A Letter of Credit (LC) is a financial document issued by a bank guaranteeing a seller will receive payment from the buyer, provided certain terms and conditions are met. This instrument is widely used in international trade to reduce risks and assure both parties that obligations will be fulfilled. Discover how Letters of Credit can protect your transactions and streamline global business in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
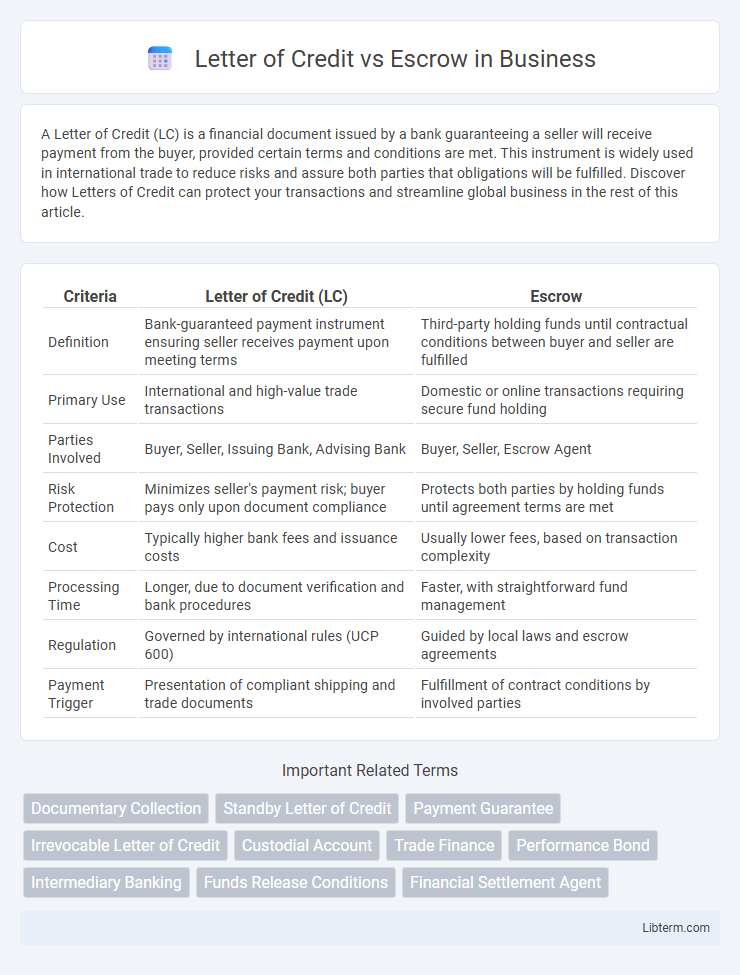
| Criteria | Letter of Credit (LC) | Escrow |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Bank-guaranteed payment instrument ensuring seller receives payment upon meeting terms | Third-party holding funds until contractual conditions between buyer and seller are fulfilled |
| Primary Use | International and high-value trade transactions | Domestic or online transactions requiring secure fund holding |
| Parties Involved | Buyer, Seller, Issuing Bank, Advising Bank | Buyer, Seller, Escrow Agent |
| Risk Protection | Minimizes seller's payment risk; buyer pays only upon document compliance | Protects both parties by holding funds until agreement terms are met |
| Cost | Typically higher bank fees and issuance costs | Usually lower fees, based on transaction complexity |
| Processing Time | Longer, due to document verification and bank procedures | Faster, with straightforward fund management |
| Regulation | Governed by international rules (UCP 600) | Guided by local laws and escrow agreements |
| Payment Trigger | Presentation of compliant shipping and trade documents | Fulfillment of contract conditions by involved parties |
Introduction to Letter of Credit and Escrow
A Letter of Credit is a financial instrument issued by a bank guaranteeing a buyer's payment to a seller upon fulfillment of specified conditions, commonly used in international trade to reduce payment risk. Escrow is a legal arrangement where a third party holds funds or assets until contractual obligations between buyer and seller are met, ensuring secure transaction completion. Both mechanisms enhance trust and mitigate risks in financial transactions by providing payment assurance under predetermined terms.
