Terraform is an open-source infrastructure as code tool that enables you to define and provision data center infrastructure using a high-level configuration language. Its capability to manage both low-level components like compute instances and high-level services such as DNS entries makes infrastructure automation more efficient and reliable. Explore the rest of this article to discover how Terraform can revolutionize your infrastructure management.
Table of Comparison
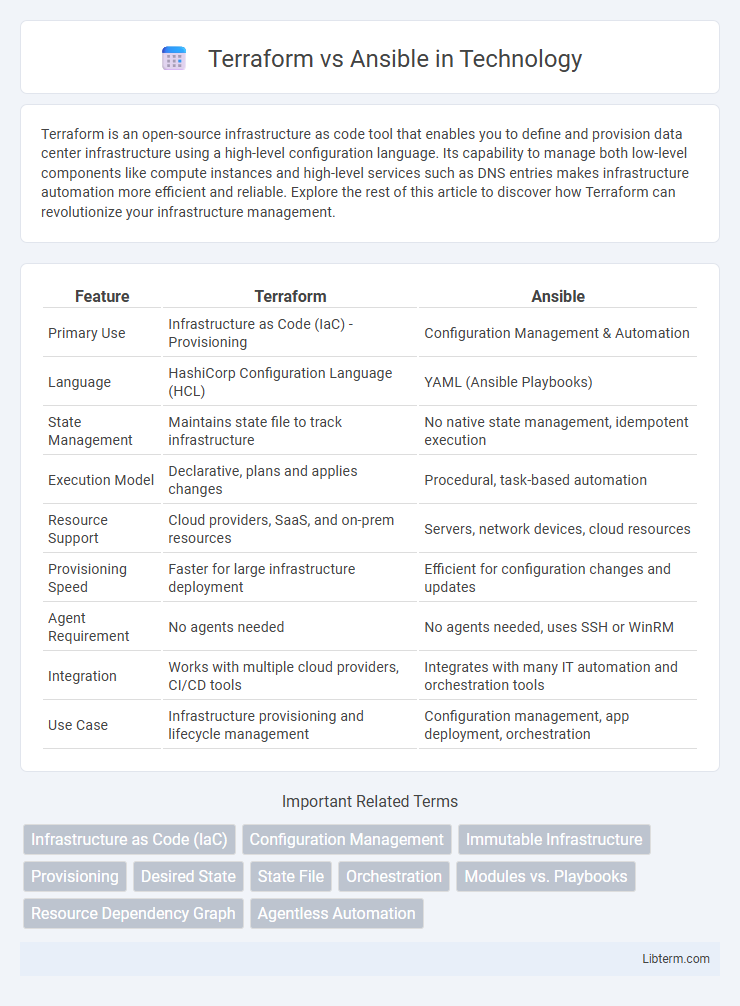
| Feature | Terraform | Ansible |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Infrastructure as Code (IaC) - Provisioning | Configuration Management & Automation |
| Language | HashiCorp Configuration Language (HCL) | YAML (Ansible Playbooks) |
| State Management | Maintains state file to track infrastructure | No native state management, idempotent execution |
| Execution Model | Declarative, plans and applies changes | Procedural, task-based automation |
| Resource Support | Cloud providers, SaaS, and on-prem resources | Servers, network devices, cloud resources |
| Provisioning Speed | Faster for large infrastructure deployment | Efficient for configuration changes and updates |
| Agent Requirement | No agents needed | No agents needed, uses SSH or WinRM |
| Integration | Works with multiple cloud providers, CI/CD tools | Integrates with many IT automation and orchestration tools |
| Use Case | Infrastructure provisioning and lifecycle management | Configuration management, app deployment, orchestration |
Introduction to Infrastructure as Code
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) revolutionizes IT operations by enabling the management of infrastructure through machine-readable configuration files rather than physical hardware setup. Terraform, a declarative IaC tool, excels in provisioning and managing cloud resources across multiple providers with immutable infrastructure principles. Ansible, primarily a configuration management tool with IaC capabilities, uses procedural automation to configure and manage existing servers, emphasizing agentless architecture and continuous configuration enforcement.
