The Balanced Scorecard is a strategic performance management tool that translates an organization's vision and strategy into measurable objectives across four perspectives: financial, customer, internal processes, and learning and growth. It helps organizations align business activities to the vision, improve internal and external communications, and monitor performance against strategic goals. Discover how the Balanced Scorecard can enhance Your organization's strategic planning and execution by reading the rest of this article.
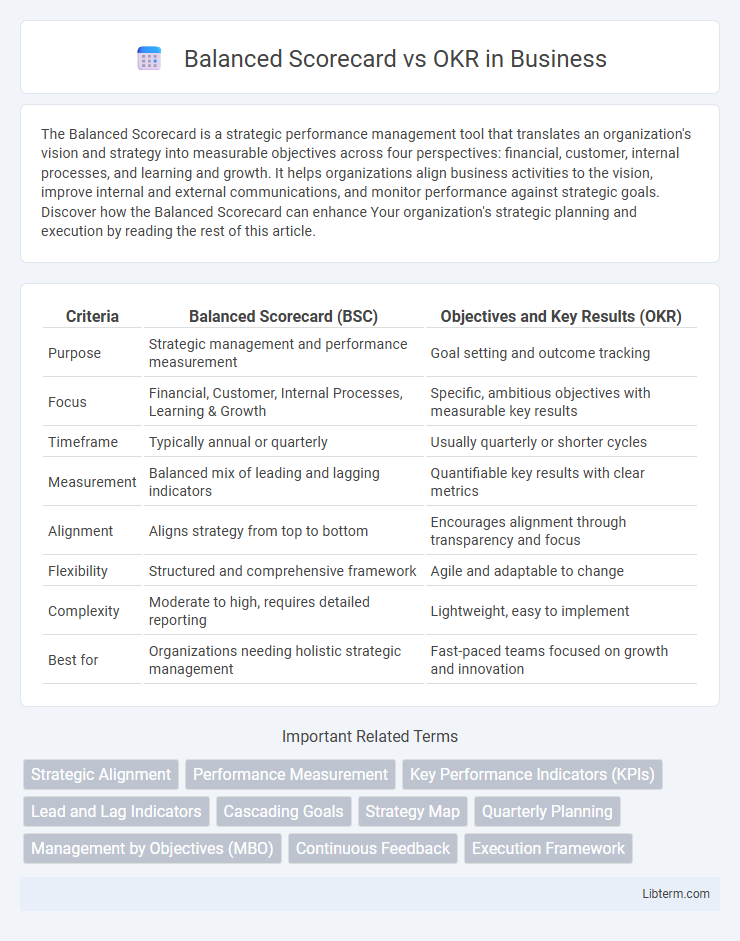
Table of Comparison
| Criteria | Balanced Scorecard (BSC) | Objectives and Key Results (OKR) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Strategic management and performance measurement | Goal setting and outcome tracking |
| Focus | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning & Growth | Specific, ambitious objectives with measurable key results |
| Timeframe | Typically annual or quarterly | Usually quarterly or shorter cycles |
| Measurement | Balanced mix of leading and lagging indicators | Quantifiable key results with clear metrics |
| Alignment | Aligns strategy from top to bottom | Encourages alignment through transparency and focus |
| Flexibility | Structured and comprehensive framework | Agile and adaptable to change |
| Complexity | Moderate to high, requires detailed reporting | Lightweight, easy to implement |
| Best for | Organizations needing holistic strategic management | Fast-paced teams focused on growth and innovation |
Introduction to Strategic Performance Management
Balanced Scorecard and OKR are essential frameworks in strategic performance management, designed to align organizational goals with measurable outcomes. Balanced Scorecard emphasizes a multi-dimensional approach, integrating financial, customer, internal process, and learning perspectives to provide a comprehensive performance overview. OKRs (Objectives and Key Results) focus on setting ambitious, quantifiable objectives with clear key results, fostering agility and continuous progress tracking within strategic initiatives.
What is the Balanced Scorecard?
