Downloading files efficiently requires a reliable internet connection and secure sources to avoid malware risks. Managing your download settings can optimize speed and storage use, enhancing overall performance. Explore the rest of the article to discover expert tips and essential tools for safer, faster downloading.
Table of Comparison
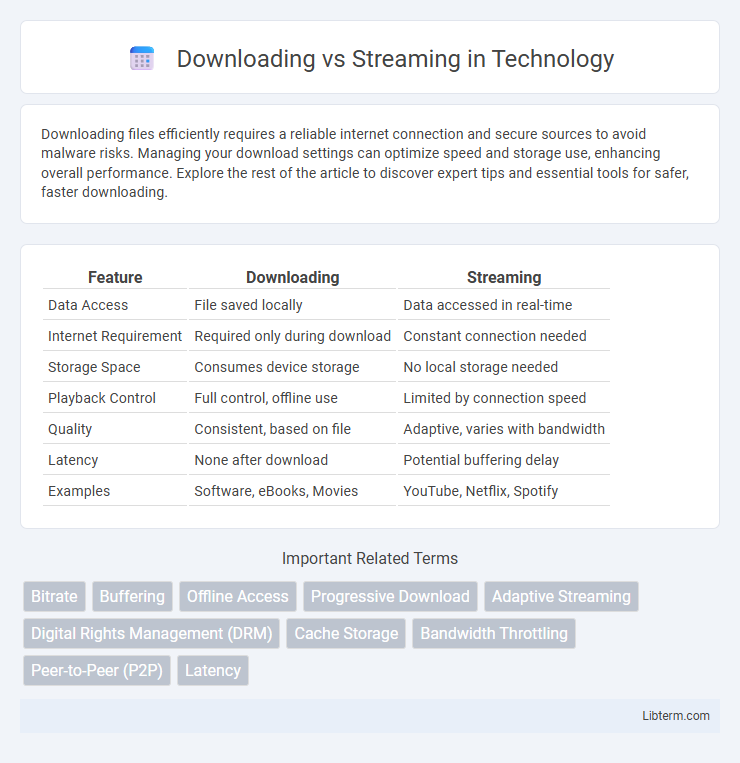
| Feature | Downloading | Streaming |
|---|---|---|
| Data Access | File saved locally | Data accessed in real-time |
| Internet Requirement | Required only during download | Constant connection needed |
| Storage Space | Consumes device storage | No local storage needed |
| Playback Control | Full control, offline use | Limited by connection speed |
| Quality | Consistent, based on file | Adaptive, varies with bandwidth |
| Latency | None after download | Potential buffering delay |
| Examples | Software, eBooks, Movies | YouTube, Netflix, Spotify |
Introduction to Downloading vs Streaming
Downloading involves transferring and storing a complete media file on a device, enabling offline access without internet connectivity. Streaming delivers real-time content over the internet without permanent storage, requiring continuous data transfer and a stable connection. Both methods serve distinct purposes depending on user needs for accessibility, convenience, and storage capacity.
How Downloading Works
Downloading involves transferring a complete file from a remote server to a local device, allowing offline access. The process starts by establishing a connection with the server, followed by sequential packet reception, which are then reassembled into the original file format. Downloading ensures full file availability without requiring continuous internet connectivity, contrasting with streaming that relies on real-time data transmission.
How Streaming Works
Streaming delivers digital content by transmitting data packets over the internet in real-time, allowing immediate playback without storing files locally. It uses protocols like HTTP Live Streaming (HLS) or Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP (DASH) to adjust video quality dynamically based on network speed and device capabilities. This technology reduces buffering and enables continuous media consumption on various devices without requiring full download.
Pros and Cons of Downloading
Downloading allows users to access content offline without requiring an internet connection, making it ideal for travel or areas with limited connectivity. It ensures faster playback without buffering issues and provides permanent access to files, but it consumes device storage space and may involve longer wait times during the initial download process. Security risks can arise if files are downloaded from untrusted sources, potentially exposing devices to malware.
Pros and Cons of Streaming
Streaming offers instant access to a vast library of content without consuming device storage, making it ideal for users with limited space or those seeking convenience. However, streaming relies heavily on a stable and high-speed internet connection, which can cause interruptions, buffering, or reduced video quality during peak usage times. Data caps and latency issues may also limit the overall viewing experience, especially for users with restricted bandwidth or mobile data plans.
Internet Speed and Accessibility
Downloading requires sufficient internet speed to complete files quickly, making it ideal for users with stable, high-bandwidth connections. Streaming depends on consistent internet speed to ensure uninterrupted playback, benefiting those with moderate to fast connectivity but limited storage capacity. Accessibility varies as downloading enables offline access regardless of connection quality, while streaming offers instant access without the need for local storage but relies heavily on a continuous internet connection.
Storage and Device Considerations
Downloading media files requires sufficient device storage capacity, which can be a limitation for users with limited disk space on smartphones, tablets, or computers. Streaming services alleviate storage concerns by enabling instant access to content via internet connection, but they depend heavily on bandwidth and data availability. Devices with higher storage capabilities allow users to build extensive offline libraries, whereas streaming prioritizes real-time consumption without the need for large storage allocation.
Content Availability and Licensing
Downloading offers permanent access to content, allowing offline use without internet dependency, but it requires licensing agreements that permit copying and local storage. Streaming provides instant access to a broad range of content without occupying device storage, relying on continuous internet connection and licensing models that often restrict offline availability or permanent retention. Content availability in streaming is frequently subject to regional licensing limitations and temporal restrictions, whereas downloaded content typically remains accessible regardless of location once legally obtained.
Cost Comparison: Downloading vs Streaming
Downloading typically involves a one-time cost for purchasing or renting content, often leading to lower long-term expenses since users can access media offline without recurring fees. Streaming services usually require ongoing subscription payments, which can accumulate over time and may result in higher total costs depending on usage frequency. Users prioritizing budget-friendly options should evaluate their consumption patterns to determine whether a single download purchase or continuous streaming subscription offers better value.
Future Trends in Digital Media Consumption
Downloading will evolve with faster, more reliable offline media access through advanced compression and storage technologies, enhancing user convenience without internet dependency. Streaming is expected to dominate digital media consumption via higher bandwidth availability, edge computing, and AI-driven personalization that deliver real-time, high-quality content globally. Emerging trends include hybrid models combining downloading and streaming benefits, immersive experiences in AR/VR platforms, and greater integration of 5G and cloud gaming that reshape media accessibility and user engagement.
Downloading Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com