Mastering composition enhances your ability to organize ideas clearly and effectively, making your writing more compelling and understandable. Key elements include structure, coherence, and the use of vivid language to engage readers. Explore our article to discover techniques that will elevate your composition skills.
Table of Comparison
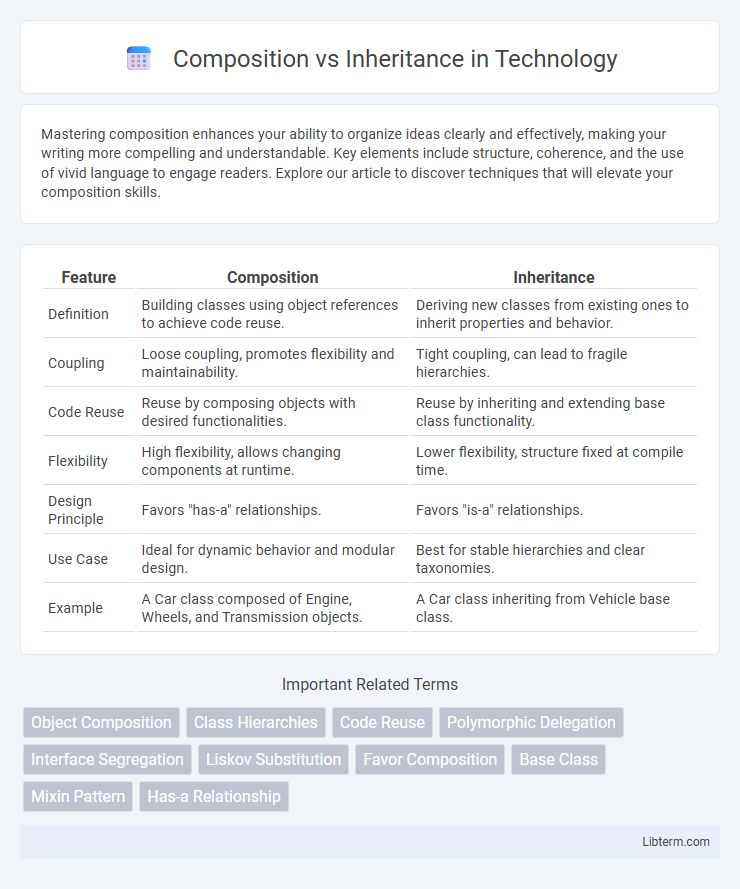
| Feature | Composition | Inheritance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Building classes using object references to achieve code reuse. | Deriving new classes from existing ones to inherit properties and behavior. |
| Coupling | Loose coupling, promotes flexibility and maintainability. | Tight coupling, can lead to fragile hierarchies. |
| Code Reuse | Reuse by composing objects with desired functionalities. | Reuse by inheriting and extending base class functionality. |
| Flexibility | High flexibility, allows changing components at runtime. | Lower flexibility, structure fixed at compile time. |
| Design Principle | Favors "has-a" relationships. | Favors "is-a" relationships. |
| Use Case | Ideal for dynamic behavior and modular design. | Best for stable hierarchies and clear taxonomies. |
| Example | A Car class composed of Engine, Wheels, and Transmission objects. | A Car class inheriting from Vehicle base class. |
Understanding Composition and Inheritance
Composition involves assembling objects using other objects, promoting flexibility and code reuse by enabling dynamic behavior changes at runtime. Inheritance creates a hierarchical relationship where a subclass inherits properties and methods from a superclass, allowing for code reuse but often resulting in tight coupling. Understanding these differences helps developers choose composition for greater modularity and inheritance for clear subtype hierarchies in object-oriented design.
Key Differences Between Composition and Inheritance
Composition involves building complex objects by combining simpler ones, promoting flexibility and runtime behavior changes, while inheritance creates a hierarchical relationship enabling code reuse through subclassing. Inheritance tightly couples parent and child classes, potentially leading to fragile hierarchies and reduced modularity, whereas composition fosters loose coupling and enhances maintainability by delegating responsibilities. Key differences include inheritance's static nature and reliance on an "is-a" relationship versus composition's dynamic approach emphasizing a "has-a" relationship between objects.
Advantages of Using Composition
Composition offers greater flexibility by allowing objects to be assembled from reusable components, promoting modularity and easier maintenance. It reduces tight coupling between classes, enabling dynamic behavior changes at runtime without altering existing code. This approach enhances testability and supports the Single Responsibility Principle, resulting in more robust and scalable software designs.
Benefits of Inheritance in OOP
Inheritance in object-oriented programming facilitates code reusability by allowing new classes to inherit properties and methods from existing ones, reducing redundancy. It supports hierarchical classification, enabling the creation of more specific classes based on general ones, which simplifies maintenance and enhances scalability. Inheritance also promotes polymorphism, allowing objects of different classes to be treated as instances of a common superclass, improving flexibility in code design.
Common Pitfalls of Inheritance
Inheritance often leads to tightly coupled code, making maintenance and scaling difficult when base classes change unexpectedly. Overusing inheritance can cause the fragile base class problem, where modifications to parent classes inadvertently break derived classes. Favoring composition over inheritance enhances flexibility by enabling objects to be built from multiple reusable components rather than relying on rigid class hierarchies.
When to Choose Composition over Inheritance
Choose composition over inheritance when flexibility and code reusability are priorities, as composition allows objects to be built from smaller, interchangeable components without rigid hierarchical constraints. Composition supports runtime behavior changes and avoids the tight coupling and fragility often associated with deep inheritance trees. Use composition to promote maintainability and adaptability in systems requiring dynamic feature combination or frequent modifications.
Real-World Examples of Composition
Real-world examples of composition include building a car by assembling different components such as an engine, wheels, and seats, where each part functions independently but collectively forms the complete vehicle. In software development, composition is demonstrated by a user interface containing buttons, text fields, and sliders, allowing flexible reuse and modification without inheriting from a common superclass. Composition provides greater modularity and decoupling compared to inheritance, enabling easier maintenance and scalability in complex systems.
Performance and Maintainability Considerations
Composition offers better maintainability by promoting modular design and easier code reuse, reducing dependencies between components. Inheritance can sometimes lead to performance overhead due to deep class hierarchies and method overriding, impacting runtime speed. Composition tends to improve performance by enabling more granular object interactions and minimizing unnecessary inheritance-related overhead.
Best Practices for Implementing Composition
Implementing composition involves designing classes that contain instances of other classes to achieve code reuse and flexibility, promoting a "has-a" relationship over the rigid "is-a" model seen in inheritance. Best practices include favoring interfaces or abstract classes to define component behaviors, keeping components loosely coupled to enhance modularity and maintainability, and delegating responsibilities to composed objects rather than extending base classes. This approach reduces the complexity of hierarchical dependencies, improves testability, and allows dynamic behavior changes at runtime by swapping composed objects.
Composition vs Inheritance: Which One to Use?
Composition offers greater flexibility by enabling objects to contain other objects, promoting code reuse and easier maintenance without rigid class hierarchies. Inheritance establishes a strong "is-a" relationship suited for shared behavior but can lead to tight coupling and less adaptable designs. Choose composition to achieve modular, extensible architectures and favor inheritance when a clear hierarchical relationship enhances code clarity and reuse.
Composition Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com