Earnings management involves the strategic manipulation of financial reports to present a desired image of a company's performance. This practice can affect investor decisions, regulatory scrutiny, and the overall transparency of financial statements. Discover how understanding earnings management can help you better evaluate corporate health in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
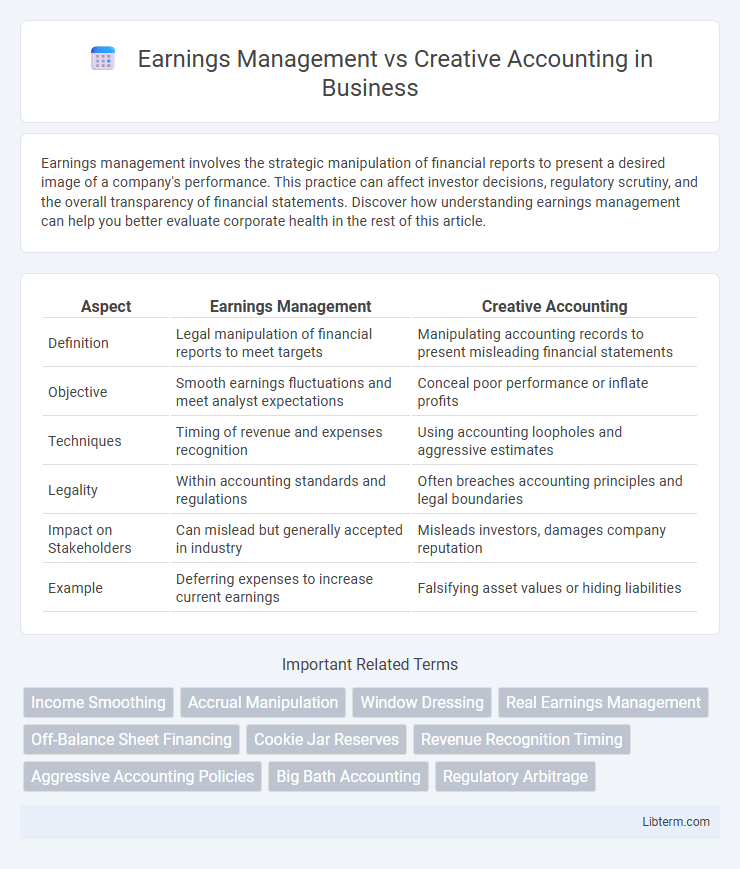
| Aspect | Earnings Management | Creative Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal manipulation of financial reports to meet targets | Manipulating accounting records to present misleading financial statements |
| Objective | Smooth earnings fluctuations and meet analyst expectations | Conceal poor performance or inflate profits |
| Techniques | Timing of revenue and expenses recognition | Using accounting loopholes and aggressive estimates |
| Legality | Within accounting standards and regulations | Often breaches accounting principles and legal boundaries |
| Impact on Stakeholders | Can mislead but generally accepted in industry | Misleads investors, damages company reputation |
| Example | Deferring expenses to increase current earnings | Falsifying asset values or hiding liabilities |
Introduction to Earnings Management and Creative Accounting
Earnings management involves the strategic manipulation of financial reports by company management to influence stakeholders' perceptions of the firm's profitability and financial health, often within the bounds of accounting standards. Creative accounting refers to the use of accounting techniques to present financial information in a misleading manner, sometimes exploiting loopholes or ambiguities in accounting regulations to distort true financial performance. Both practices impact financial transparency, but earnings management typically operates within accepted frameworks, whereas creative accounting often skirts ethical and legal boundaries.
Key Definitions and Concepts
Earnings management involves the strategic manipulation of financial reports by altering accounting methods to meet specific financial targets or expectations, often within legal boundaries. Creative accounting refers to more aggressive and sometimes unethical practices that distort financial statements to present a misleading view of a company's financial health. Both practices impact the reliability and transparency of financial information, with earnings management typically seen as subtle adjustments and creative accounting involving deliberate deception.
