GraphQL revolutionizes data querying by allowing clients to request exactly the data they need, minimizing over-fetching and under-fetching issues common in REST APIs. Its flexible schema and type system enable efficient, real-time data interactions, optimizing performance for modern applications. Discover how implementing GraphQL can enhance your development workflow and improve user experiences by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
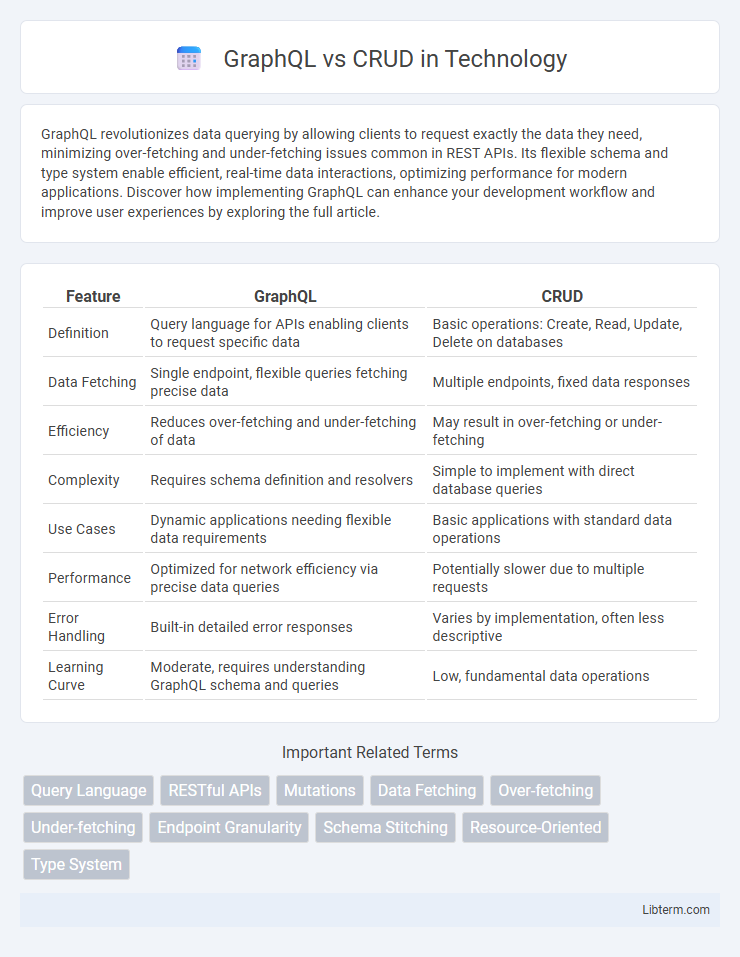
| Feature | GraphQL | CRUD |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Query language for APIs enabling clients to request specific data | Basic operations: Create, Read, Update, Delete on databases |
| Data Fetching | Single endpoint, flexible queries fetching precise data | Multiple endpoints, fixed data responses |
| Efficiency | Reduces over-fetching and under-fetching of data | May result in over-fetching or under-fetching |
| Complexity | Requires schema definition and resolvers | Simple to implement with direct database queries |
| Use Cases | Dynamic applications needing flexible data requirements | Basic applications with standard data operations |
| Performance | Optimized for network efficiency via precise data queries | Potentially slower due to multiple requests |
| Error Handling | Built-in detailed error responses | Varies by implementation, often less descriptive |
| Learning Curve | Moderate, requires understanding GraphQL schema and queries | Low, fundamental data operations |
Introduction to GraphQL and CRUD
GraphQL is a query language for APIs that enables clients to request exactly the data they need, reducing over-fetching and under-fetching problems common in traditional RESTful CRUD operations. CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) represents the fundamental functions required for persistent storage and is typically implemented in REST architecture, where each operation corresponds to specific HTTP methods. Unlike CRUD's rigid endpoints, GraphQL exposes a single endpoint with a flexible query structure, optimizing data retrieval and manipulation efficiency.
