Surrealism explores the unconscious mind through dream-like imagery and unexpected juxtapositions, challenging traditional perceptions of reality. This art movement, originating in the early 20th century, blends imagination with subconscious thoughts to create thought-provoking and often bizarre visuals. Discover how surrealism can influence your creativity and perception by reading the rest of the article.
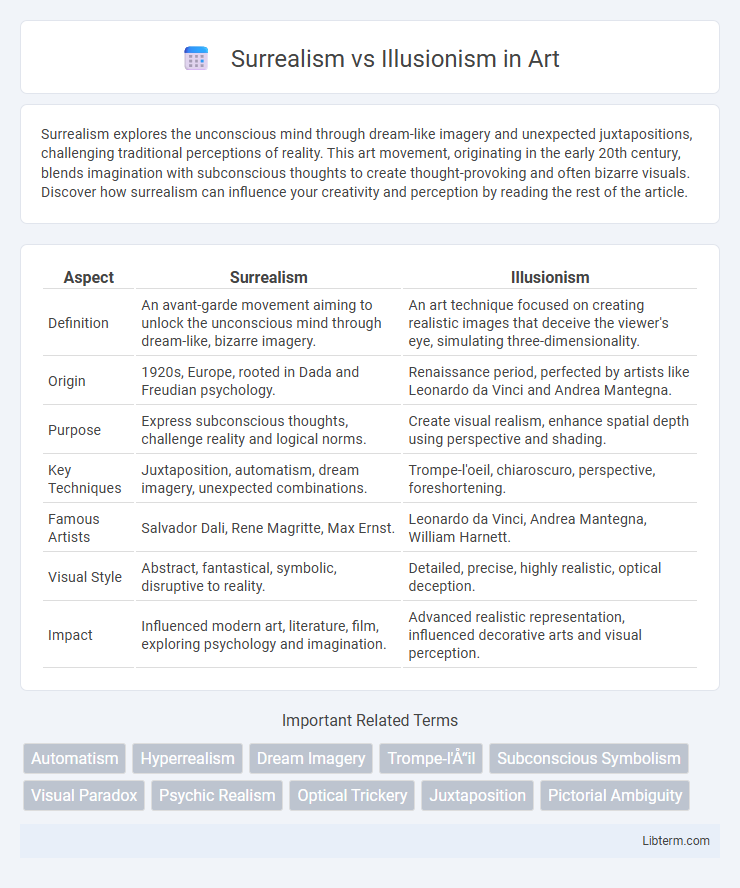
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Surrealism | Illusionism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | An avant-garde movement aiming to unlock the unconscious mind through dream-like, bizarre imagery. | An art technique focused on creating realistic images that deceive the viewer's eye, simulating three-dimensionality. |
| Origin | 1920s, Europe, rooted in Dada and Freudian psychology. | Renaissance period, perfected by artists like Leonardo da Vinci and Andrea Mantegna. |
| Purpose | Express subconscious thoughts, challenge reality and logical norms. | Create visual realism, enhance spatial depth using perspective and shading. |
| Key Techniques | Juxtaposition, automatism, dream imagery, unexpected combinations. | Trompe-l'oeil, chiaroscuro, perspective, foreshortening. |
| Famous Artists | Salvador Dali, Rene Magritte, Max Ernst. | Leonardo da Vinci, Andrea Mantegna, William Harnett. |
| Visual Style | Abstract, fantastical, symbolic, disruptive to reality. | Detailed, precise, highly realistic, optical deception. |
| Impact | Influenced modern art, literature, film, exploring psychology and imagination. | Advanced realistic representation, influenced decorative arts and visual perception. |
Introduction to Surrealism and Illusionism
Surrealism emerged in the early 20th century as an avant-garde movement that sought to unlock the creative potential of the unconscious mind through dreamlike, illogical scenes and bizarre imagery. Illusionism, rooted in classical art traditions, centers on creating highly realistic representations that deceive the viewer's eye, often utilizing techniques like chiaroscuro and perspective to simulate three-dimensionality. Both styles challenge perception but diverge in intent: surrealism explores the subconscious and abstract, whereas illusionism emphasizes precise visual mimicry and realism.
Historical Origins and Influential Figures
Surrealism emerged in the early 1920s as an avant-garde movement led by Andre Breton, seeking to unlock the unconscious mind through dream-like, fantastical imagery that defied logical reasoning. Illusionism, rooted in Renaissance art, emphasizes hyper-realistic depictions by artists like Andrea Mantegna and later trompe-l'oeil painters who created optical illusions to deceive viewers' perception of reality. While surrealism challenges the boundaries of reality and imagination, illusionism focuses on technical mastery to replicate visual accuracy and depth.
