MBO (Management by Objectives) is a strategic management model that aligns employees' goals with the organization's objectives, enhancing productivity and accountability. This approach involves setting clear, measurable targets and regularly reviewing progress to ensure continuous improvement. Explore the rest of the article to discover how MBO can transform your management practices and drive success.
Table of Comparison
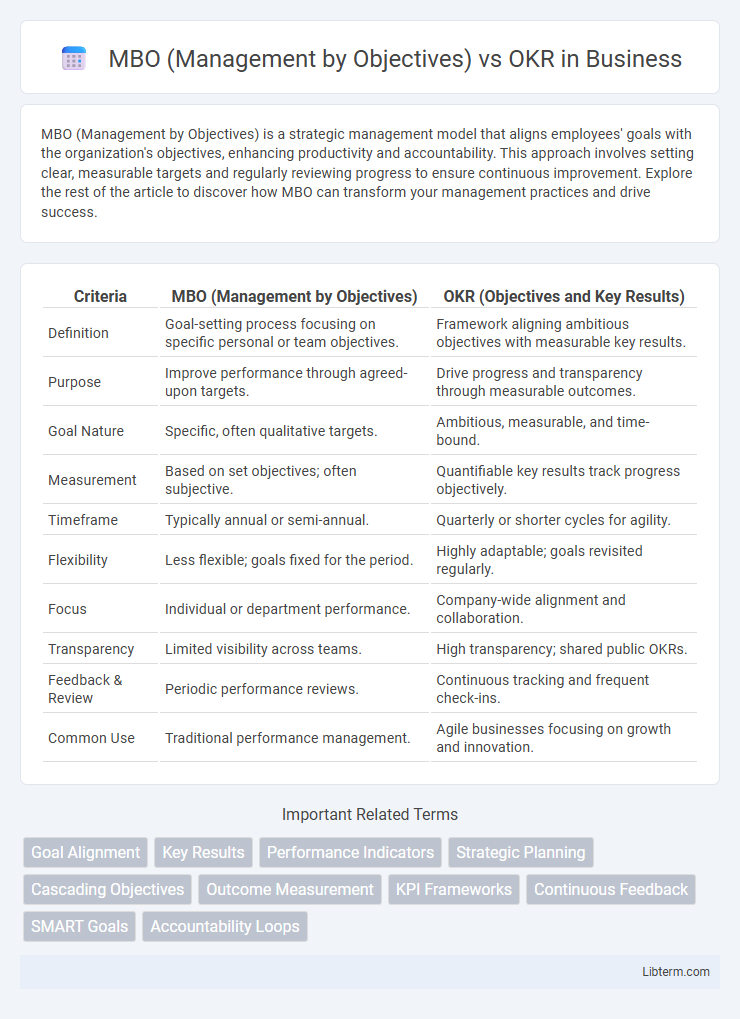
| Criteria | MBO (Management by Objectives) | OKR (Objectives and Key Results) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Goal-setting process focusing on specific personal or team objectives. | Framework aligning ambitious objectives with measurable key results. |
| Purpose | Improve performance through agreed-upon targets. | Drive progress and transparency through measurable outcomes. |
| Goal Nature | Specific, often qualitative targets. | Ambitious, measurable, and time-bound. |
| Measurement | Based on set objectives; often subjective. | Quantifiable key results track progress objectively. |
| Timeframe | Typically annual or semi-annual. | Quarterly or shorter cycles for agility. |
| Flexibility | Less flexible; goals fixed for the period. | Highly adaptable; goals revisited regularly. |
| Focus | Individual or department performance. | Company-wide alignment and collaboration. |
| Transparency | Limited visibility across teams. | High transparency; shared public OKRs. |
| Feedback & Review | Periodic performance reviews. | Continuous tracking and frequent check-ins. |
| Common Use | Traditional performance management. | Agile businesses focusing on growth and innovation. |
Introduction to MBO and OKR
Management by Objectives (MBO) is a strategic management model that emphasizes setting clear, measurable goals collaboratively between managers and employees to improve organizational performance. Objectives and Key Results (OKR) extends this approach by integrating ambitious objectives with specific, time-bound key results that facilitate transparency and real-time progress tracking. Both frameworks drive goal alignment and accountability but OKRs promote more frequent evaluation cycles and adaptability compared to traditional MBO practices.
