Shared hosting offers an affordable and efficient solution for hosting multiple websites on a single server, making it ideal for small businesses and personal projects. It provides essential features such as user-friendly control panels, email accounts, and basic security measures. Explore the full article to discover how shared hosting can meet your web hosting needs.
Table of Comparison
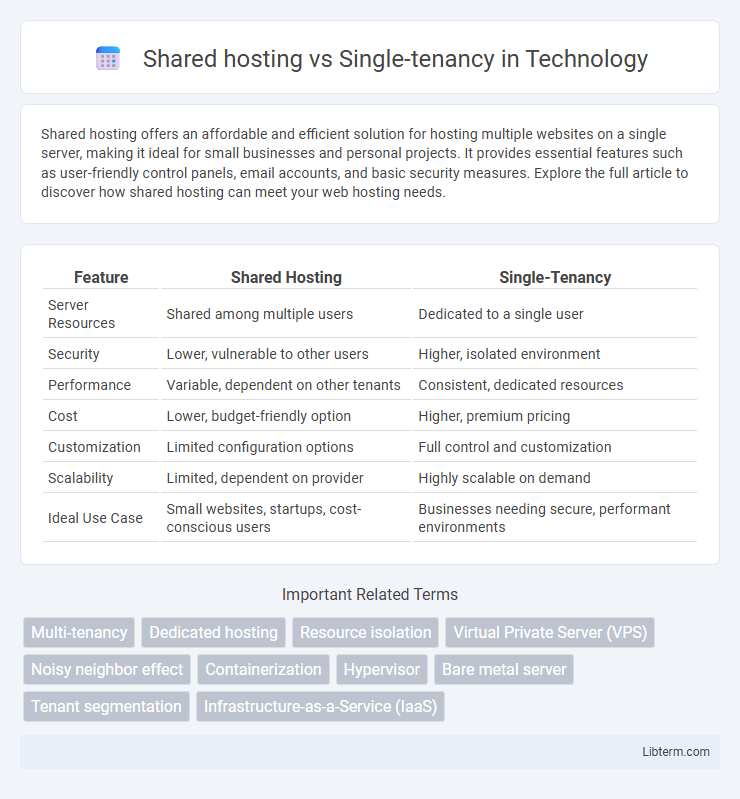
| Feature | Shared Hosting | Single-Tenancy |
|---|---|---|
| Server Resources | Shared among multiple users | Dedicated to a single user |
| Security | Lower, vulnerable to other users | Higher, isolated environment |
| Performance | Variable, dependent on other tenants | Consistent, dedicated resources |
| Cost | Lower, budget-friendly option | Higher, premium pricing |
| Customization | Limited configuration options | Full control and customization |
| Scalability | Limited, dependent on provider | Highly scalable on demand |
| Ideal Use Case | Small websites, startups, cost-conscious users | Businesses needing secure, performant environments |
Introduction to Shared Hosting and Single-Tenancy
Shared hosting involves multiple websites hosted on a single server, sharing resources such as bandwidth, storage, and CPU, making it cost-effective and ideal for small to medium-sized websites with moderate traffic. Single-tenancy provides an isolated server environment dedicated to one client, ensuring enhanced security, performance, and customization options crucial for enterprises with high transactional websites or sensitive data needs. Understanding these foundational hosting models helps businesses select the optimal infrastructure based on their scalability, security, and budget requirements.
Defining Shared Hosting: Key Features
Shared hosting involves multiple websites residing on a single server, sharing resources like CPU, RAM, and disk space, which optimizes cost efficiency for small to medium-sized websites. Key features include limited control over server configurations, standardized security protocols, and simplified management through a common control panel. Resource allocation is dynamic, ensuring that server capacity is distributed among users but can lead to performance variability during traffic spikes.
What is Single-Tenancy? Core Principles Explained
Single-tenancy refers to a hosting architecture where a single client leases an entire server or resource environment exclusively, ensuring dedicated performance, enhanced security, and customization options tailored to that client's needs. This model contrasts with shared hosting, where multiple clients share the same server resources, potentially affecting performance and data privacy. Core principles of single-tenancy include isolated data storage, dedicated resource allocation, and customizable software configurations, providing greater control and compliance for businesses with specific security or operational requirements.
Performance Comparison: Shared Hosting vs Single-Tenancy
Shared hosting environments allocate server resources among multiple users, often leading to variable performance due to resource contention, while single-tenancy provides dedicated resources that ensure consistent and optimized performance levels. Websites hosted on single-tenant servers experience faster load times and better handling of traffic spikes compared to shared hosting, which can suffer from slower response times during peak usage. Performance benchmarks reveal that single-tenancy environments offer superior CPU, memory, and bandwidth allocation, making them ideal for high-demand applications requiring reliability and speed.
Security Considerations in Hosting Environments
Shared hosting environments pose higher security risks due to resource and data sharing among multiple tenants, increasing vulnerability to cross-site attacks and unauthorized access. Single-tenancy hosting offers enhanced security by isolating each tenant's infrastructure, reducing risks of data breaches and providing stricter control over access permissions and compliance with regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA. Organizations with critical data and stringent security requirements typically prefer single-tenancy models to ensure robust protection and minimize exposure to cyber threats.
Cost Analysis: Affordability and Value
Shared hosting offers affordability by distributing server costs among multiple users, making it ideal for small businesses and startups with limited budgets. Single-tenancy provides higher value through dedicated resources and enhanced security, but at a significantly higher price point suitable for enterprises with critical data and performance needs. Evaluating cost versus benefits requires analyzing the total cost of ownership, including maintenance, scalability, and potential downtime risks.
Scalability and Resource Management
Shared hosting offers limited scalability as resources like CPU, RAM, and bandwidth are distributed among multiple users on a single server, leading to potential performance bottlenecks during traffic spikes. Single-tenancy environments provide dedicated resources, enabling seamless scalability by allocating additional computing power and storage based on demand without affecting other tenants. Effective resource management in single-tenancy reduces the risk of resource contention, ensuring consistent performance and optimized utilization for growing applications.
Customization and Control Options
Shared hosting limits customization and control options due to resource sharing among multiple users on the same server. Single-tenancy offers extensive customization and full control over the server environment, allowing tailored software configurations and dedicated resource allocation. Businesses requiring specific security policies or performance optimizations prefer single-tenancy for enhanced flexibility.
Use Cases: When to Choose Shared Hosting or Single-Tenancy
Shared hosting suits small businesses, personal websites, and startups seeking cost-effective solutions with minimal management, ideal for low to moderate traffic and standard security needs. Single-tenancy is optimal for enterprises requiring dedicated resources, enhanced security, and compliance, accommodating high-traffic applications, complex databases, or sensitive customer data. Choosing between shared hosting and single-tenancy depends on workload complexity, budget constraints, performance demands, and regulatory requirements.
Conclusion: Which Hosting Solution is Right for You?
Choosing between shared hosting and single-tenancy depends on your website's traffic, security needs, and budget. Shared hosting offers cost-effective resources for small to medium websites with moderate traffic but may limit customization and security. Single-tenancy provides dedicated resources, enhanced performance, and stronger security, making it ideal for high-traffic sites, sensitive data handling, and businesses requiring full control.
Shared hosting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com