Dividend investing focuses on selecting stocks that regularly distribute a portion of their earnings to shareholders, providing a steady income stream and potential for capital appreciation. This strategy can enhance portfolio stability and generate passive income, particularly beneficial during market volatility. Explore this article to learn how dividend investing can boost your financial growth and help you build long-term wealth.
Table of Comparison
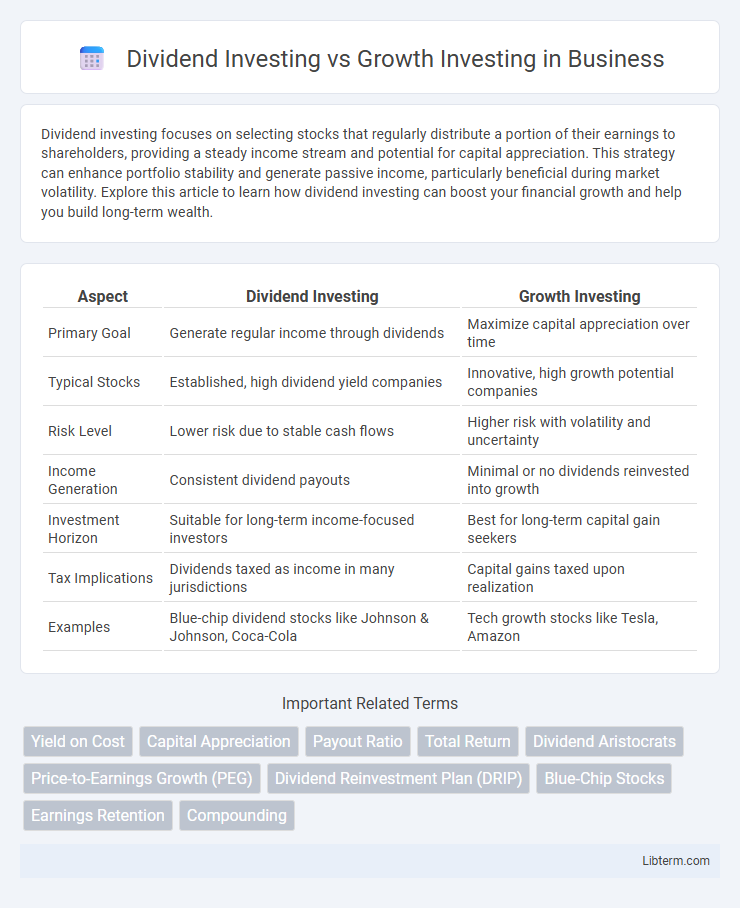
| Aspect | Dividend Investing | Growth Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Generate regular income through dividends | Maximize capital appreciation over time |
| Typical Stocks | Established, high dividend yield companies | Innovative, high growth potential companies |
| Risk Level | Lower risk due to stable cash flows | Higher risk with volatility and uncertainty |
| Income Generation | Consistent dividend payouts | Minimal or no dividends reinvested into growth |
| Investment Horizon | Suitable for long-term income-focused investors | Best for long-term capital gain seekers |
| Tax Implications | Dividends taxed as income in many jurisdictions | Capital gains taxed upon realization |
| Examples | Blue-chip dividend stocks like Johnson & Johnson, Coca-Cola | Tech growth stocks like Tesla, Amazon |
Introduction to Dividend and Growth Investing
Dividend investing focuses on stocks that pay regular dividends, providing investors with a steady income stream and potential for long-term capital appreciation. Growth investing targets companies with high revenue and earnings growth potential, aiming to maximize capital gains rather than immediate income. Both strategies require understanding market cycles, company fundamentals, and risk tolerance to align with specific financial goals.
Key Differences Between Dividend and Growth Investing
Dividend investing focuses on generating regular income through companies that consistently pay dividends, often characterized by stable, mature firms with reliable cash flows. Growth investing targets capital appreciation by investing in companies with high earnings growth potential, typically reinvesting profits rather than paying dividends. The key differences lie in the investor's goal: income generation versus capital gains, and the type of companies preferred--dividend-paying blue-chip stocks versus high-growth innovators.
Advantages of Dividend Investing
Dividend investing offers consistent income through regular payouts, providing a reliable cash flow stream even during market downturns. This strategy often involves investing in established companies with strong financial health, contributing to lower volatility and enhanced portfolio stability. Dividend reinvestment can accelerate wealth accumulation by compounding returns over time, making it a powerful approach for long-term financial growth and retirement planning.
Pros and Cons of Growth Investing
Growth investing offers the potential for substantial capital appreciation by targeting companies with above-average revenue and earnings growth, often in innovative sectors like technology and healthcare. However, this strategy carries higher volatility and risk since many growth stocks reinvest earnings rather than paying dividends, making returns heavily reliant on market sentiment and future growth prospects. Investors may face extended periods of underperformance, but successful growth investments can outperform dividend stocks over the long term through significant price appreciation.
Risk Factors in Dividend vs Growth Strategies
Dividend investing typically involves lower risk due to steady income from regular dividend payouts and the stability of established companies. Growth investing carries higher risk as it targets companies reinvesting earnings for expansion, often with volatile stock prices and uncertain future profitability. Market fluctuations and economic downturns can impact growth stocks more severely, while dividend stocks may offer some downside protection through income generation.
Income Generation: Dividends vs Capital Appreciation
Dividend investing focuses on income generation by targeting stocks that regularly pay dividends, providing a steady cash flow to investors. Growth investing prioritizes capital appreciation by selecting companies with high potential for revenue and earnings expansion, resulting in increased stock prices over time. Both strategies offer distinct financial benefits, with dividend investing emphasizing immediate income and growth investing aiming for long-term wealth accumulation.
Suitability for Different Investor Profiles
Dividend investing suits risk-averse investors seeking steady income through regular dividend payments from established companies with stable cash flows. Growth investing appeals to risk-tolerant individuals aiming for long-term capital appreciation by targeting companies with high earnings growth potential, often reinvesting profits rather than paying dividends. Investor profiles influenced by time horizon, income needs, and risk tolerance determine the optimal strategy between dividend and growth investing approaches.
Tax Implications: Dividend vs Growth Investments
Dividend investing often results in regular taxable income through dividend payouts, which may be taxed at different rates depending on whether dividends are qualified or non-qualified, impacting overall returns. Growth investing typically defers tax liability until assets are sold, resulting in capital gains tax, which can benefit from lower long-term rates if held beyond one year. Understanding these tax implications helps investors optimize portfolio strategy by balancing immediate income from dividends against potential tax-efficient capital appreciation.
Historical Performance Comparison
Dividend investing has historically delivered steady income and lower volatility, with S&P 500 dividend-paying stocks generating average annual returns of around 9-10% over the past five decades. Growth investing, characterized by reinvesting earnings for expansion, has outperformed dividend strategies during bull markets, with tech-heavy indices like the NASDAQ exhibiting average returns exceeding 12% annually since the 1990s. Historical data suggests dividend investing offers resilience in bear markets, while growth investing provides higher upside potential during economic expansions.
Choosing the Right Strategy for Your Goals
Dividend investing focuses on generating regular income through stocks that pay consistent dividends, making it ideal for investors seeking steady cash flow and lower risk. Growth investing targets companies with high potential for capital appreciation, appealing to those aiming for long-term wealth accumulation despite higher volatility. Selecting the right strategy depends on your financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment horizon.
Dividend Investing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com