Historical Background and Evolution
Earnings management and creative accounting have evolved from early 20th-century financial reporting practices aiming to meet investor expectations and regulatory requirements. The historical background reveals earnings management as intentional manipulation within accounting standards to influence reported profits, while creative accounting exploits loopholes and aggressive interpretations to present a favorable financial position. Over time, increased regulatory scrutiny and advancements in accounting standards have shaped the evolution of these practices, highlighting the ongoing tension between transparent reporting and managerial discretion.
Motivations Behind Earnings Management
Earnings management is driven by the motivation to meet or exceed financial benchmarks to influence investor perceptions and secure favorable conditions such as stock prices or executive bonuses. Companies may manipulate accruals or judiciously time revenues and expenses, aiming to present a stable or improved financial outlook. In contrast, creative accounting often involves more aggressive, borderline legal strategies to distort financial statements, motivated by pressures to conceal poor performance or enhance capital market access.
Techniques Used in Creative Accounting
Creative accounting employs techniques such as income smoothing, revenue recognition manipulation, and off-balance-sheet financing to alter financial statements without outright falsification. Earnings management, while overlapping, often uses accrual-based adjustments and discretionary expense timing to influence reported profits within accounting standards. The strategic selection and timing of these techniques enable firms to present desired financial outcomes, impacting investor perception and regulatory scrutiny.
Regulatory Perspectives and Legal Boundaries
Earnings management involves manipulating financial reports within the framework of accounting standards to meet specific targets, while creative accounting often exploits loopholes to distort financial reality beyond acceptable legal limits, raising significant regulatory concerns. Regulatory bodies such as the SEC impose strict guidelines and disclosure requirements to distinguish legitimate earnings management from fraudulent practices, emphasizing transparency and accuracy in financial reporting. Legal boundaries are defined by accounting principles like GAAP or IFRS, with violations potentially leading to sanctions, highlighting the critical role of auditors and regulators in maintaining market integrity.
Impact on Financial Statements and Stakeholders
Earnings management manipulates financial results within accounting standards to influence investor perceptions, often resulting in distorted asset values and income figures on financial statements. Creative accounting involves aggressive or deceptive techniques that may violate accounting principles, leading to misleading financial disclosures and eroding stakeholder trust. Both practices compromise the reliability of financial reports, increasing risks for investors, creditors, and regulators by obscuring a company's true economic performance.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples
Earnings management and creative accounting often intertwine in case studies like Enron and WorldCom, where executives manipulated financial reports to present misleading profitability and sustain stock prices. Real-world examples reveal that earnings management exploits accounting flexibility within generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP), while creative accounting involves deliberate distortion or omission of financial data to deceive stakeholders. Analysis of these cases highlights the critical need for robust regulatory frameworks and transparent auditing practices to deter financial misreporting.
Detection Methods and Red Flags
Earnings management involves manipulating financial reports within accounting standards to present an overly positive financial position, while creative accounting pushes boundaries by exploiting loopholes to distort financial statements. Detection methods include ratio analysis, trend analysis, and forensic accounting techniques such as data mining and Benford's Law to identify inconsistencies or irregularities in financial data. Key red flags signaling potential earnings manipulation include unusual revenue recognition patterns, significant fluctuations in accruals, and discrepancies between cash flow and reported earnings.
Ethical Implications and Future Trends
Earnings management involves the manipulation of financial reports within legal boundaries to influence stakeholders' perceptions, often blurring ethical lines, while creative accounting stretches accounting rules to present an overly favorable view, sometimes crossing into fraudulent territory. Both practices risk undermining trust and transparency in financial markets, raising significant ethical concerns about integrity and corporate responsibility. Future trends indicate increased regulatory scrutiny and adoption of advanced auditing technologies like AI to detect and prevent such manipulations, promoting greater financial accountability.
Earnings Management Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com