Unified commerce integrates all sales channels and customer touchpoints into a single, seamless platform, enhancing operational efficiency and delivering a consistent shopping experience. By centralizing data and processes, businesses can respond to customer needs more quickly and personalize interactions to boost loyalty. Dive deeper into this article to discover how unified commerce can transform your retail strategy.
Table of Comparison
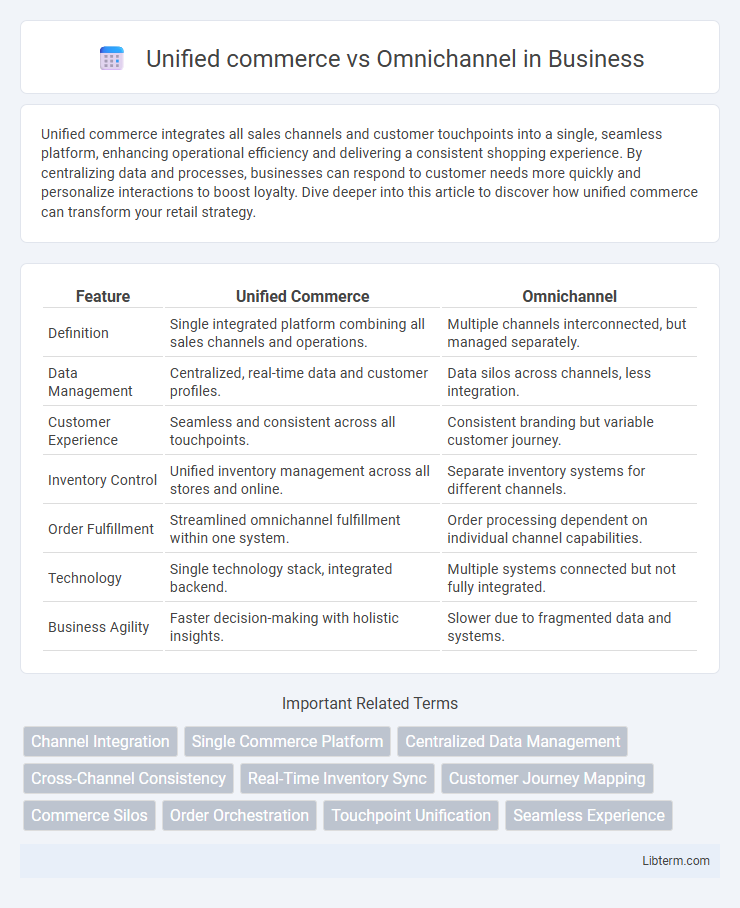
| Feature | Unified Commerce | Omnichannel |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Single integrated platform combining all sales channels and operations. | Multiple channels interconnected, but managed separately. |
| Data Management | Centralized, real-time data and customer profiles. | Data silos across channels, less integration. |
| Customer Experience | Seamless and consistent across all touchpoints. | Consistent branding but variable customer journey. |
| Inventory Control | Unified inventory management across all stores and online. | Separate inventory systems for different channels. |
| Order Fulfillment | Streamlined omnichannel fulfillment within one system. | Order processing dependent on individual channel capabilities. |
| Technology | Single technology stack, integrated backend. | Multiple systems connected but not fully integrated. |
| Business Agility | Faster decision-making with holistic insights. | Slower due to fragmented data and systems. |
Introduction to Unified Commerce and Omnichannel
Unified commerce integrates all sales channels into a single platform, enabling real-time inventory management, consistent customer data, and seamless shopping experiences across digital and physical touchpoints. Omnichannel refers to the multi-channel retail strategy that aims to provide customers with a cohesive experience across online websites, mobile apps, and brick-and-mortar stores, though systems and data often remain siloed. Unified commerce advances omnichannel by consolidating backend processes and customer interactions into one unified system, enhancing operational efficiency and personalization.