Defining MBO: Key Principles and Process
Management by Objectives (MBO) is a performance management approach centered on setting clear, measurable goals collaboratively between managers and employees, ensuring alignment with organizational objectives. The key principles of MBO involve goal specificity, participative decision-making, and regular performance reviews to monitor progress and provide feedback. The MBO process typically includes defining individual objectives, monitoring outcomes, evaluating performance, and adjusting goals to enhance productivity and accountability.
Understanding OKR: Framework and Components
OKR (Objectives and Key Results) is a goal-setting framework that differs from MBO by emphasizing measurable key results linked to ambitious objectives, fostering transparency and alignment across teams. The components of OKR include clear, qualitative objectives paired with specific, quantitative key results, enabling regular progress tracking and iterative adjustments. This structure enhances organizational focus and agility compared to the typically annual and broader MBO approach.
Historical Evolution: MBO vs OKR
Management by Objectives (MBO), developed by Peter Drucker in the 1950s, introduced goal-setting as a core management practice emphasizing employee alignment with organizational targets. Objectives and Key Results (OKR), popularized by Intel in the 1970s and later adopted by tech giants like Google, evolved from MBO by integrating measurable key results to enhance goal tracking and agility. Compared to MBO, OKR offers a more dynamic and transparent framework, fostering continuous performance evaluation and iterative progress updates.
Goal Setting Approaches: MBO vs OKR
Management by Objectives (MBO) emphasizes setting specific, measurable goals collaboratively between managers and employees, focusing on clear performance targets within defined timeframes. Objectives and Key Results (OKR) prioritize ambitious, transparent goals with quantifiable key results that align individual and team efforts to broader organizational priorities. OKRs promote continuous progress tracking and adaptability, while MBO typically relies on periodic evaluations, making OKRs more dynamic for fast-changing environments.
Alignment and Transparency in MBO and OKR
MBO (Management by Objectives) emphasizes alignment by setting specific, measurable goals collaboratively between managers and employees, fostering clear accountability, while its transparency is often limited to individual or departmental levels. OKR (Objectives and Key Results) enhances alignment through ambitious, company-wide objectives combined with quantifiable key results, driving cross-functional collaboration and strategic focus. Transparency is a core feature of OKRs, with progress and outcomes regularly shared across the entire organization to promote engagement and adaptability.
Measurement and Performance Tracking
MBO (Management by Objectives) emphasizes setting specific, measurable goals and uses periodic reviews to track performance against these objectives, primarily focusing on outcome-focused metrics. OKR (Objectives and Key Results) integrates continuous performance tracking with clearly defined, quantifiable key results that align with ambitious objectives, enabling real-time progress assessment and agile adjustments. OKRs foster transparent and dynamic measurement systems that enhance alignment and accountability compared to traditional MBO approaches.
Flexibility and Adaptability Comparison
MBO (Management by Objectives) emphasizes setting specific, measurable goals with less frequent reviews, which can limit flexibility in dynamic environments. OKR (Objectives and Key Results) promotes continuous tracking and regular updates, enhancing adaptability to changing priorities and fast-paced market conditions. The iterative nature of OKRs allows organizations to pivot strategies efficiently, whereas MBOs tend to be more rigid due to their fixed goal-setting cycles.
Pros and Cons: MBO vs OKR
MBO (Management by Objectives) emphasizes setting specific, measurable goals aligned with organizational objectives but often lacks flexibility and quick adaptability. OKR (Objectives and Key Results) promotes transparency, frequent progress tracking, and alignment through ambitious yet achievable goals, fostering innovation but potentially causing stress due to aggressive targets. MBO offers clear accountability with a top-down approach, whereas OKR encourages continuous feedback and employee engagement, making it better suited for dynamic environments.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Organization
MBO (Management by Objectives) focuses on setting clear, specific goals aligned with organizational targets, often evaluated on annual or semi-annual cycles, making it suitable for stable environments with predictable outcomes. OKR (Objectives and Key Results) emphasizes ambitious, measurable goals with frequent progress tracking and adaptability, ideal for dynamic organizations seeking rapid innovation and continuous improvement. Choosing the right approach depends on your organization's culture, flexibility needs, and the desired balance between structured accountability and agile performance management.
MBO (Management by Objectives) Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com