage or loss, while cold wallets balance higher initial expenses with reliable protection and usability.
Best Use Cases for Each Wallet Type
Paper wallets offer an ideal solution for long-term storage of cryptocurrency assets, providing offline security by generating and printing private keys that remain disconnected from the internet. Cold wallets, including hardware devices like Ledger or Trezor, are best suited for frequent or medium-term users who require enhanced security with easy transaction capabilities through encrypted physical hardware. Each wallet type excels in specific scenarios: paper wallets minimize hacking risks for dormant funds, while cold wallets balance security and usability for managing active crypto portfolios.
Which Wallet Should You Choose?
Choosing between a paper wallet and a cold wallet depends on your security needs and ease of access. Paper wallets offer offline storage by printing private keys on paper, making them immune to hacking but vulnerable to physical damage or loss. Cold wallets, such as hardware devices, provide enhanced security through encrypted storage and user-friendly interfaces, making them ideal for long-term holding and frequent transactions.
Paper Wallet Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com