Psychological pricing leverages human perception to influence buying decisions by setting prices that appear more attractive, such as $9.99 instead of $10. This strategy taps into consumers' subconscious, making your products seem better deals and encouraging quicker purchasing. Discover how to implement psychological pricing techniques effectively to boost your sales by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
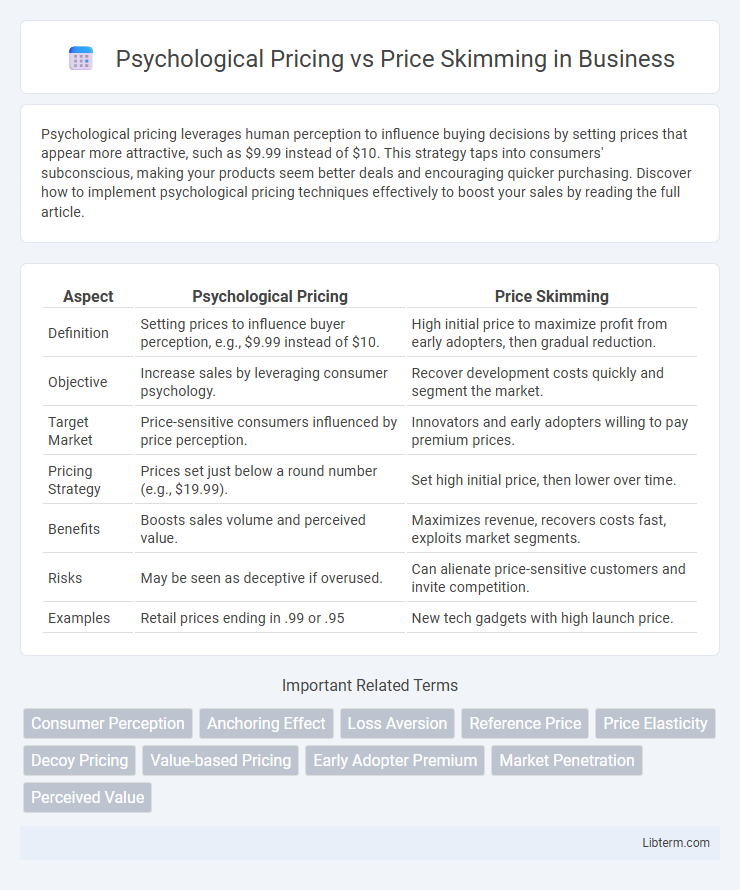
| Aspect | Psychological Pricing | Price Skimming |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Setting prices to influence buyer perception, e.g., $9.99 instead of $10. | High initial price to maximize profit from early adopters, then gradual reduction. |
| Objective | Increase sales by leveraging consumer psychology. | Recover development costs quickly and segment the market. |
| Target Market | Price-sensitive consumers influenced by price perception. | Innovators and early adopters willing to pay premium prices. |
| Pricing Strategy | Prices set just below a round number (e.g., $19.99). | Set high initial price, then lower over time. |
| Benefits | Boosts sales volume and perceived value. | Maximizes revenue, recovers costs fast, exploits market segments. |
| Risks | May be seen as deceptive if overused. | Can alienate price-sensitive customers and invite competition. |
| Examples | Retail prices ending in .99 or .95 | New tech gadgets with high launch price. |
Introduction to Psychological Pricing and Price Skimming
Psychological pricing leverages consumer perception by setting prices just below a round number, such as $9.99 instead of $10, to create a sense of better value and encourage purchases. Price skimming involves setting a high initial price for a new or innovative product to maximize profits from early adopters before gradually lowering the price to attract more price-sensitive customers. Both strategies aim to optimize revenue but target different consumer behaviors and market conditions.