What is Terraform?
Terraform is an open-source infrastructure as code (IaC) tool developed by HashiCorp that enables users to define and provision data center infrastructure using a declarative configuration language. It allows automation of cloud resource management across multiple service providers such as AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, and private clouds, simplifying infrastructure scalability and versioning. Terraform's state management and execution plans provide predictable infrastructure changes and infrastructure lifecycle management.
What is Ansible?
Ansible is an open-source automation tool designed for configuration management, application deployment, and task automation across multiple servers. It uses simple, human-readable YAML-based playbooks to define infrastructure as code, enabling consistent and repeatable setups. Ansible operates agentlessly, leveraging SSH for secure and efficient communication with managed nodes, making it ideal for orchestrating complex IT environments.
Core Differences Between Terraform and Ansible
Terraform specializes in infrastructure provisioning by using declarative configuration files to create and manage cloud resources, ensuring consistent infrastructure state across providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud. Ansible focuses on configuration management and application deployment, using procedural playbooks to automate software installation, system updates, and service orchestration on existing servers. While Terraform manages infrastructure lifecycle with state management and dependency graphs, Ansible operates agentlessly to automate IT tasks without maintaining state, making them complementary tools in DevOps workflows.
Provisioning and Configuration Management
Terraform excels in provisioning infrastructure by enabling declarative infrastructure as code to create, update, and manage cloud resources across multiple providers. Ansible specializes in configuration management by automating software installation, system setup, and application deployment on existing infrastructure using procedural playbooks. While Terraform manages infrastructure lifecycle, Ansible ensures consistent system configuration and application state management after provisioning.
State Management and Idempotence
Terraform uses a declarative approach with a state file to track infrastructure changes, ensuring accurate state management and enabling seamless resource updates. Ansible operates in an agentless manner and relies on idempotent playbooks to guarantee consistent configuration without maintaining a centralized state file. Terraform's state management provides precise drift detection, while Ansible emphasizes execution idempotence to converge systems toward the desired state.
Use Cases for Terraform
Terraform excels in infrastructure provisioning by enabling declarative configuration of cloud resources across multiple providers such as AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud. It is ideal for managing complex, scalable environments through Infrastructure as Code, automating the creation, updating, and versioning of infrastructure components like virtual machines, networks, and storage. Use cases include setting up multi-cloud architectures, orchestrating immutable infrastructure, and managing infrastructure lifecycle for continuous integration and deployment pipelines.
Use Cases for Ansible
Ansible excels in configuration management and application deployment by automating repetitive tasks across multiple systems, making it ideal for continuous delivery and infrastructure as code. It supports orchestrating complex IT workflows with simple, human-readable YAML playbooks, enhancing operational efficiency in environments needing consistent system setup and software updates. Ansible's agentless architecture and strong integration with cloud platforms streamline managing hybrid and multi-cloud environments without requiring additional software installation.
Pros and Cons Comparison
Terraform excels in infrastructure automation with its declarative configuration and state management, enabling consistent provisioning across multiple cloud providers, while its limitation lies in less effective configuration management compared to Ansible. Ansible offers powerful configuration orchestration with agentless architecture, ease of use, and extensive module support, but it lacks native infrastructure provisioning and state tracking capabilities. Choosing between Terraform and Ansible depends on whether infrastructure provisioning or configuration management is the primary focus, with Terraform best suited for immutable infrastructure and Ansible for dynamic configuration tasks.
Choosing the Right Tool for Your Workflow
Terraform excels in infrastructure provisioning with its declarative configuration and state management, making it ideal for creating and managing cloud resources consistently. Ansible offers flexible configuration management and automation through imperative tasks, suited for application deployment and system updates. Selecting the right tool depends on your workflow needs: use Terraform for infrastructure as code and predictable environment setups, whereas Ansible is better for detailed configuration, orchestration, and ongoing system maintenance.
Terraform Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com