Gradual rollout is a strategic approach to deploying new software updates or features by releasing them incrementally to a subset of users. This method helps identify potential issues early, minimizing risks and enhancing overall user experience. Explore the rest of the article to learn how you can implement a successful gradual rollout for your projects.
Table of Comparison
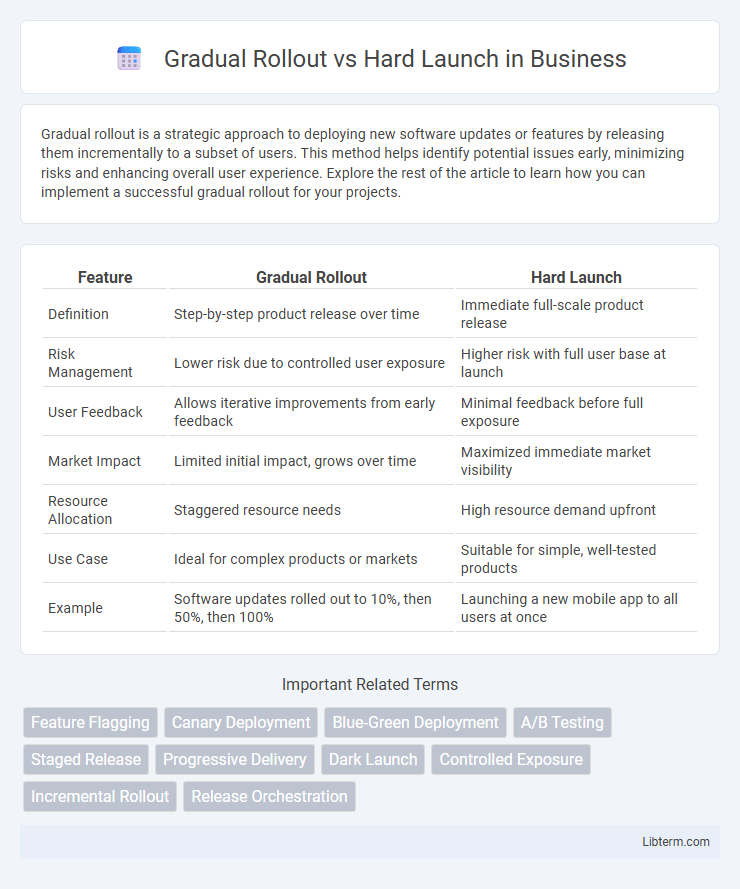
| Feature | Gradual Rollout | Hard Launch |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Step-by-step product release over time | Immediate full-scale product release |
| Risk Management | Lower risk due to controlled user exposure | Higher risk with full user base at launch |
| User Feedback | Allows iterative improvements from early feedback | Minimal feedback before full exposure |
| Market Impact | Limited initial impact, grows over time | Maximized immediate market visibility |
| Resource Allocation | Staggered resource needs | High resource demand upfront |
| Use Case | Ideal for complex products or markets | Suitable for simple, well-tested products |
| Example | Software updates rolled out to 10%, then 50%, then 100% | Launching a new mobile app to all users at once |
Understanding Gradual Rollout and Hard Launch
Gradual rollout involves releasing a product or feature incrementally to a subset of users, enabling real-time monitoring of performance and early identification of issues before full deployment, which minimizes risk and enhances user experience. A hard launch, in contrast, entails releasing the product to the entire target audience simultaneously, resulting in immediate widespread adoption but with higher exposure to potential bugs and system failures. Understanding these approaches helps businesses balance speed and quality control during product deployment strategies.
Key Differences Between Gradual Rollout and Hard Launch
Gradual rollout involves releasing a product feature to a small segment of users before expanding access, allowing for real-time feedback and iterative improvements, while hard launch deploys the product to all users simultaneously without phased testing. Key differences include risk management, where gradual rollout minimizes impact by isolating potential issues, and user experience control, with hard launches often generating higher initial visibility but greater vulnerability to widespread problems. Data-driven insights gathered from gradual rollout support informed decision-making, contrasting with the immediate full-scale exposure typical of hard launch strategies.
Advantages of a Gradual Rollout Strategy
A gradual rollout strategy minimizes risks by limiting exposure to potential defects, enabling immediate issue detection and faster resolution before full-scale deployment. This approach enhances user experience and satisfaction through incremental feature releases that gather real-world feedback for iterative improvements. It also optimizes resource allocation by allowing teams to prioritize fixes and adjustments based on early performance data, reducing operational costs associated with large-scale failures.
Benefits of a Hard Launch Approach
A hard launch offers immediate wide-scale exposure, enabling rapid user feedback and quicker validation of product-market fit. It maximizes initial market impact, creating strong momentum that can drive early adoption and brand recognition. This approach also simplifies tracking performance metrics by providing a comprehensive dataset from the entire target audience at once.
Potential Risks of Gradual Rollout
Gradual rollout carries potential risks such as prolonged exposure to latent bugs that might only surface under specific user conditions, leading to inconsistent user experiences. This approach can also cause fragmented user feedback, making it challenging to identify and prioritize critical issues efficiently. Moreover, the risk of incomplete performance data complicates decision-making, potentially delaying a full-scale launch or necessitating unexpected rollbacks.
Common Challenges With Hard Launches
Hard launches often face significant challenges such as server overload, critical bugs, and negative first impressions due to sudden high user traffic that can cause system crashes. Customer support teams may become overwhelmed by a spike in complaints and issues that were not identified during testing phases. The inability to gather incremental user feedback leads to missed opportunities for timely improvements, increasing the risk of long-term retention problems.
Choosing the Right Launch Method for Your Product
Choosing the right launch method depends on your product's complexity, target audience, and risk tolerance. A gradual rollout allows incremental exposure, facilitating real-time feedback and minimizing potential disruptions, ideal for iterative improvements. Conversely, a hard launch delivers full availability immediately, maximizing initial impact but requiring confidence in product stability and operational readiness.
Real-World Examples: Gradual Rollout vs Hard Launch
Spotify's gradual rollout of its personalized playlist feature allowed the company to collect user feedback and optimize algorithms before a full launch, minimizing risks and enhancing user satisfaction. In contrast, Facebook's hard launch of its News Feed initially faced backlash due to a lack of phased testing but rapidly gained traction through widespread exposure. These real-world examples demonstrate that gradual rollouts prioritize user adaptation and system stability, while hard launches favor immediate market penetration and rapid scale.
Metrics to Measure Launch Success
Tracking user engagement rates, retention metrics, and conversion percentages provides key insights into the success of both gradual rollouts and hard launches. Monitoring error rates, feature adoption speed, and customer feedback helps identify issues early in a gradual rollout, minimizing risk. In a hard launch, rapid spikes in traffic and server load alongside initial user satisfaction scores are critical metrics to assess overall launch performance.
Best Practices for a Successful Product Launch
Gradual rollout enables controlled feature exposure to targeted user segments, minimizing risk and collecting real-time feedback for iterative improvements. Hard launch delivers full product availability instantly, requiring extensive pre-launch testing, marketing coordination, and scalable infrastructure to ensure seamless user experience. Best practices include setting clear metrics, monitoring user behavior closely, and maintaining rapid response plans to address issues promptly during both rollout strategies.
Gradual Rollout Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com