Traditional infrastructure relies on physical hardware and established networks to support organizational operations, often requiring significant maintenance and manual updates. This approach can result in higher costs and slower scalability compared to modern alternatives like cloud computing. Explore the rest of the article to understand how transitioning from traditional infrastructure can benefit your business.
Table of Comparison
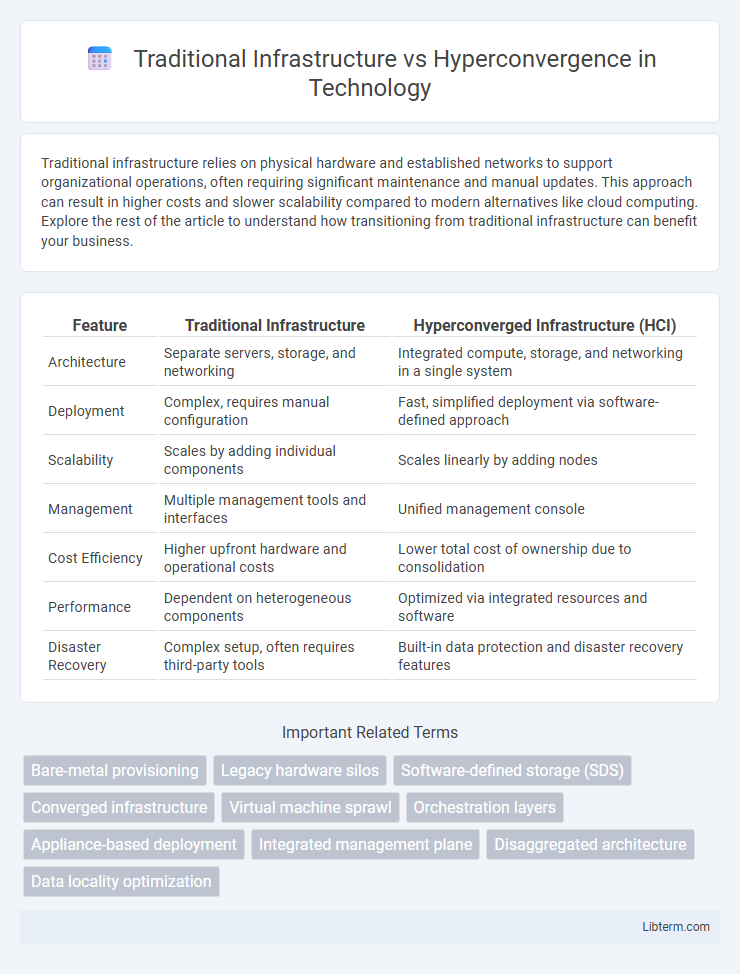
| Feature | Traditional Infrastructure | Hyperconverged Infrastructure (HCI) |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Separate servers, storage, and networking | Integrated compute, storage, and networking in a single system |
| Deployment | Complex, requires manual configuration | Fast, simplified deployment via software-defined approach |
| Scalability | Scales by adding individual components | Scales linearly by adding nodes |
| Management | Multiple management tools and interfaces | Unified management console |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher upfront hardware and operational costs | Lower total cost of ownership due to consolidation |
| Performance | Dependent on heterogeneous components | Optimized via integrated resources and software |
| Disaster Recovery | Complex setup, often requires third-party tools | Built-in data protection and disaster recovery features |
Introduction to IT Infrastructure Evolution
Traditional infrastructure relies on separate physical components such as servers, storage, and networking devices, often leading to complex management and scalability challenges. Hyperconvergence integrates compute, storage, and networking into a single software-driven solution, streamlining deployment and improving resource efficiency. The evolution from traditional to hyperconverged infrastructure reflects the IT industry's shift towards flexibility, automation, and simplified data center operations.