Defining CRUD Operations
GraphQL defines CRUD operations by using queries for reading data, mutations for creating, updating, or deleting records, and subscriptions for real-time updates, providing more granular control compared to traditional CRUD APIs. Unlike standard RESTful CRUD that maps directly to HTTP verbs (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE), GraphQL allows clients to specify exactly which fields they need, optimizing data transfer and reducing over-fetching. This semantic approach to CRUD operations enhances flexibility and efficiency in managing complex data interactions.
What is GraphQL?
GraphQL is a query language and runtime for APIs that enables clients to request exactly the data they need, improving efficiency compared to traditional CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations over REST APIs. Unlike CRUD, which requires multiple endpoints for each data operation, GraphQL consolidates these into a single endpoint, allowing more flexible and precise data retrieval. This reduces over-fetching and under-fetching of data, making it highly suitable for complex applications with diverse data needs.
Core Differences Between GraphQL and CRUD
GraphQL delivers flexible queries by allowing clients to specify exactly what data they need, whereas CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operates with predefined endpoints for each data operation. Unlike CRUD's fixed resource structure, GraphQL uses a single endpoint that handles multiple query types and nested data fetching in one request. GraphQL's schema-driven approach enhances data retrieval efficiency, reducing over-fetching and under-fetching common in traditional CRUD APIs.
Data Fetching: RESTful CRUD vs. GraphQL
RESTful CRUD operations typically require multiple endpoints to fetch related data, resulting in over-fetching or under-fetching issues and increased network requests. GraphQL enables clients to request precisely the data they need in a single query, reducing payload size and minimizing latency. This efficiency in data fetching improves application performance and simplifies client-server interactions compared to traditional RESTful APIs.
Flexibility and Query Efficiency
GraphQL outperforms traditional CRUD operations by allowing clients to request only the specific data fields they need, significantly improving query efficiency and reducing network overhead. Unlike fixed REST endpoints, GraphQL's flexible query structure enables dynamic data retrieval tailored to diverse client requirements without multiple round-trips to the server. This adaptability enhances performance in complex applications where minimizing data transfer and precise fetching is critical.
Performance and Overfetching Issues
GraphQL significantly improves performance by allowing clients to request only the specific data fields they need, reducing overfetching and minimizing unnecessary server responses. In contrast, traditional CRUD APIs often return entire data objects, leading to performance bottlenecks due to overfetching and increased payload sizes. By optimizing data retrieval, GraphQL enhances network efficiency and reduces latency, especially in complex applications with varied data requirements.
Error Handling and Validation
GraphQL enhances error handling by providing detailed, field-specific error messages within a single response, enabling clients to precisely identify and address validation issues. Unlike CRUD APIs that often return generic HTTP status codes and may require multiple requests to pinpoint errors, GraphQL leverages a structured errors object that conveys validation failures alongside successful data. This approach improves front-end validation workflows and reduces the need for redundant error handling logic across multiple endpoints.
Use Cases: When to Choose GraphQL or CRUD
GraphQL excels in applications requiring complex queries and real-time data fetching, such as social media platforms and dynamic dashboards, where clients need specific subsets of data efficiently. CRUD operations remain ideal for straightforward, resource-based systems like inventory management or simple content management systems where standard create, read, update, and delete interactions suffice. Choosing GraphQL enhances flexibility and reduces over-fetching in data-intensive apps, while CRUD simplifies development and maintenance for basic, well-defined data models.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Approach
Choosing between GraphQL and CRUD depends on the complexity and flexibility requirements of your data operations. GraphQL excels in scenarios demanding precise data retrieval and reduced network overhead, while CRUD remains effective for straightforward, resource-based interactions. Evaluating application scalability, client needs, and development resources ensures the optimal approach for efficient API design.
GraphQL Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com