Venture capital financing provides essential funding to startups and high-growth companies in exchange for equity, enabling innovation and expansion. This form of investment typically involves significant risk but offers potential for substantial returns. Explore the rest of this article to understand how venture capital can accelerate your business growth.
Table of Comparison
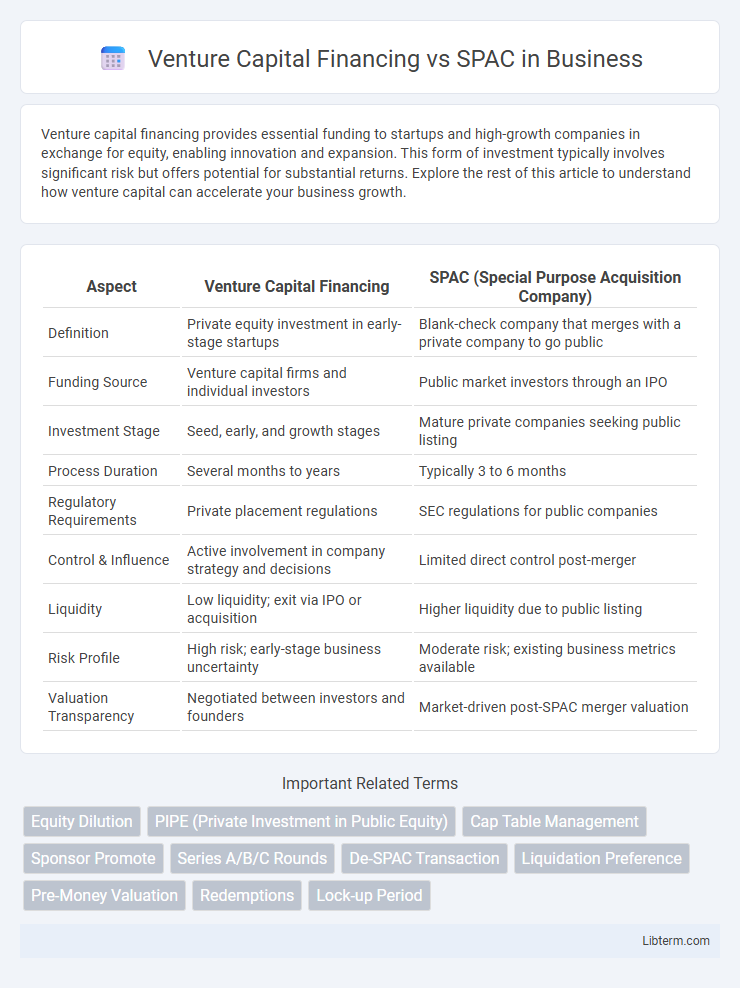
| Aspect | Venture Capital Financing | SPAC (Special Purpose Acquisition Company) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Private equity investment in early-stage startups | Blank-check company that merges with a private company to go public |
| Funding Source | Venture capital firms and individual investors | Public market investors through an IPO |
| Investment Stage | Seed, early, and growth stages | Mature private companies seeking public listing |
| Process Duration | Several months to years | Typically 3 to 6 months |
| Regulatory Requirements | Private placement regulations | SEC regulations for public companies |
| Control & Influence | Active involvement in company strategy and decisions | Limited direct control post-merger |
| Liquidity | Low liquidity; exit via IPO or acquisition | Higher liquidity due to public listing |
| Risk Profile | High risk; early-stage business uncertainty | Moderate risk; existing business metrics available |
| Valuation Transparency | Negotiated between investors and founders | Market-driven post-SPAC merger valuation |
Introduction to Venture Capital Financing and SPACs
Venture capital financing involves raising equity capital from investors to fund startup companies with high growth potential, providing not only capital but also strategic guidance and networking opportunities. Special Purpose Acquisition Companies (SPACs) are publicly traded shell companies formed to raise capital through an initial public offering (IPO) with the objective of acquiring or merging with an existing private company. Both venture capital financing and SPACs serve as alternative funding mechanisms for private companies seeking growth or public market access, with venture capital typically focusing on early-stage investments and SPACs offering a quicker route to public listing.
Key Differences Between Venture Capital and SPACs
Venture capital financing involves direct investment in early-stage companies, providing equity in exchange for capital to foster growth, while SPACs (Special Purpose Acquisition Companies) raise funds through an IPO to acquire existing private companies and take them public. Venture capital typically requires long-term commitment and hands-on involvement, whereas SPACs offer a faster route to public markets with less operational engagement from initial investors. Key differences include investment timing, risk profile, and the liquidity timeline, with venture capital focusing on early innovation risk and SPACs on merger arbitrage and market timing.