Defining Traditional Infrastructure
Traditional infrastructure refers to a data center setup where servers, storage, and networking components are deployed as separate, standalone units, requiring individual management and integration. This approach often involves dedicated hardware for each function, leading to complex configurations and slower scalability. Enterprises implementing traditional infrastructure face challenges in flexibility and operational efficiency compared to hyperconverged solutions that unify resources under a single management platform.
What is Hyperconvergence?
Hyperconvergence integrates compute, storage, and networking into a single software-defined system, eliminating the need for separate hardware components. This approach simplifies infrastructure management by using a unified platform that supports virtualization and automates resource allocation. Compared to traditional infrastructure, hyperconverged systems provide scalability, cost efficiency, and enhanced performance for modern data centers.
Architecture: Core Differences
Traditional infrastructure relies on separate, dedicated hardware components for storage, networking, and computing, each managed individually, which often results in complexity and increased maintenance. Hyperconverged architecture integrates storage, compute, and networking into a single software-driven platform, enabling unified management and scalability through virtualization. This core difference enhances operational efficiency and reduces the need for specialized skills, making hyperconvergence a more agile and flexible solution compared to traditional setups.
Scalability and Flexibility Comparison
Traditional infrastructure often requires extensive manual configuration and physical hardware additions to scale, resulting in longer deployment times and higher operational complexity. Hyperconverged infrastructure (HCI) streamlines scalability by integrating compute, storage, and networking into a single software-driven platform, enabling dynamic resource allocation and rapid expansion. This flexible architecture supports seamless scaling with minimal downtime, making it ideal for businesses demanding agile and efficient growth.
Cost Analysis: Upfront and Long-term
Traditional infrastructure often requires significant upfront capital expenditures for separate servers, storage, and networking hardware, leading to higher initial costs and complex integration processes. Hyperconverged infrastructure (HCI) reduces upfront expenses by combining compute, storage, and networking into a single, software-defined system, enabling streamlined deployment and lower operational costs over time. Long-term cost benefits of HCI include simplified management, scalability without major hardware investments, and reduced power and cooling requirements, resulting in improved total cost of ownership (TCO) compared to traditional setups.
Performance and Efficiency
Traditional infrastructure relies on separate storage, computing, and networking components, often causing latency and inefficiencies due to complex data flow and management overhead. Hyperconverged infrastructure (HCI) integrates these resources into a single software-driven platform, optimizing performance through reduced data movement and streamlined resource allocation. This consolidation improves efficiency by enabling faster deployment, simplified scalability, and minimized operational costs.
Security Considerations
Traditional infrastructure often relies on multiple discrete components such as firewalls, switches, and storage arrays, creating diverse attack surfaces that require comprehensive, specialized security measures. Hyperconverged infrastructure integrates compute, storage, and networking into a unified platform, simplifying security management with centralized policies and automated updates that reduce vulnerabilities. Despite its streamlined approach, hyperconvergence necessitates robust encryption, strict access controls, and continuous monitoring to protect against emerging cyber threats within its consolidated architecture.
Use Cases and Industry Adoption
Traditional infrastructure remains prevalent in large enterprises requiring specialized hardware for high-performance workloads and granular control, particularly in sectors like finance, healthcare, and government. Hyperconverged infrastructure (HCI) excels in use cases demanding rapid scalability, simplified management, and cost efficiency, making it popular in SMBs, remote offices, and cloud integration within industries such as retail, technology, and education. Industry adoption trends highlight increasing HCI deployment driven by digital transformation initiatives, while traditional infrastructure persists where legacy applications and stringent compliance standards dominate.
Choosing the Right Infrastructure for Your Business
Traditional infrastructure offers dedicated hardware components for compute, storage, and networking, providing customization and control ideal for businesses with complex, specific workload requirements. Hyperconvergence integrates these components into a single software-driven platform, simplifying management and scaling, which benefits businesses prioritizing agility and operational efficiency. Selecting the right infrastructure depends on factors such as budget, scalability needs, IT expertise, and long-term growth strategies to ensure optimal performance and cost-effectiveness.
Traditional Infrastructure Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com