Public domain technology refers to innovations and inventions no longer protected by intellectual property laws, allowing unrestricted use by anyone. This open access fosters creativity, collaboration, and widespread adoption without licensing fees or legal barriers. Explore the rest of this article to understand how public domain technology can benefit your projects and inspire new ideas.
Table of Comparison
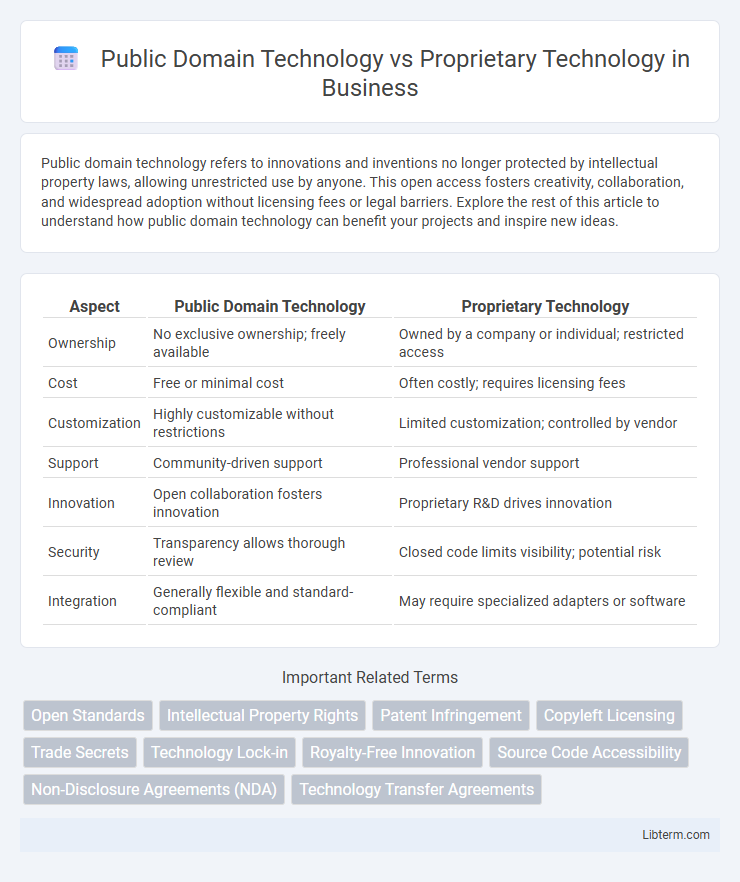
| Aspect | Public Domain Technology | Proprietary Technology |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership | No exclusive ownership; freely available | Owned by a company or individual; restricted access |
| Cost | Free or minimal cost | Often costly; requires licensing fees |
| Customization | Highly customizable without restrictions | Limited customization; controlled by vendor |
| Support | Community-driven support | Professional vendor support |
| Innovation | Open collaboration fosters innovation | Proprietary R&D drives innovation |
| Security | Transparency allows thorough review | Closed code limits visibility; potential risk |
| Integration | Generally flexible and standard-compliant | May require specialized adapters or software |
Introduction to Public Domain and Proprietary Technology
Public domain technology refers to innovations and inventions freely available for public use without restrictions, enabling widespread access and collaboration. Proprietary technology is owned by individuals or organizations, protected by patents or copyrights, restricting usage and requiring licenses for access. Understanding the distinction guides strategic decisions in technology adoption and intellectual property management.
Defining Public Domain Technology
Public Domain Technology refers to innovations, inventions, and knowledge that are not protected by intellectual property rights, making them freely accessible and usable by anyone without restrictions. This technology promotes open use, modification, and distribution, fostering collaboration and rapid advancement in various fields. Public domain status arises when patents expire, are forfeited, or when creators choose not to pursue intellectual property protection.
Characteristics of Proprietary Technology
Proprietary technology is characterized by exclusive ownership, restricted access, and controlled distribution, often protected by patents, copyrights, or trade secrets. It requires licensing fees or agreements for legal use, ensuring the originator retains competitive advantage and revenue. This technology typically offers specialized features tailored to specific market needs but limits modification or sharing by external users.
Accessibility and Licensing Differences
Public domain technology offers unrestricted accessibility, allowing anyone to use, modify, and distribute it without licensing fees or permissions. Proprietary technology requires users to obtain licenses, often involving fees and usage limitations set by the owner, restricting access and modification rights. These licensing differences significantly impact innovation, with public domain fostering open collaboration, while proprietary models emphasize controlled development and profit.
Innovation and Collaboration Potential
Public domain technology fosters greater innovation and collaboration potential by allowing unrestricted access to source materials, enabling developers and researchers worldwide to build upon existing knowledge without legal barriers. Proprietary technology often limits collaboration due to exclusive rights and licensing restrictions, which can slow innovation as advancements are confined to the owning entity. Open access in public domain technologies accelerates creativity and collective problem-solving, driving faster technological progress across industries.
Cost Implications for Users and Developers
Public domain technology offers minimal upfront costs and no licensing fees, enabling users and developers to reduce expenses significantly compared to proprietary technology, which often requires costly licenses and ongoing fees. Development with public domain tools fosters innovation without financial barriers, while proprietary systems may impose restrictions that increase total cost of ownership due to maintenance and support charges. Cost implications heavily influence technology adoption decisions, as open-source alternatives provide scalable and budget-friendly solutions for businesses and individual developers alike.
Security and Privacy Considerations
Public Domain Technology offers greater transparency due to open-source code, enabling extensive security audits and reducing backdoor risks, which enhances trustworthiness in privacy management. Proprietary Technology relies on closed-source systems, limiting external security evaluations and potentially obscuring vulnerabilities, posing challenges to thorough privacy protection. Organizations must weigh the visibility and community scrutiny of public domain tools against the controlled, but opaque, security environment of proprietary solutions when prioritizing security and privacy.
Influence on Market Competition
Public domain technology fosters greater market competition by enabling unrestricted access and use, which lowers entry barriers for startups and encourages innovation. Proprietary technology restricts usage through patents or licenses, often creating monopolies or oligopolies that limit market rivalry. Companies with proprietary technology can dominate sectors by controlling critical intellectual property, reducing consumer choices and increasing prices.
Case Studies: Successful Implementations
Public domain technology enables widespread innovation by allowing unrestricted access, as demonstrated by the Linux operating system, which powers numerous enterprise servers and cloud infrastructures globally. Proprietary technology, exemplified by Apple's iOS ecosystem, drives revenue through exclusive control and continuous software updates, fostering a loyal user base and consistent market growth. Case studies reveal that public domain solutions excel in collaborative development and scalability, while proprietary systems often succeed in delivering optimized user experiences and monetization strategies.
Future Trends and Evolving Policies
Future trends in public domain technology emphasize open innovation, increased collaboration, and widespread adoption driven by evolving policies promoting data accessibility and intellectual property reform. Proprietary technology faces tightening regulations and shifts toward transparency, balancing competitive advantage with compliance to protect user privacy and foster ethical AI development. Emerging policies aim to harmonize both domains, encouraging interoperability and sustainable growth across industries.
Public Domain Technology Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com