ESG investing prioritizes environmental, social, and governance factors to foster sustainable and ethical business practices. By aligning your investment portfolio with ESG criteria, you can support companies that demonstrate responsibility while potentially reducing risk. Discover how ESG investing can impact your financial goals by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
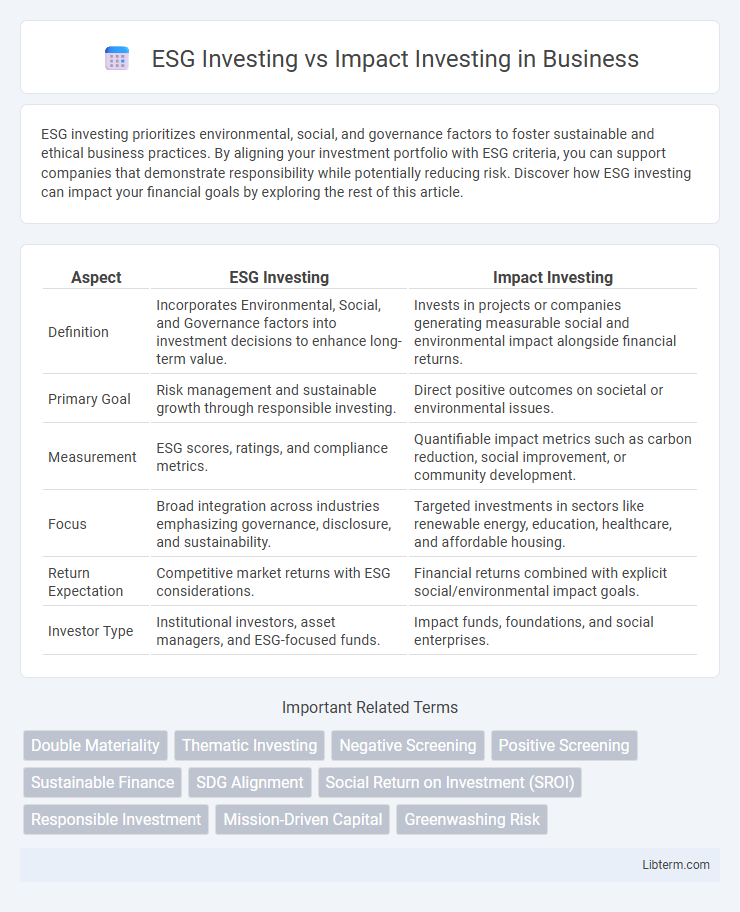
| Aspect | ESG Investing | Impact Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Incorporates Environmental, Social, and Governance factors into investment decisions to enhance long-term value. | Invests in projects or companies generating measurable social and environmental impact alongside financial returns. |
| Primary Goal | Risk management and sustainable growth through responsible investing. | Direct positive outcomes on societal or environmental issues. |
| Measurement | ESG scores, ratings, and compliance metrics. | Quantifiable impact metrics such as carbon reduction, social improvement, or community development. |
| Focus | Broad integration across industries emphasizing governance, disclosure, and sustainability. | Targeted investments in sectors like renewable energy, education, healthcare, and affordable housing. |
| Return Expectation | Competitive market returns with ESG considerations. | Financial returns combined with explicit social/environmental impact goals. |
| Investor Type | Institutional investors, asset managers, and ESG-focused funds. | Impact funds, foundations, and social enterprises. |
Introduction to ESG and Impact Investing
ESG investing evaluates companies based on environmental, social, and governance criteria to identify sustainable and ethical business practices that minimize risk and promote long-term value. Impact investing specifically targets investments that generate measurable social and environmental benefits alongside financial returns, emphasizing intentional positive change. Both strategies prioritize responsible investing but differ in their approach, with ESG integrating criteria into traditional analysis and impact investing focusing on direct contributions to societal goals.
Defining ESG Investing
ESG investing focuses on integrating environmental, social, and governance criteria into financial analysis to evaluate a company's long-term sustainability and ethical impact. This strategy prioritizes factors like carbon footprint, labor practices, and corporate governance to identify risks and opportunities that affect financial performance. Investors use ESG metrics to promote responsible business conduct while seeking competitive returns.