Core Philosophies: Dream vs. Deception
Surrealism prioritizes the exploration of the subconscious mind through dream-like imagery, emphasizing a genuine connection to inner psychological realities rather than external appearances. Illusionism centers on the artful deception of the viewer's perception, creating hyper-realistic representations that challenge the boundaries between reality and artifice. Surrealism's core philosophy embraces the authenticity of dreams as expressions of deeper truths, while illusionism masters visual trickery to manipulate beliefs about what is real.
Techniques and Visual Approaches
Surrealism employs techniques such as automatic drawing, collage, and dreamlike juxtapositions to evoke the unconscious mind and challenge reality through bizarre, unexpected imagery. Illusionism focuses on meticulous detail, perspective, and shading to create lifelike representations that deceive the eye into perceiving three-dimensionality on a flat surface. While surrealism emphasizes imaginative and symbolic content, illusionism prioritizes technical precision to achieve visual realism.
Iconic Artworks: Surrealist and Illusionist Examples
Iconic surrealist artworks such as Salvador Dali's "The Persistence of Memory" showcase dreamlike scenes with distorted time and bizarre imagery, emphasizing the subconscious mind's influence. In contrast, illusionist art is exemplified by works like M.C. Escher's "Relativity," which employs precise mathematical structures to create impossible perspectives and mind-bending visual paradoxes. These masterpieces highlight surrealism's focus on fantastical, irrational compositions versus illusionism's dedication to optical tricks and realistic deception.
Psychological Impact and Interpretation
Surrealism evokes a profound psychological impact by accessing the unconscious mind through dreamlike, bizarre imagery that challenges logical perception and invites multiple interpretations. Illusionism, by contrast, relies on realistic depictions that deceive the viewer's senses, creating a tangible but false reality that prompts cognitive engagement with visual trickery. The interpretation of Surrealism leans toward exploring internal emotional states and subconscious fears, while Illusionism emphasizes visual accuracy and external reality manipulation.
Symbolism in Surrealism vs Illusionism
Surrealism employs symbolism to explore the unconscious mind and dreamscapes, often using bizarre and fantastical imagery to provoke emotional and psychological responses. Illusionism, on the other hand, focuses on creating highly realistic representations that deceive the eye, emphasizing technical skill and perspective to mimic reality. Symbolism in Surrealism prioritizes metaphorical and abstract meanings, contrasting with Illusionism's dedication to lifelike portrayal and visual accuracy.
Influence on Modern and Contemporary Art
Surrealism revolutionized modern and contemporary art by unlocking the unconscious mind, inspiring artists like Salvador Dali and Rene Magritte to explore dreamlike imagery and bizarre juxtapositions that challenge reality. Illusionism, with its hyper-realistic techniques pioneered by artists such as William Harnett and Richard Estes, pushed the boundaries of visual perception, influencing photorealism and trompe-l'oeil art forms. Both movements shifted artistic focus, with Surrealism emphasizing psychological depth and Illusionism prioritizing technical mastery, shaping diverse aesthetic approaches in today's art world.
Surrealism and Illusionism in Popular Culture
Surrealism in popular culture is characterized by dream-like visuals, unexpected juxtapositions, and bizarre imagery that challenge reality and provoke emotional responses, as seen in the works of Salvador Dali and films like David Lynch's "Eraserhead." Illusionism, by contrast, focuses on creating lifelike representations that deceive the viewer's perception, often utilized in magic acts, virtual reality experiences, and hyper-realistic art forms such as those by Chuck Close. Both styles influence media, advertising, and entertainment, with Surrealism fueling creativity and subconscious exploration while Illusionism enhances immersive and sensory experiences.
Conclusion: Distinctive Legacies and Future Evolution
Surrealism's legacy lies in its challenge to rational thought and exploration of the unconscious, influencing modern art and literature by embracing dreamlike, fantastical imagery. Illusionism's enduring impact is evident in its meticulous realism and techniques that create convincing visual deception, advancing the fields of painting, sculpture, and digital media. Future evolution may see Surrealism integrating with virtual reality and AI to deepen psychological exploration, while Illusionism leverages augmented reality and holography to enhance immersive experiences.
Surrealism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com