Grey-box testing combines elements of both black-box and white-box testing, allowing testers to evaluate software with partial knowledge of its internal structures. This method helps identify vulnerabilities and logic errors by examining code paths while focusing on functional outcomes. Discover how grey-box testing can enhance your software quality and security in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
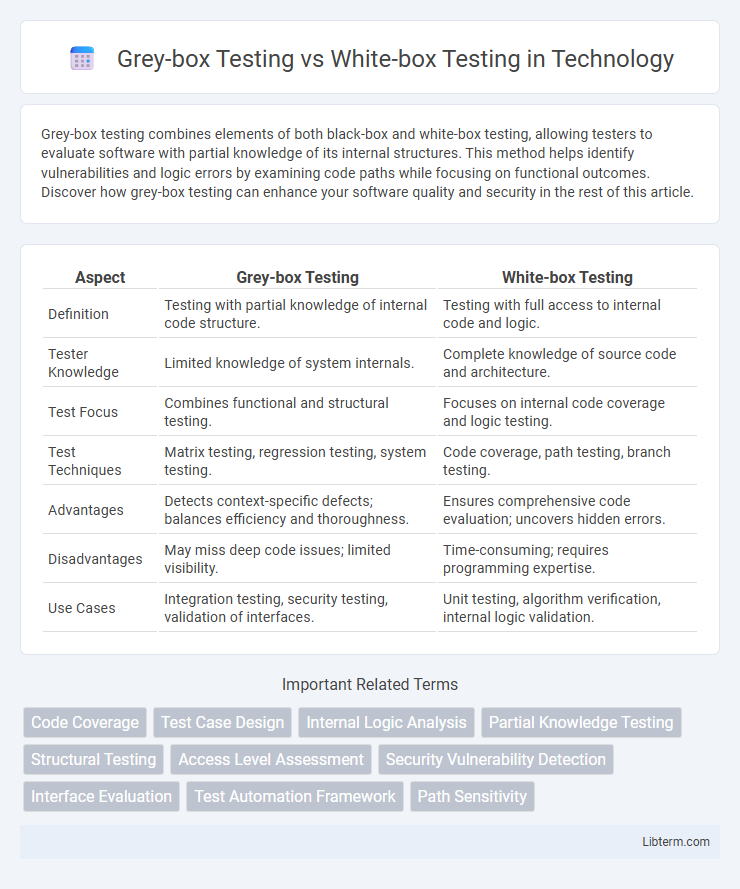
| Aspect | Grey-box Testing | White-box Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Testing with partial knowledge of internal code structure. | Testing with full access to internal code and logic. |
| Tester Knowledge | Limited knowledge of system internals. | Complete knowledge of source code and architecture. |
| Test Focus | Combines functional and structural testing. | Focuses on internal code coverage and logic testing. |
| Test Techniques | Matrix testing, regression testing, system testing. | Code coverage, path testing, branch testing. |
| Advantages | Detects context-specific defects; balances efficiency and thoroughness. | Ensures comprehensive code evaluation; uncovers hidden errors. |
| Disadvantages | May miss deep code issues; limited visibility. | Time-consuming; requires programming expertise. |
| Use Cases | Integration testing, security testing, validation of interfaces. | Unit testing, algorithm verification, internal logic validation. |
Introduction to Software Testing Methods
Grey-box testing combines elements of both white-box and black-box testing by using partial knowledge of the internal code structure, allowing testers to design test cases based on limited system insight. White-box testing, also known as clear-box or glass-box testing, requires complete visibility of the source code, enabling thorough validation of internal logic, paths, and conditions. These methods are fundamental in software testing, ensuring efficient defect identification through different levels of access to the software's inner workings.
Defining Grey-box Testing
Grey-box testing combines elements of both black-box and white-box testing by using limited knowledge of the internal system architecture to design test cases. This method allows testers to access some source code or system internals while primarily focusing on the software's functional behavior and outputs. By leveraging partial transparency, grey-box testing efficiently identifies security vulnerabilities, logic errors, and integration issues that may not be visible in pure black-box or white-box approaches.
Understanding White-box Testing
White-box testing involves examining the internal structure, design, and coding of an application to ensure thorough validation of logic and potential security vulnerabilities. Testers require detailed knowledge of the source code, enabling them to create test cases that cover all possible execution paths, conditions, and branches. This approach contrasts with grey-box testing, where testers have partial knowledge of the internal workings, balancing between code-based and black-box techniques.
Key Differences Between Grey-box and White-box Testing
Grey-box testing combines elements of both black-box and white-box testing by using partial knowledge of the internal code structure, whereas white-box testing requires complete access to the source code to design test cases. Grey-box testing targets vulnerabilities with limited visibility into internal logic, focusing on inputs, outputs, and data flow, while white-box testing involves thorough examination of branches, paths, and conditions within the code. The primary distinction lies in the level of transparency and detail of code access, influencing test design, scope, and detection of security flaws or logical errors.
Advantages of Grey-box Testing
Grey-box testing combines advantages from both black-box and white-box testing by allowing testers partial knowledge of the internal code structure, which helps in identifying security vulnerabilities and logical errors more effectively than black-box testing alone. This approach improves test coverage and efficiency by focusing on critical areas prone to defects while maintaining an unbiased perspective. Grey-box testing is particularly beneficial for integration and penetration testing, providing comprehensive insight without requiring full access to the source code.
Benefits of White-box Testing
White-box testing provides comprehensive code coverage by allowing testers to examine internal structures and logic, resulting in early detection of hidden errors and vulnerabilities. It enhances optimization through detailed analysis of code paths, loops, and conditions, ensuring robust and efficient software performance. This method also facilitates thorough validation of security mechanisms by enabling direct testing of executable code segments and internal functions.
Limitations of Grey-box and White-box Testing
Grey-box testing is limited by its partial knowledge of the internal code structure, which may lead to incomplete test coverage and missed defects hidden deep within the software. White-box testing requires comprehensive access to the source code, making it time-consuming and less effective for identifying issues related to user experience or system integration. Both methods struggle to detect undiscovered security vulnerabilities without combining other testing techniques like black-box or penetration testing.
When to Use Grey-box vs White-box Testing
Grey-box testing is ideal when testers have partial knowledge of the internal code structure, enabling more efficient identification of functional issues and security vulnerabilities without requiring complete access to the source code. White-box testing is best utilized during unit and integration testing phases where in-depth code analysis, logic validation, and path coverage are essential to ensure code quality and detect hidden errors. Choose grey-box testing for testing third-party applications or systems with limited access, and white-box testing for thorough verification by developers familiar with the codebase.
Real-world Applications and Case Studies
Grey-box testing merges aspects of both black-box and white-box testing, making it highly effective in real-world applications like web application security assessments and integration testing, where partial knowledge of the internal code helps identify vulnerabilities without exhaustive code review. White-box testing, with complete transparency into the source code, is crucial for code coverage analysis and debugging critical systems such as embedded software in medical devices or aerospace controls. Case studies from leading tech firms demonstrate grey-box testing's efficiency in uncovering security flaws during penetration testing, while white-box testing excels in ensuring thorough validation of complex algorithms and system logic.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Testing Approach
Selecting between grey-box testing and white-box testing depends on project requirements, resource availability, and security needs. Grey-box testing combines partial internal knowledge with external testing techniques, enabling efficient defect detection without extensive code analysis. White-box testing involves thorough code examination, providing deeper insight into vulnerabilities but demanding higher expertise and time commitment.
Grey-box Testing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com