Defining Unified Commerce
Unified commerce integrates customer data, inventory management, and transaction processes into a single platform, enabling seamless shopping experiences across all channels. This approach centralizes backend operations, improving data accuracy and real-time visibility compared to omnichannel strategies that often rely on disconnected systems. Retailers leveraging unified commerce benefit from enhanced personalization, streamlined workflows, and consistent customer interactions regardless of the touchpoint.
Understanding Omnichannel Strategy
Omnichannel strategy integrates multiple sales channels, including physical stores, online platforms, and mobile apps, to create a seamless customer experience. It emphasizes consistent messaging, synchronized inventory, and unified customer data across all touchpoints. Understanding omnichannel strategy enables businesses to enhance customer engagement, increase loyalty, and drive revenue growth by meeting customers wherever they choose to shop.
Key Differences Between Unified Commerce and Omnichannel
Unified commerce integrates all sales channels into a single platform, enabling seamless customer experiences and real-time data synchronization across inventory, orders, and customer profiles. Omnichannel focuses on providing multiple sales channels but often operates with disconnected systems, leading to inconsistencies in inventory and customer data. Unified commerce enhances operational efficiency and personalization by unifying backend processes, while omnichannel primarily emphasizes the availability of various shopping touchpoints.
Benefits of Unified Commerce for Retailers
Unified commerce centralizes all retail operations onto a single platform, enabling real-time inventory visibility, seamless customer data integration, and consistent shopping experiences across online and offline channels. Retailers benefit from improved operational efficiency, streamlined order management, and enhanced customer personalization, driving higher sales and loyalty. Unlike omnichannel approaches that often rely on siloed systems, unified commerce provides a holistic solution that reduces costs and accelerates decision-making through unified analytics.
Advantages of Omnichannel Approaches
Omnichannel approaches enhance customer experience by providing seamless interactions across multiple platforms, including physical stores, websites, and mobile apps, ensuring consistent brand engagement. The integration of marketing, sales, and customer service channels allows businesses to gather comprehensive data, which helps personalize communications and improve customer retention. This strategy increases convenience and flexibility for consumers, leading to higher satisfaction and increased sales opportunities.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Approach
Unified commerce faces challenges in integrating disparate systems into a single platform, often requiring significant IT investment and organizational change. Omnichannel limitations include inconsistent customer experiences across channels due to fragmented data and lack of real-time inventory synchronization. Both approaches must address data silos and real-time communication gaps to optimize customer engagement and operational efficiency.
Impact on Customer Experience
Unified commerce integrates all sales channels and customer data into a single platform, enabling seamless, personalized interactions that enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty. Omnichannel strategies connect multiple channels but often operate on separate systems, potentially causing inconsistent experiences and fragmented customer journeys. By providing real-time inventory updates, unified payment processes, and unified customer profiles, unified commerce significantly improves convenience and engagement across touchpoints.
Technology Requirements for Unified Commerce and Omnichannel
Unified commerce requires a centralized technology platform that integrates inventory, customer data, and sales channels into a single system, enabling seamless real-time updates and consistent customer experiences across all touchpoints. Omnichannel technology typically involves coordinating multiple separate systems, such as disparate inventory management, CRM, and POS solutions, which communicate but remain distinct, often causing delays or inconsistencies. Unified commerce demands robust API integrations, cloud-based infrastructure, and advanced data analytics to provide a holistic view of operations, while omnichannel relies more on middleware and synchronization tools to bridge existing independent platforms.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Business
Unified commerce integrates all sales channels and backend systems into a single platform, enabling real-time inventory management, personalized customer experiences, and streamlined operations. Omnichannel connects multiple sales channels but often relies on separate systems, which can lead to data silos and inconsistent customer experiences. Choosing the right solution depends on business size, complexity, and growth goals; unified commerce suits enterprises seeking seamless integration and scalability, while omnichannel may fit smaller businesses prioritizing multi-channel presence without extensive backend unification.
Unified commerce Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com