How Venture Capital Financing Works
Venture capital financing involves investors providing capital to startups and early-stage companies in exchange for equity, typically through multiple funding rounds such as seed, Series A, and beyond, allowing entrepreneurs to scale operations and accelerate growth. Investors perform rigorous due diligence and valuation assessments to determine ownership stakes and potential returns while often offering strategic guidance and industry connections to portfolio companies. This method contrasts with SPACs, where companies merge with publicly traded shell companies to access public markets quickly without traditional venture funding stages.
Understanding the SPAC Process
The SPAC process involves raising capital through an initial public offering by a blank-check company with the purpose of acquiring a private firm within a specified timeframe, often 18-24 months. Unlike traditional venture capital financing that invests directly in startups for equity stakes and long-term growth, SPACs provide an expedited route to public markets, offering liquidity and valuation transparency. Investors in a SPAC benefit from a trust-held capital structure and shareholder approval mechanisms before deal completion, making it a unique alternative to conventional venture funding.
Advantages of Venture Capital Financing
Venture capital financing offers startups access to experienced investors who provide strategic guidance, mentorship, and extensive industry networks, which can accelerate growth and improve business scalability. This form of financing typically involves rigorous due diligence, promoting discipline and transparency that enhance long-term operational performance. Furthermore, venture capital funding often comes with flexible investment structures that align incentives between entrepreneurs and investors, fostering sustainable value creation.
Benefits and Drawbacks of SPACs
SPACs (Special Purpose Acquisition Companies) offer faster access to public markets and reduced regulatory scrutiny compared to traditional Venture Capital financing, enabling startups to secure significant capital efficiently. However, SPAC transactions often face criticism for potential misalignment between sponsors and investors, leading to overvaluation and post-merger performance risks. While Venture Capital provides strategic guidance and industry connections, SPACs primarily focus on liquidity and speed, bringing unique benefits and drawbacks depending on the company's growth stage and capital needs.
Risk Profiles: Venture Capital vs SPAC
Venture capital financing carries high risk due to early-stage startup investments with uncertain market acceptance and product development outcomes, often requiring long-term capital lock-up. SPACs (Special Purpose Acquisition Companies) present moderate risk by offering public market access prior to business acquisition, yet face challenges like overvaluation and regulatory scrutiny during the merger process. Investors in venture capital must endure potential total loss but benefit from outsized returns in successful exits, whereas SPAC investors face dilution risk and deal execution uncertainty but gain more liquidity and shorter investment horizons.
Regulatory Considerations for VC and SPAC Deals
Venture capital financing involves rigorous regulatory compliance under the Securities Act of 1933 and the Investment Company Act of 1940, requiring private offerings to adhere to exemptions like Regulation D to avoid public registration. Special Purpose Acquisition Companies (SPACs) face stringent SEC scrutiny on disclosure obligations, including detailed financial statements and risk factors during the initial public offering and subsequent business combination. Navigating these regulatory frameworks is critical for structuring deals that optimize investor protection and ensure transaction legitimacy in both VC and SPAC markets.
Suitability for Startups and Mature Companies
Venture capital financing is highly suitable for startups due to its focus on early-stage funding, providing not only capital but strategic guidance for growth and innovation. SPACs (Special Purpose Acquisition Companies) are more appropriate for mature companies seeking faster access to public markets, offering liquidity and capital infusion without the prolonged IPO process. Startups often lack the financial history and scale needed for SPACs, making venture capital a more viable option for their developmental stage.
Future Trends: Venture Capital Financing vs SPAC
Emerging trends indicate venture capital financing increasingly targets early-stage startups leveraging AI, fintech, and biotech innovations, emphasizing long-term value creation through hands-on mentorship and scalability. In contrast, SPACs (Special Purpose Acquisition Companies) gain momentum for providing expedited public market access to mature private companies, especially in sectors like electric vehicles and technology, driven by growing investor appetite for alternative, high-growth assets. Data suggests future market dynamics will balance between venture capital's early-stage risk tolerance and SPACs' streamlined capital raising, signaling a complementary coexistence shaped by regulatory frameworks and investor preferences.
Venture Capital Financing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com