VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks) segment your network into distinct broadcast domains, improving security and reducing congestion by isolating traffic. Implementing VLANs can enhance network performance and simplify management across various departments or device groups. Explore the article to understand how VLANs can optimize your network infrastructure effectively.
Table of Comparison
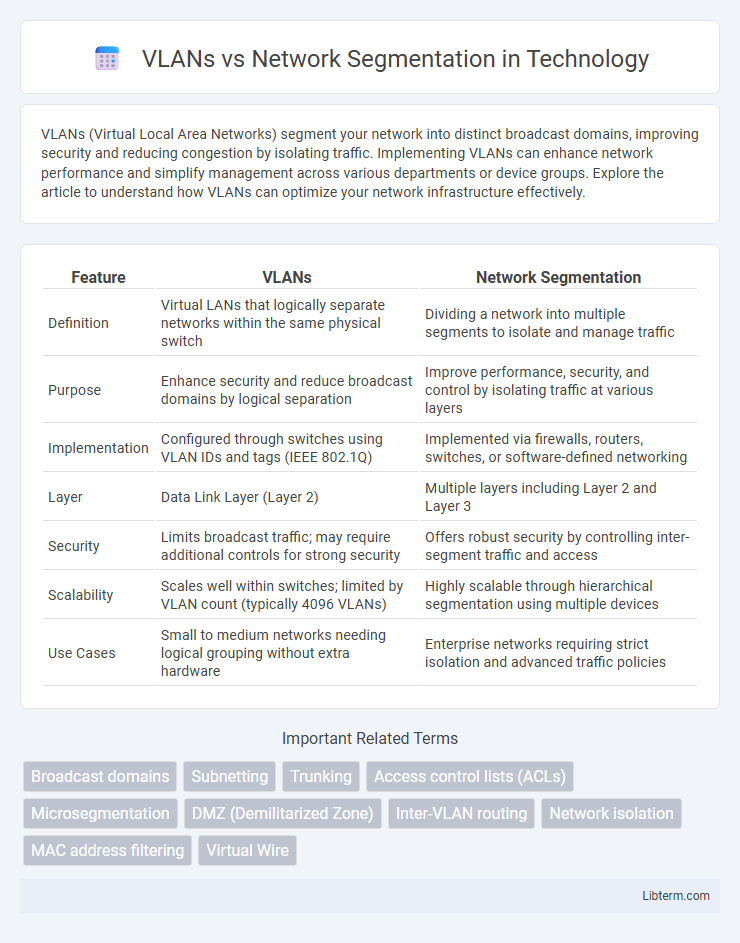
| Feature | VLANs | Network Segmentation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Virtual LANs that logically separate networks within the same physical switch | Dividing a network into multiple segments to isolate and manage traffic |
| Purpose | Enhance security and reduce broadcast domains by logical separation | Improve performance, security, and control by isolating traffic at various layers |
| Implementation | Configured through switches using VLAN IDs and tags (IEEE 802.1Q) | Implemented via firewalls, routers, switches, or software-defined networking |
| Layer | Data Link Layer (Layer 2) | Multiple layers including Layer 2 and Layer 3 |
| Security | Limits broadcast traffic; may require additional controls for strong security | Offers robust security by controlling inter-segment traffic and access |
| Scalability | Scales well within switches; limited by VLAN count (typically 4096 VLANs) | Highly scalable through hierarchical segmentation using multiple devices |
| Use Cases | Small to medium networks needing logical grouping without extra hardware | Enterprise networks requiring strict isolation and advanced traffic policies |
Introduction to VLANs and Network Segmentation
VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks) enable logical separation of devices within the same physical network infrastructure, enhancing security and traffic management by segmenting broadcast domains. Network segmentation divides a larger network into smaller segments or subnets, improving performance, reducing congestion, and limiting the spread of cyber threats. Implementing VLANs is a key technique in achieving effective network segmentation by isolating traffic and enforcing access controls.
Understanding Core Concepts: VLANs
VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks) enable logical segmentation of a physical network into multiple broadcast domains, enhancing traffic management and security in enterprise environments. By assigning devices to VLANs based on function or department, network administrators reduce broadcast traffic and contain potential security breaches within specific segments. VLANs operate at Layer 2 of the OSI model, making them essential for efficient network segmentation without requiring additional physical infrastructure.
Defining Network Segmentation
Network segmentation divides a larger network into smaller, isolated segments to enhance security, reduce congestion, and improve performance by limiting broadcast traffic. VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks) are a common method for implementing network segmentation through logical grouping of devices, regardless of their physical location. Effective network segmentation requires careful planning of IP address schemes, access control policies, and inter-segment communication rules to ensure optimal isolation and security.
Key Differences Between VLANs and Network Segmentation
VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks) create isolated broadcast domains within a single physical network by logically segmenting devices, primarily using network switches. Network segmentation encompasses broader methods, including VLANs, physical separation, and firewall policies, to divide a network into distinct zones for improved security and performance. The key difference lies in VLANs being a specific technique based on logical grouping within Layer 2, while network segmentation involves a range of strategies across multiple layers to control traffic flow and reduce attack surfaces.
Advantages of Deploying VLANs
VLANs enhance network segmentation by logically dividing a physical network into multiple isolated broadcast domains, improving security and reducing congestion. They simplify management by allowing centralized control over different subnetworks without requiring additional hardware, optimizing resource utilization. VLAN deployment also increases flexibility in network design, enabling easier policy enforcement and faster fault isolation across diverse organizational units.
Benefits of Network Segmentation
Network segmentation enhances security by isolating sensitive data and limiting the spread of cyber threats within an enterprise network. It improves network performance through reduced congestion and optimized traffic flow across segmented zones. This approach also simplifies management and compliance by enabling targeted policy enforcement and easier monitoring of network segments.
Common Use Cases: VLANs vs Network Segmentation
VLANs are commonly used to segment a physical network into multiple logical networks to improve bandwidth management and enhance security by isolating sensitive departments such as finance or human resources. Network segmentation encompasses broader practices, including VLANs, firewalls, and subnetting, to reduce attack surfaces and restrict lateral movement of threats across enterprise networks. Organizations deploy VLANs mainly for internal traffic separation and efficient resource allocation, while network segmentation supports compliance requirements and comprehensive security strategies across both internal and external network boundaries.
Security Implications and Best Practices
VLANs enhance network segmentation by isolating traffic at the data link layer, reducing broadcast domains and limiting attack surfaces within a LAN environment. Effective security practices involve implementing VLAN tagging (802.1Q), enforcing strict access control lists (ACLs), and segregating sensitive resources to prevent lateral movement during breaches. Network segmentation beyond VLANs includes physical separation and software-defined segmentation, offering layered defense strategies to contain threats and minimize risk exposure.
Performance Impact and Scalability Considerations
VLANs enhance network performance by isolating broadcast domains, reducing traffic congestion and improving overall efficiency through logical segmentation within a single physical network. Network segmentation offers a broader approach by dividing the network into distinct segments, potentially spanning multiple VLANs, which optimizes resource allocation and limits the scope of security breaches. Scalability considerations favor VLANs for simpler environments due to easier management and cost-effectiveness, while full network segmentation supports complex, large-scale infrastructures by enabling tailored policies and advanced traffic control.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Network
Choosing the right approach between VLANs and network segmentation depends on your network's scale, security requirements, and performance goals. VLANs offer logical separation of devices within the same physical infrastructure, improving traffic management and reducing broadcast domains. Network segmentation goes beyond VLANs by isolating entire network segments, enhancing security through stricter access controls and minimizing lateral movement during cyberattacks.
VLANs Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com