The Executive Board plays a crucial role in shaping your organization's strategic direction and ensuring effective governance. Its members bring diverse expertise to drive decision-making and oversee operational performance. Discover how the Executive Board influences success throughout this article.
Table of Comparison
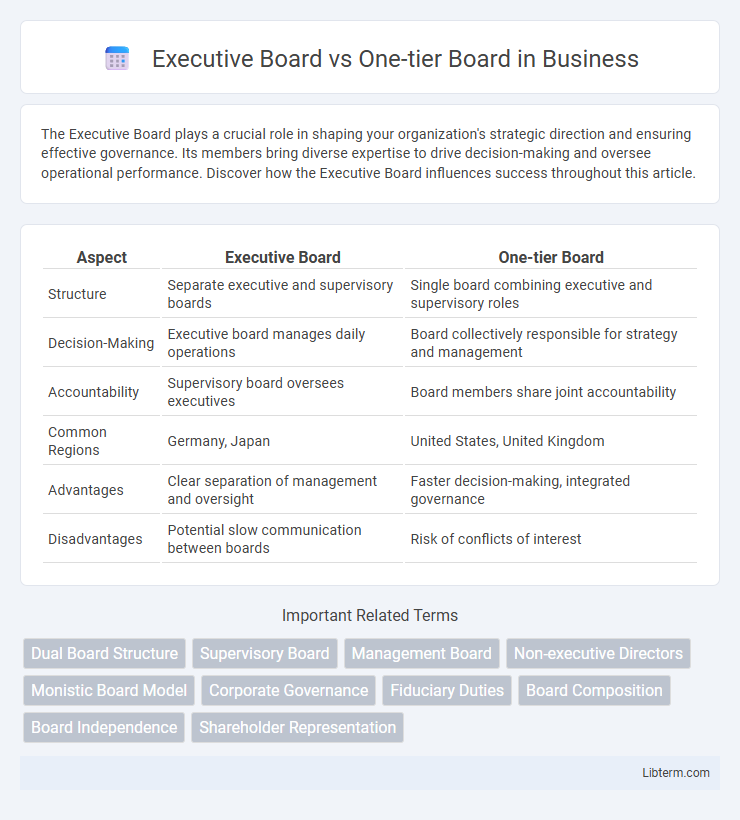
| Aspect | Executive Board | One-tier Board |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Separate executive and supervisory boards | Single board combining executive and supervisory roles |
| Decision-Making | Executive board manages daily operations | Board collectively responsible for strategy and management |
| Accountability | Supervisory board oversees executives | Board members share joint accountability |
| Common Regions | Germany, Japan | United States, United Kingdom |
| Advantages | Clear separation of management and oversight | Faster decision-making, integrated governance |
| Disadvantages | Potential slow communication between boards | Risk of conflicts of interest |
Introduction to Board Structures
The Executive Board structure separates management and supervisory functions by having distinct executive directors responsible for daily operations and non-executive directors overseeing governance. In contrast, the One-tier Board combines these roles within a single board, comprising both executive and non-executive members who collectively make strategic decisions and supervise management. Understanding these board structures is crucial for aligning corporate governance with organizational goals and regulatory requirements.
Defining the Executive Board
The Executive Board is a management structure commonly used in German corporate governance, consisting of appointed executives responsible for day-to-day operations and strategic decision-making. Unlike the One-tier Board, which combines supervisory and management functions into a single entity, the Executive Board operates alongside a separate Supervisory Board that oversees and monitors its decisions. This dual-board system ensures a clear separation of management and oversight duties, enhancing corporate accountability and governance.
Understanding the One-tier Board
A one-tier board integrates executive and non-executive directors into a single decision-making body, streamlining governance and fostering direct communication between management and oversight functions. This structure enhances transparency and accountability by uniting strategic management and supervisory roles within one entity, contrasting with the duality seen in executive boards. The one-tier board is prevalent in countries like the UK and Germany, supporting agile decision-making and cohesive corporate governance.
Key Roles and Responsibilities
The Executive Board comprises senior executives who manage daily operations and implement company strategy, emphasizing operational decision-making and performance management. In contrast, the One-tier Board combines executive and non-executive directors, balancing strategic oversight with direct management involvement to ensure unified governance. Key roles include the Executive Board's focus on execution and management accountability, while the One-tier Board prioritizes integrated supervision and strategic direction within a single entity.
Decision-Making Processes
Executive Boards centralize decision-making authority within a small group of executives, facilitating rapid execution and streamlined communication. One-tier Boards combine executive and non-executive directors, promoting diverse perspectives and collaborative governance in decision-making processes. This integrated structure enhances accountability and balances strategic oversight with operational management.
Corporate Governance Implications
An Executive Board separates management and oversight by appointing executives who handle daily operations and non-executive directors who supervise, enhancing checks and balances in corporate governance. A One-tier Board integrates executive and non-executive directors within a single body, promoting unified decision-making but potentially reducing independence in oversight. The choice between these structures impacts accountability, transparency, and the effectiveness of board supervision in corporate governance frameworks.
Advantages of the Executive Board
The Executive Board offers clear separation between management and supervisory functions, enhancing accountability and decision-making efficiency. Its structure allows executive directors to focus on day-to-day operational responsibilities while non-executive members provide unbiased oversight. This dual-board system reduces conflicts of interest and fosters transparent corporate governance.
Benefits of the One-tier Board System
The one-tier board system integrates executive directors and non-executive directors within a single board, enhancing communication and decision-making efficiency by fostering direct collaboration between management and oversight functions. This structure streamlines governance, allowing faster responses to business challenges and unified strategic direction. Concentrated accountability in the one-tier board system improves transparency and alignment with shareholder interests, promoting stronger corporate governance.
Comparative Analysis: Executive Board vs One-tier Board
An Executive Board typically separates management and supervisory functions into two distinct bodies, enhancing oversight by distinct executive and non-executive members, while a One-tier Board integrates both roles within a single board structure composed of executive and non-executive directors. The Executive Board model, common in countries like Germany, supports clearer accountability through dual boards, whereas the One-tier Board, prevalent in the UK and the US, encourages faster decision-making with unified leadership. Comparative studies reveal that the choice between these structures impacts corporate governance effectiveness, risk management, and stakeholder representation, with the Executive Board often offering stronger checks and balances and the One-tier Board favoring agility and alignment.
Choosing the Right Board Structure for Your Organization
Selecting the right board structure hinges on organizational size, complexity, and governance goals. Executive Boards, typically consisting of both executive and non-executive members, provide strategic oversight with integrated operational input, ideal for dynamic enterprises requiring close alignment between management and oversight. One-tier Boards, combining supervisory and managerial roles into a single group, offer streamlined decision-making advantages for smaller or less complex organizations focused on agility and simplified governance.
Executive Board Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com