Landscaping enhances the natural beauty and value of your property by integrating plants, hardscapes, and water features into a cohesive design. Effective landscape planning ensures functional outdoor spaces that promote relaxation and enjoyment throughout the seasons. Explore the rest of the article to discover creative ideas and expert tips for transforming your landscape.
Table of Comparison
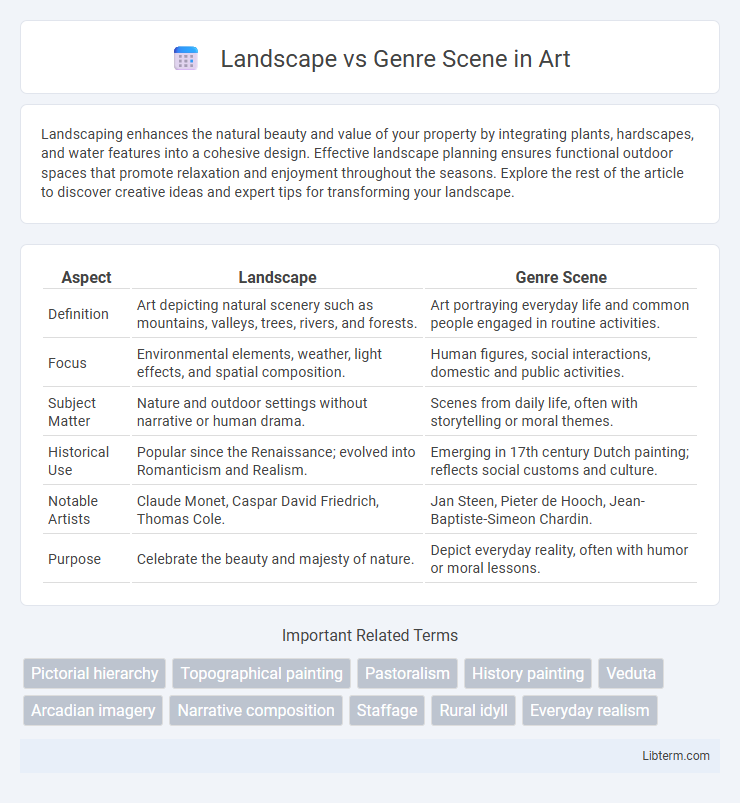
| Aspect | Landscape | Genre Scene |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Art depicting natural scenery such as mountains, valleys, trees, rivers, and forests. | Art portraying everyday life and common people engaged in routine activities. |
| Focus | Environmental elements, weather, light effects, and spatial composition. | Human figures, social interactions, domestic and public activities. |
| Subject Matter | Nature and outdoor settings without narrative or human drama. | Scenes from daily life, often with storytelling or moral themes. |
| Historical Use | Popular since the Renaissance; evolved into Romanticism and Realism. | Emerging in 17th century Dutch painting; reflects social customs and culture. |
| Notable Artists | Claude Monet, Caspar David Friedrich, Thomas Cole. | Jan Steen, Pieter de Hooch, Jean-Baptiste-Simeon Chardin. |
| Purpose | Celebrate the beauty and majesty of nature. | Depict everyday reality, often with humor or moral lessons. |
Defining Landscape and Genre Scene
Landscape art captures natural scenery such as mountains, forests, rivers, and skies, emphasizing the beauty and atmosphere of outdoor environments. Genre scenes depict everyday life and ordinary people engaged in common activities, highlighting social interactions and cultural customs. Both genres offer unique perspectives on human experience, with landscapes focusing on nature's forms and genre scenes portraying daily human moments.
Historical Origins of Each Art Form
Landscape art originated in ancient cave paintings and gained prominence during the Renaissance as artists began to explore nature's beauty and human interaction with the environment. Genre scenes, depicting everyday life and common people, trace back to the Dutch Golden Age in the 17th century when artists emphasized realistic portrayals of domestic and social activities. Both art forms evolved to reflect cultural values and societal norms, highlighting the human experience through distinct visual narratives.
Core Features of Landscapes
Landscapes primarily emphasize natural elements such as mountains, rivers, trees, and skies, showcasing environmental features and atmospheric conditions. Core features include the depiction of spatial depth, natural light effects, and seasonal changes to evoke mood and place. Unlike genre scenes, landscapes focus less on human activity and more on the portrayal of nature's vastness and detail.
Key Elements of Genre Scenes
Genre scenes depict everyday life with detailed representations of people engaged in common activities, emphasizing social interactions and cultural customs. Key elements include realistic figures, domestic or public settings, and narrative moments that convey stories or moral messages. These scenes focus on human behavior and environment rather than purely natural landscapes, distinguishing them from landscape art.
Techniques Unique to Landscape Painting
Landscape painting techniques emphasize the use of atmospheric perspective, capturing natural light variations, and detailed texturing of vegetation and terrain to create depth and realism. Artists employ glazing and wet-on-wet watercolor methods to achieve smooth color transitions and subtle tonal shifts reflecting sky and earth elements. Unlike genre scenes, landscapes prioritize spatial composition and mood enhancement through brushstroke techniques that evoke natural forms and environmental conditions.
Techniques Unique to Genre Scene Art
Genre scene art uniquely employs narrative techniques that capture everyday life with intimate detail and emotional depth, often using chiaroscuro to highlight human interactions. Artists utilize spontaneous brushstrokes and dynamic compositions to convey movement and storytelling, setting genre scenes apart from the more static and structured landscape paintings. Careful attention to domestic interiors, clothing, and expressions provides cultural context, emphasizing the social realism distinctive to genre scene art.
Notable Artists and Iconic Works
Landscape art features notable artists like Claude Monet, whose "Impression, Sunrise" revolutionized the genre with its emphasis on natural light and atmosphere. Genre scenes are exemplified by Johannes Vermeer, known for his iconic work "The Milkmaid," capturing everyday domestic life with meticulous detail. Both genres highlight different aspects of visual storytelling, with landscapes emphasizing nature and genre scenes focusing on human activity.
How Subject Matter Influences Interpretation
Landscape paintings evoke emotional responses through natural settings, emphasizing environment and atmosphere to convey mood and place. Genre scenes portray everyday life with human figures, allowing viewers to interpret social interactions, cultural context, and narratives embedded in daily activities. The subject matter directs perception by prioritizing either the external world's beauty or the introspective insight into human behavior and society.
Contemporary Relevance of Both Styles
Landscape and genre scenes continue to hold significant contemporary relevance by capturing diverse cultural and environmental narratives. Landscape art emphasizes the depiction of natural and urban environments, often highlighting climate change and ecological mindfulness, while genre scenes portray everyday life, social interactions, and cultural diversity, reflecting societal values and human experiences. Both styles remain vital for artists to explore identity, place, and community in today's globalized world.
Choosing Between Landscape and Genre Scene in Artistic Practice
Choosing between landscape and genre scene in artistic practice depends on the desired narrative and emotional impact. Landscape art emphasizes natural scenery, light, and atmosphere, making it ideal for exploring environmental mood and spatial depth. Genre scenes focus on everyday life and human activity, providing intimate storytelling opportunities and cultural context through detailed character interactions.
Landscape Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com