Defining Psychological Pricing: Concepts and Strategies
Psychological pricing involves setting prices that create a perception of value or affordability, such as charm pricing (e.g., $9.99) or prestige pricing to influence consumer behavior. This strategy leverages cognitive biases and emotional responses to drive purchases, making products appear cheaper or more attractive without necessarily reducing the price. Companies implement psychological pricing to increase sales volume, enhance brand image, and gain competitive advantage by aligning prices with consumer expectations and perceived value.
Understanding Price Skimming: How It Works
Price skimming involves setting a high initial price for a new product to maximize profits from early adopters willing to pay more before gradually lowering the price to attract more price-sensitive customers. This strategy leverages consumer segments with varying willingness to pay, capturing maximum revenue at each stage of the product lifecycle. Understanding how price skimming works requires analyzing market demand, competitive landscape, and product uniqueness to optimize timing and price reductions effectively.
Key Differences Between Psychological Pricing and Price Skimming
Psychological pricing leverages consumers' perception by setting prices just below a round number, such as $9.99 instead of $10, to create an impression of affordability and encourage purchases. Price skimming involves initially setting a high price for a new or innovative product to maximize profit from early adopters before gradually lowering the price to attract a broader market. The key difference lies in psychological pricing targeting consumer behavior through price perception, while price skimming focuses on strategic timing and market segmentation to capture different customer willingness to pay.
Psychological Triggers in Consumer Behavior
Psychological pricing leverages consumer behavior triggers such as perceived value and price-quality inference by setting prices just below round numbers (e.g., $9.99) to create a sense of urgency and affordability. Price skimming capitalizes on early adopters' willingness to pay a premium, gradually lowering prices to attract more price-sensitive customers while reinforcing exclusivity and innovation appeal. Understanding psychological triggers like loss aversion, scarcity, and social proof enables marketers to strategically implement both pricing strategies for maximizing revenue and consumer engagement.
Advantages of Psychological Pricing for Businesses
Psychological pricing leverages consumer perception by setting prices slightly below whole numbers, such as $9.99 instead of $10, which encourages higher sales volumes and enhances perceived value. This strategy helps businesses increase demand without altering product quality, fostering greater customer satisfaction and loyalty. Unlike price skimming, psychological pricing sustains long-term competitive advantage by maintaining steady revenue and consistent market presence.
Benefits and Risks of Price Skimming
Price skimming allows businesses to maximize profits by targeting early adopters willing to pay premium prices, helping to quickly recover research and development costs. This strategy carries risks such as alienating price-sensitive customers and inviting competitors to enter the market with lower prices. Effective implementation requires careful market analysis to balance initial high margins against potential drops in long-term market share.
When to Use Psychological Pricing vs Price Skimming
Psychological pricing is most effective when targeting price-sensitive customers who respond to perceived value, such as setting prices ending in .99 to increase sales volume and attract impulse buyers. Price skimming is ideal for new, innovative products entering the market with little competition, allowing businesses to maximize profit margins by initially charging high prices before gradually lowering them. Choose psychological pricing in competitive markets to boost conversion rates, while price skimming suits early product launches aiming to capitalize on early adopters willing to pay premium prices.
Real-World Examples of Each Pricing Strategy
Psychological pricing, commonly used by retailers like Walmart, employs tactics such as setting prices at $9.99 to create a perception of value and affordability. Price skimming, practiced by tech giants like Apple, involves launching new products like the iPhone at high prices before gradually lowering them to capture consumer surplus. Both strategies effectively target different consumer behaviors, with psychological pricing driving impulse purchases and price skimming maximizing profits from early adopters.
Choosing the Right Pricing Strategy for Your Business
Psychological pricing leverages consumer perception by setting prices just below round numbers, such as $9.99 instead of $10, to increase perceived value and drive sales volume. Price skimming involves setting high initial prices for innovative or limited products to maximize early profits before gradually lowering prices to attract broader market segments. Selecting the right pricing strategy depends on factors like product uniqueness, competition, customer sensitivity, and long-term business objectives to optimize revenue and market penetration effectively.
Psychological Pricing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com