Definition and Key Features of Letter of Credit
A Letter of Credit (LC) is a financial instrument issued by a bank guaranteeing a buyer's payment to a seller upon fulfilling specific documentary conditions. Key features of an LC include bank involvement for payment assurance, strictly defined terms requiring presentation of compliant shipping or trade documents, and reduced risk of non-payment in international trade. Unlike escrow, which holds funds until agreed conditions are met, an LC leverages bank credit to facilitate secure transactions between distant parties.
Definition and Key Features of Escrow
Escrow is a financial arrangement where a neutral third party holds funds or assets until all contractual conditions are met, ensuring secure transactions in various industries such as real estate and online commerce. Key features of escrow include impartial custody of funds, predefined release conditions, and protection against fraud by safeguarding both buyer and seller interests. Unlike a Letter of Credit, which is issued by a bank to guarantee payment, escrow provides a managed holding account that facilitates trust between transacting parties.
How Letter of Credit Works
A Letter of Credit (LC) is a financial instrument issued by a bank guaranteeing a buyer's payment to a seller upon presentation of specific documents verifying shipment or delivery. It ensures payment security in international trade by mitigating risks for both parties and is typically used when buyers and sellers do not have established trust. The LC process involves an issuing bank, advising bank, and beneficiary, with payment released only after compliance with agreed terms, offering assurance that funds are available if conditions are met.
How Escrow Works
Escrow works by involving a neutral third party who holds funds or assets securely until all predefined conditions of a transaction are met by both the buyer and seller. This process ensures that the payment is only released when the goods or services have been delivered as agreed, protecting both parties from fraud or default. Escrow services are commonly used in real estate, online sales, and business acquisitions to provide trust and transparency throughout the transaction.
Major Differences Between Letter of Credit and Escrow
A Letter of Credit is a bank-guaranteed payment method primarily used in international trade to ensure that payment will be made to the seller upon presentation of specified documents, while Escrow involves a neutral third party holding funds or assets until predetermined conditions are met by both buyer and seller. Letters of Credit require strict compliance with documentation and are typically governed by the Uniform Customs and Practice for Documentary Credits (UCP 600), whereas Escrow agreements are contractual and flexible, tailored to domestic or online transactions without stringent formalities. The key difference lies in the risk mitigation approach: Letters of Credit focus on payment assurance through banking institutions, whereas Escrow secures transaction terms by retaining funds until mutual obligations are fulfilled.
Advantages of Using Letter of Credit
A Letter of Credit offers secure payment guarantees by involving reputable banks that ensure funds are released only when contractual terms are met, minimizing payment risk for sellers. It provides greater financial assurance to exporters and importers by validating creditworthiness and mitigating default risk. This instrument enhances international trade confidence by streamlining transactions and reducing disputes over payment.
Advantages of Using Escrow
Escrow offers enhanced security by holding funds in a neutral third-party account until all contractual obligations are met, reducing risk for both buyers and sellers. It ensures timely and conditional release of payments, preventing fraud and fostering trust in high-value transactions. Escrow services often provide greater flexibility and transparency compared to Letters of Credit, especially in online and real estate deals.
When to Use Letter of Credit vs Escrow
Letter of Credit is ideal for international transactions requiring guaranteed payment upon delivery, especially in complex trade deals involving multiple parties and regulatory compliance. Escrow is best suited for domestic or smaller transactions where trust issues exist, offering a neutral third party to hold funds until contractual obligations are met. Choosing between Letter of Credit and Escrow depends on transaction complexity, geographic scope, and the need for financial risk mitigation.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Payment Method
Choosing between a Letter of Credit and Escrow depends on the transaction's complexity, risk level, and parties' trust. Letters of Credit offer strong assurance in international trade by guaranteeing payment upon meeting specified documents, ideal for high-value or cross-border deals. Escrow services provide secure, neutral fund holding until contract terms are fulfilled, suitable for domestic transactions needing impartial fund management.
Letter of Credit Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com