The Balanced Scorecard is a strategic planning and management system used to align business activities with an organization's vision and strategy by tracking performance across four key perspectives: financial, customer, internal processes, and learning and growth. It enables organizations to monitor both leading and lagging indicators to improve decision-making and performance management. Unlike OKRs, which emphasize goal setting and agile progress tracking, the Balanced Scorecard provides a comprehensive framework for long-term strategic alignment and balanced performance measurement.
What are OKRs (Objectives and Key Results)?
OKRs (Objectives and Key Results) are a goal-setting framework used to define and track measurable outcomes, aligning individual and team efforts with organizational priorities. Objectives represent clear, ambitious goals, while Key Results are specific, quantifiable metrics used to assess progress toward those objectives. OKRs emphasize transparency, focus, and continuous improvement, making them especially effective for dynamic environments requiring frequent performance evaluation.
Key Components: Balanced Scorecard vs OKR
The Balanced Scorecard framework emphasizes four key components: financial metrics, customer perspectives, internal business processes, and learning and growth objectives, creating a comprehensive performance management system. OKR (Objectives and Key Results) centers on setting ambitious objectives paired with measurable key results, fostering alignment and focus within teams. The Balanced Scorecard integrates strategic goals into multiple operational layers, while OKRs prioritize agility and transparency in tracking progress towards specific outcomes.
Differences in Goal Setting Approaches
Balanced Scorecard emphasizes translating an organization's vision into specific, measurable objectives across four perspectives: financial, customer, internal processes, and learning and growth. OKR (Objectives and Key Results) focuses on setting ambitious, qualitative objectives paired with quantitative key results that track progress and drive alignment. The Balanced Scorecard often involves comprehensive, long-term strategic planning, while OKRs promote agility with shorter, iterative goal-setting cycles.
Alignment with Organizational Strategy
Balanced Scorecard aligns with organizational strategy by translating vision and goals into four perspectives: financial, customer, internal processes, and learning and growth, ensuring a comprehensive strategic focus. OKRs drive alignment through setting ambitious, measurable objectives linked to key results that cascade from top management to individual contributors, fostering transparency and accountability. Both frameworks enhance strategic alignment but differ in scope and flexibility, with Balanced Scorecard providing structured measurement and OKRs encouraging agile goal-setting.
Implementation Challenges and Best Practices
Implementing Balanced Scorecard requires alignment of financial and non-financial metrics across organizational levels, often challenged by siloed departments and unclear strategic communication. OKR implementation faces obstacles in setting measurable, ambitious objectives that motivate teams without causing burnout or misalignment with overall company goals. Best practices involve continuous training, transparent progress tracking, and iterative feedback loops to ensure clarity, engagement, and real-time adjustment in both methodologies.
Real-World Use Cases and Examples
Balanced Scorecard excels in aligning strategic objectives with long-term performance metrics, demonstrated by companies like Siemens, which use it to monitor financial, customer, internal processes, and learning growth perspectives. In contrast, OKRs (Objectives and Key Results) thrive in dynamic environments such as Google and Intel, where rapid goal setting and quarterly progress tracking drive innovation and agility. Organizations often combine Balanced Scorecard for strategic oversight with OKRs for operational execution, leveraging each framework's strengths to enhance overall performance management.
Selecting the Right Framework for Your Organization
Choosing between Balanced Scorecard and OKR depends on organizational goals and culture. Balanced Scorecard emphasizes comprehensive performance measurement across financial, customer, internal processes, and learning growth perspectives, ideal for established companies seeking strategic alignment. OKR (Objectives and Key Results) drives agile goal setting with measurable outcomes, best suited for fast-growing or innovation-focused organizations aiming for transparency and adaptability.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Balanced Scorecard and OKR
Choosing between Balanced Scorecard and OKR depends on organizational goals, with Balanced Scorecard excelling in long-term strategic management by tracking financial and non-financial metrics across multiple perspectives. OKRs are ideal for fostering agility and alignment through clear, measurable objectives and key results, driving rapid execution and adaptability. Companies seeking comprehensive strategy mapping should adopt Balanced Scorecard, while those prioritizing flexibility and frequent progress reviews benefit more from OKRs.
Balanced Scorecard Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com