A joint venture combines resources and expertise from two or more businesses to achieve a specific goal, spreading both risks and profits. This strategic partnership enhances market reach and innovation potential while allowing partners to leverage each other's strengths. Discover how a joint venture could benefit your business by exploring the details in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
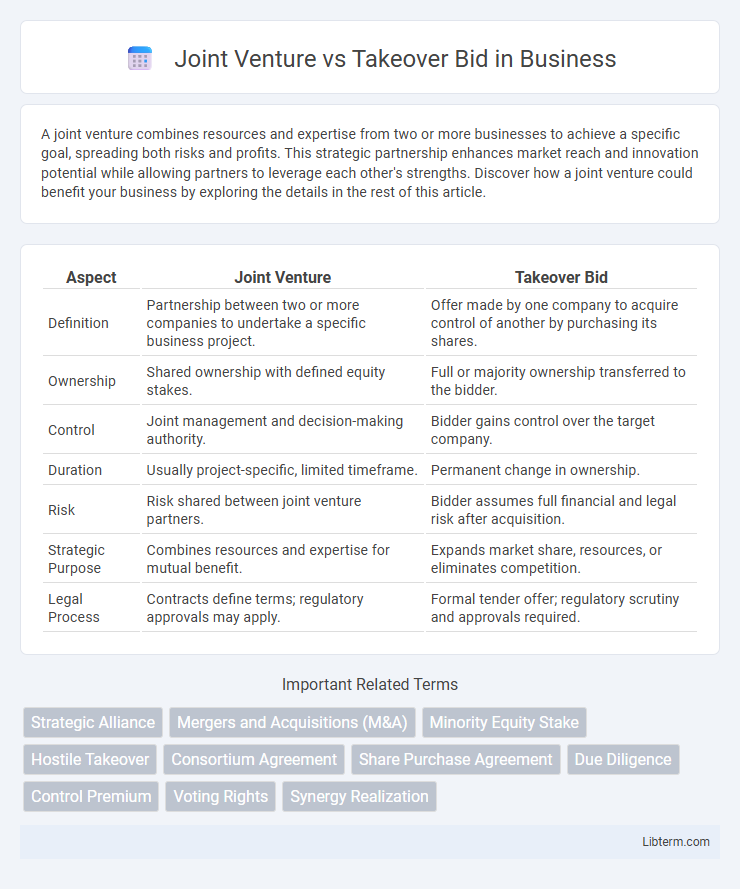
| Aspect | Joint Venture | Takeover Bid |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Partnership between two or more companies to undertake a specific business project. | Offer made by one company to acquire control of another by purchasing its shares. |
| Ownership | Shared ownership with defined equity stakes. | Full or majority ownership transferred to the bidder. |
| Control | Joint management and decision-making authority. | Bidder gains control over the target company. |
| Duration | Usually project-specific, limited timeframe. | Permanent change in ownership. |
| Risk | Risk shared between joint venture partners. | Bidder assumes full financial and legal risk after acquisition. |
| Strategic Purpose | Combines resources and expertise for mutual benefit. | Expands market share, resources, or eliminates competition. |
| Legal Process | Contracts define terms; regulatory approvals may apply. | Formal tender offer; regulatory scrutiny and approvals required. |
Introduction to Joint Ventures and Takeover Bids
Joint ventures involve two or more companies collaborating to achieve shared business objectives while remaining independent entities, often pooling resources and expertise for mutual benefit. Takeover bids occur when one company proposes to acquire control of another, typically by purchasing a majority of its shares to integrate operations and gain strategic advantages. Both strategies serve distinct roles in corporate growth, with joint ventures emphasizing partnership and synergy, while takeover bids focus on ownership transfer and consolidation.
Defining Joint Ventures: Structure and Purpose
A joint venture is a strategic alliance where two or more parties pool resources to accomplish a specific business objective while retaining their separate identities. This collaboration often involves shared ownership, governance, and profits, structured through contractual agreements that define roles and contributions. Joint ventures enable companies to combine expertise, reduce risks, and penetrate new markets without full mergers or acquisitions.
Understanding Takeover Bids: Key Concepts
Takeover bids involve one company making an offer to acquire control of another by purchasing a significant portion or all of its shares, often at a premium price to attract shareholders. These bids can be friendly, with board approval, or hostile, where the acquiring company bypasses management to appeal directly to shareholders. Success in a takeover bid depends on factors such as valuation, shareholder acceptance, regulatory approval, and strategic fit between the acquiring and target companies.
Strategic Objectives: Joint Venture vs Takeover Bid
Joint ventures align strategic objectives by combining complementary resources and capabilities to achieve shared long-term goals, often facilitating market entry and innovation. Takeover bids prioritize acquiring full control over the target company to rapidly expand market presence, increase operational efficiency, or eliminate competition. While joint ventures emphasize cooperation and mutual benefit, takeover bids focus on ownership consolidation and strategic dominance.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
Joint ventures require compliance with contractual agreements, antitrust laws, and regulatory approvals governing shared control and resource contributions, often involving detailed due diligence on partner liabilities. Takeover bids are subject to stricter securities regulations, mandatory disclose requirements, and potential scrutiny under takeover defense laws to protect minority shareholders and ensure fair market conduct. Both structures necessitate adherence to jurisdiction-specific corporate governance rules and regulatory filings to legitimize the transaction and prevent legal disputes.
Financial Implications and Risks
A joint venture financially distributes risks and capital investment between partners, reducing individual exposure while allowing shared profits from combined resources and market access. A takeover bid involves acquiring a controlling interest in a company, often requiring significant upfront capital and potentially increasing debt, but offers full operational control and integration of assets. Financial risks in joint ventures include disagreements over profit-sharing and strategy, whereas takeover bids risk overvaluation, cultural clashes, and regulatory hurdles impacting shareholder value.
Impact on Management and Control
A joint venture allows both parties to share management responsibilities and control, fostering collaborative decision-making and aligning strategic goals. In a takeover bid, the acquiring company typically assumes full control and replaces or overrides existing management, leading to significant shifts in leadership and operational direction. The impact on management in a takeover bid is more direct and immediate, whereas joint ventures require ongoing negotiation and mutual agreement.
Cultural Integration and Operational Synergy
Joint ventures facilitate cultural integration by promoting collaboration and mutual respect between partnering firms, allowing for shared decision-making and blending organizational values, which often results in smoother operational synergy. In contrast, takeover bids frequently face cultural clashes due to abrupt changes in management and corporate identity, potentially disrupting workflows and reducing operational efficiency during integration. Effective cultural alignment in joint ventures fosters sustained operational synergy through cooperative strategy implementation, whereas takeover bids require significant change management efforts to realize comparable synergies.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
The 2011 joint venture between Sony and Ericsson combined Sony's consumer electronics expertise with Ericsson's telecommunications technology, creating a successful mobile handset business that leveraged both companies' strengths. In contrast, Vodafone's 2013 takeover bid for Kabel Deutschland exemplifies a strategic acquisition aiming to consolidate market share and enhance infrastructure control in Germany's telecommunications sector. These cases illustrate how joint ventures foster cooperative innovation, while takeover bids focus on ownership transfer and market dominance.
Choosing the Right Approach for Business Growth
Selecting between a joint venture and a takeover bid hinges on strategic business goals, risk tolerance, and resource availability. Joint ventures offer shared control, access to new markets, and combined expertise, making them ideal for collaborative growth and innovation. Takeover bids provide full ownership and control, enabling streamlined decision-making and rapid integration, suitable for companies seeking aggressive expansion and market dominance.
Joint Venture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com