Licensing plays a crucial role in protecting intellectual property and ensuring legal use of products and services. Understanding the types of licenses and their specific terms helps you avoid potential legal issues and maximize the benefits of your assets. Explore the rest of the article to learn how licensing can impact your business and creative endeavors.
Table of Comparison
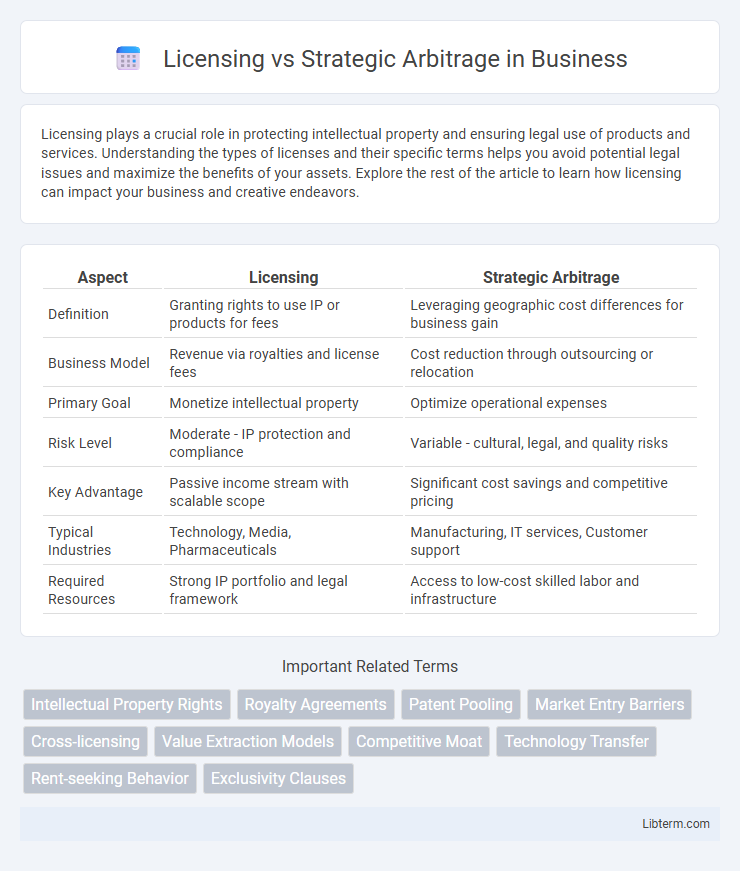
| Aspect | Licensing | Strategic Arbitrage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Granting rights to use IP or products for fees | Leveraging geographic cost differences for business gain |
| Business Model | Revenue via royalties and license fees | Cost reduction through outsourcing or relocation |
| Primary Goal | Monetize intellectual property | Optimize operational expenses |
| Risk Level | Moderate - IP protection and compliance | Variable - cultural, legal, and quality risks |
| Key Advantage | Passive income stream with scalable scope | Significant cost savings and competitive pricing |
| Typical Industries | Technology, Media, Pharmaceuticals | Manufacturing, IT services, Customer support |
| Required Resources | Strong IP portfolio and legal framework | Access to low-cost skilled labor and infrastructure |
Introduction to Licensing and Strategic Arbitrage
Licensing allows a company to grant rights to another entity to produce, market, or use its intellectual property, generating revenue without heavy capital investment. Strategic arbitrage involves leveraging global differences, such as labor costs or market demand, to maximize competitive advantage and profitability. Both approaches optimize resources and market presence but differ in execution and risk management strategies.
Defining Licensing: Scope and Concepts
Licensing involves granting permission to use intellectual property, such as patents, trademarks, or technology, under defined terms and conditions to generate revenue without direct operational control. The scope of licensing includes exclusive, non-exclusive, and cross-licensing agreements, which dictate usage rights, territorial limits, and financial arrangements like royalties or fees. Understanding licensing concepts is essential for leveraging assets strategically, managing risks, and expanding market reach while maintaining core ownership.
Understanding Strategic Arbitrage in Business
Strategic arbitrage in business involves leveraging disparities in markets, resources, or costs across different regions to gain competitive advantages and maximize profitability. Unlike licensing, which grants rights to use intellectual property, strategic arbitrage actively exploits global variations in labor, materials, and expertise to optimize operations and reduce expenses. This approach enables companies to innovate efficiently and scale rapidly by integrating diverse international capabilities.
Key Differences Between Licensing and Strategic Arbitrage
Licensing involves granting permission to use intellectual property, such as patents or trademarks, under specific terms for a fee or royalty, emphasizing legal rights and controlled usage. Strategic arbitrage capitalizes on geographical or market inefficiencies, leveraging cost differentials, talent availability, or resource access to create competitive advantages without transferring ownership rights. The key difference lies in licensing's focus on legal permission and IP monetization, while strategic arbitrage centers on exploiting external market disparities to optimize operational or strategic outcomes.
Advantages of Licensing for Businesses
Licensing offers businesses the advantage of rapid market entry with minimal capital investment by leveraging established brand recognition and intellectual property. It enables companies to generate steady revenue streams through royalties while reducing operational risks and costs associated with manufacturing and distribution. This strategic approach also facilitates expansion into new geographic regions by partnering with local licensees who possess market-specific expertise.
Benefits of Strategic Arbitrage Strategies
Strategic arbitrage maximizes global competitive advantages by leveraging cost differentials, market inefficiencies, and resource disparities across regions to enhance profitability. This approach enables firms to optimize supply chains, access talent pools, and adapt swiftly to regulatory environments, surpassing static licensing benefits. Companies employing strategic arbitrage often achieve superior innovation pipelines and operational flexibility, driving sustainable growth in complex international markets.
Risk Factors in Licensing vs. Strategic Arbitrage
Licensing involves transferring intellectual property rights, carrying risks such as loss of control over technology, potential IP infringement, and dependency on the licensee's performance. Strategic arbitrage focuses on leveraging cost differentials in global markets, with risks including geopolitical instability, cultural misalignment, and fluctuating labor costs. Evaluating these risk factors helps businesses decide between the predictable but restrictive nature of licensing and the more flexible yet volatile environment of strategic arbitrage.
Real-World Examples: Licensing Success Stories
Licensing success stories like Disney's collaboration with Hasbro demonstrate how intellectual property can generate substantial revenue through brand expansion without direct manufacturing. IBM's licensing of its patents to tech startups highlights strategic arbitrage by leveraging existing innovations to fuel industry growth. These real-world examples showcase licensing as a powerful tool for maximizing asset value and accelerating market penetration across diverse sectors.
Case Studies: Strategic Arbitrage in Action
Strategic arbitrage involves leveraging geographic or economic differences to optimize business operations, as demonstrated by case studies like Apple's manufacturing in China to reduce costs while maintaining innovation quality. Licensing strategies contrast by granting rights to third parties, evident in companies like Disney licensing content globally to expand market reach without direct operational control. Companies utilizing strategic arbitrage often achieve significant cost advantages and market agility, exemplified by tech firms outsourcing software development to skilled labor markets in India and Eastern Europe.
Choosing the Right Approach: Licensing or Strategic Arbitrage
Choosing the right approach between licensing and strategic arbitrage depends on factors like control, risk tolerance, and resource allocation. Licensing offers companies a way to monetize intellectual property with lower operational involvement, while strategic arbitrage exploits geographical cost differentials for operational efficiency. Evaluating market conditions, competitive advantage, and long-term business goals helps determine whether licensing agreements or leveraging strategic arbitrage aligns best with organizational objectives.
Licensing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com