Understanding Impact Investing
Impact investing prioritizes generating measurable social and environmental benefits alongside financial returns, targeting sectors like renewable energy, affordable housing, and healthcare. This approach contrasts with ESG investing, which integrates environmental, social, and governance criteria primarily to manage risks and enhance long-term value. Investors in impact funds seek tangible outcomes such as carbon emission reductions, job creation in underserved communities, and improved access to essential services.
Key Differences Between ESG and Impact Investing
ESG investing integrates environmental, social, and governance criteria into financial analysis to manage risks and identify opportunities, primarily aiming for sustainable financial returns. Impact investing intentionally targets measurable social and environmental benefits alongside financial gains, emphasizing direct positive outcomes in areas like renewable energy, affordable housing, or education. The key difference lies in ESG's focus on risk management and value enhancement through sustainability factors, whereas impact investing prioritizes generating tangible, positive societal or environmental impact.
Investment Strategies and Approaches
ESG investing integrates environmental, social, and governance factors into traditional financial analysis to manage risks and identify sustainable opportunities, focusing on long-term value creation. Impact investing targets measurable positive social or environmental outcomes alongside financial returns, emphasizing direct contributions to specific causes or projects. ESG strategies often involve screening and engagement with companies, while impact investing prioritizes funding enterprises or initiatives with intentional, quantifiable impacts.
Measuring Outcomes: ESG vs Impact Metrics
ESG investing primarily uses standardized metrics such as carbon emissions, board diversity, and labor practices to assess a company's environmental, social, and governance performance, enabling investors to gauge risk and sustainability. Impact investing, by contrast, emphasizes measuring direct, positive social or environmental outcomes through specific impact metrics like the number of clean water projects implemented or jobs created for underserved communities. The distinction in measurement approaches reflects ESG's focus on managing risks and improving corporate behavior, while impact investing seeks to generate quantifiable, intentional benefits tied to specific goals.
Risk and Return Considerations
ESG investing integrates environmental, social, and governance factors to mitigate risks such as regulatory fines or reputational damage, potentially enhancing long-term returns through sustainable business practices. Impact investing targets measurable social or environmental outcomes alongside financial returns, often accepting higher risk or lower liquidity due to investments in early-stage ventures or emerging markets. Both strategies require careful assessment of risk-return profiles, with ESG investing leaning toward risk management and impact investing prioritizing intentional positive impact with varied return expectations.
Regulatory Landscape and Industry Standards
ESG investing and impact investing are shaped by evolving regulatory frameworks such as the EU Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation (SFDR) and the SEC's enhanced climate risk disclosure rules, which emphasize transparency and accountability in sustainability claims. Industry standards like the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) and the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) provide structured methodologies for measuring and reporting ESG factors, while impact investing often aligns with the Impact Management Project's metrics to assess social and environmental outcomes. Regulatory clarity and adherence to these standards are critical for investors to differentiate between ESG integration, which focuses on risk management, and impact investing, which prioritizes intentional positive impact.
Trends and Market Growth
ESG investing has experienced rapid growth driven by increasing regulatory requirements and demand for sustainable corporate practices, with global assets under management in ESG funds surpassing $40 trillion in 2023. Impact investing, which targets measurable social and environmental outcomes alongside financial returns, is projected to expand at a CAGR of 18% through 2028, driven by growing investor interest in aligning portfolios with specific impact goals. Both ESG and impact investing trends reflect a broader shift toward integrating sustainability in investment strategies, though impact investing emphasizes direct, positive societal impact while ESG focuses on risk management and corporate responsibility metrics.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Portfolio
ESG investing integrates environmental, social, and governance criteria to identify companies with sustainable practices, enhancing long-term risk management and financial performance. Impact investing prioritizes generating measurable social or environmental benefits alongside financial returns, aligning closely with specific values or missions. Choosing the right approach depends on portfolio goals, whether seeking broad sustainability integration through ESG metrics or targeted outcomes via impact-driven investments.
ESG Investing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com