Insourcing enhances control over business processes by utilizing internal resources and expertise, leading to increased efficiency and cost savings. It enables companies to align operations more closely with their strategic goals while maintaining higher quality standards and data security. Explore the rest of the article to discover how insourcing can transform your organization's performance and competitiveness.
Table of Comparison
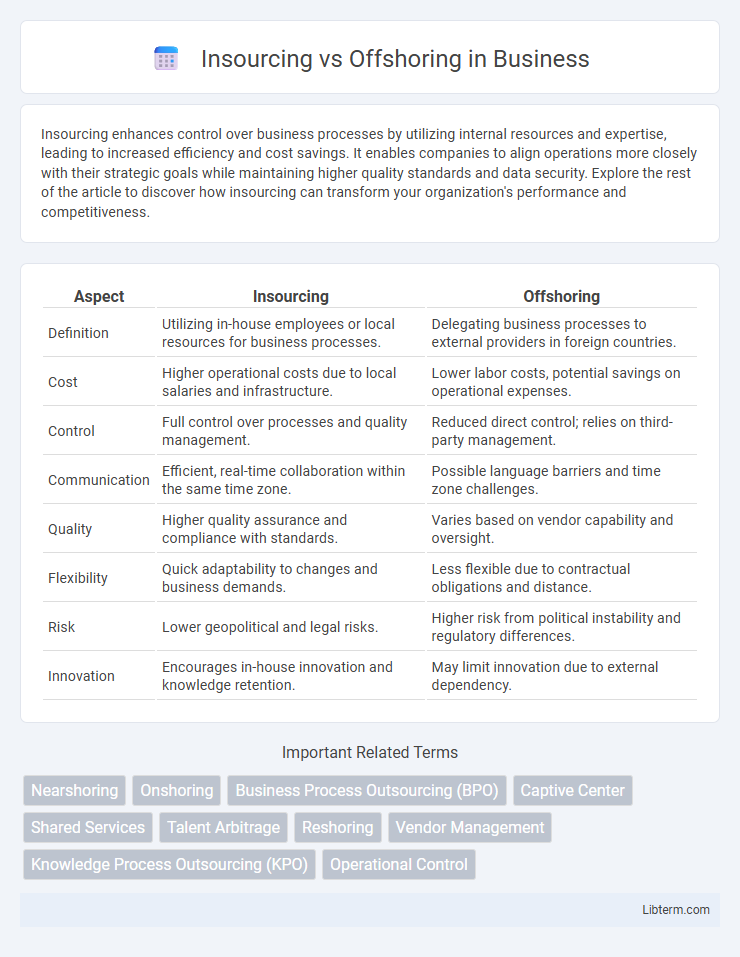
| Aspect | Insourcing | Offshoring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Utilizing in-house employees or local resources for business processes. | Delegating business processes to external providers in foreign countries. |
| Cost | Higher operational costs due to local salaries and infrastructure. | Lower labor costs, potential savings on operational expenses. |
| Control | Full control over processes and quality management. | Reduced direct control; relies on third-party management. |
| Communication | Efficient, real-time collaboration within the same time zone. | Possible language barriers and time zone challenges. |
| Quality | Higher quality assurance and compliance with standards. | Varies based on vendor capability and oversight. |
| Flexibility | Quick adaptability to changes and business demands. | Less flexible due to contractual obligations and distance. |
| Risk | Lower geopolitical and legal risks. | Higher risk from political instability and regulatory differences. |
| Innovation | Encourages in-house innovation and knowledge retention. | May limit innovation due to external dependency. |
Understanding Insourcing and Offshoring
Insourcing involves utilizing internal resources and employees within a company to perform tasks or services, enhancing control and aligning operations closely with organizational goals. Offshoring refers to relocating business processes or services to foreign countries, typically to leverage cost advantages, access specialized skills, or enter new markets. Understanding the strategic benefits and challenges of insourcing and offshoring enables businesses to optimize operational efficiency and competitive advantage.
Key Differences Between Insourcing and Offshoring
Insourcing involves utilizing a company's internal resources to perform business processes, enhancing control and alignment with organizational goals, while offshoring transfers these processes to external providers in foreign countries to reduce labor costs and leverage specialized expertise. Key differences include geographic location--insourcing keeps operations domestic, offshoring moves them abroad--and cost implications, with insourcing often incurring higher labor expenses but offering increased quality control. Furthermore, insourcing promotes direct communication and faster response times, whereas offshoring can encounter language barriers and time zone challenges impacting collaboration efficiency.
Advantages of Insourcing
Insourcing enhances direct control over business processes, improving quality assurance and communication within the company. It allows for better protection of proprietary information and intellectual property, reducing risks associated with data breaches. By utilizing internal resources, insourcing can increase workforce skill development and promote organizational alignment with company values.
Benefits of Offshoring
Offshoring offers significant cost savings by leveraging lower labor expenses in international markets, resulting in reduced operational expenses for businesses. Access to specialized skills and expertise in global talent pools enhances innovation and efficiency for companies targeting offshoring strategies. Time zone advantages enable round-the-clock productivity, accelerating project timelines and improving customer support responsiveness.
Challenges of Insourcing
Insourcing faces challenges such as higher labor costs and limited access to specialized expertise compared to offshoring. Managing in-house teams demands significant investment in infrastructure, training, and technology to maintain competitive productivity. Companies must also address scalability issues and potential cultural barriers within domestic operations.
Drawbacks of Offshoring
Offshoring often results in communication barriers due to time zone differences and language discrepancies, which can hinder project efficiency and lead to misunderstandings. Quality control challenges arise from limited oversight and varying standards in distant locations, increasing the risk of subpar deliverables. Furthermore, hidden costs such as travel expenses, management complexity, and potential intellectual property risks can reduce the overall cost-effectiveness of offshoring strategies.
Decision Factors: Choosing Insourcing or Offshoring
Choosing between insourcing and offshoring depends on factors such as cost efficiency, quality control, and proximity to core business activities. Insourcing offers greater oversight and alignment with company culture, enhancing security and communication. Offshoring provides access to specialized skills and lower labor costs but may involve challenges with time zones and language barriers.
Cost Implications and ROI Analysis
Insourcing often involves higher upfront costs due to infrastructure, employee salaries, and training but can yield better control, quality, and long-term ROI through increased productivity and reduced communication overhead. Offshoring typically offers lower labor costs and immediate savings, yet may incur hidden expenses such as coordination challenges, cultural differences, and slower turnaround times, potentially impacting overall ROI. A thorough cost-benefit analysis comparing direct expenses, operational efficiencies, and risk factors is essential to determine the optimal strategy for maximizing return on investment.
Impact on Quality and Productivity
Insourcing typically enhances quality control and productivity by leveraging in-house expertise and direct oversight, reducing communication barriers and allowing for faster issue resolution. Offshoring often lowers operational costs but may introduce challenges such as cultural differences, time zone gaps, and variable quality standards, potentially impacting consistency and efficiency. Companies must weigh the trade-offs between cost savings and maintaining high-quality output to optimize overall productivity.
Future Trends in Insourcing and Offshoring
Future trends in insourcing emphasize advanced automation and AI integration to enhance operational efficiency and reduce dependency on external vendors. Offshoring is increasingly shifting toward nearshoring models, leveraging proximity to target markets for improved responsiveness and cost-effectiveness. Both strategies incorporate sustainability initiatives as companies prioritize environmental impact and social responsibility in global supply chains.
Insourcing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com