Self-control problems arise when individuals struggle to regulate their impulses, leading to choices that undermine long-term goals and well-being. These challenges often stem from a conflict between immediate desires and future benefits, impacting decision-making in areas such as health, finance, and productivity. Explore the rest of the article to understand how you can strengthen your self-control and make better decisions.
Table of Comparison
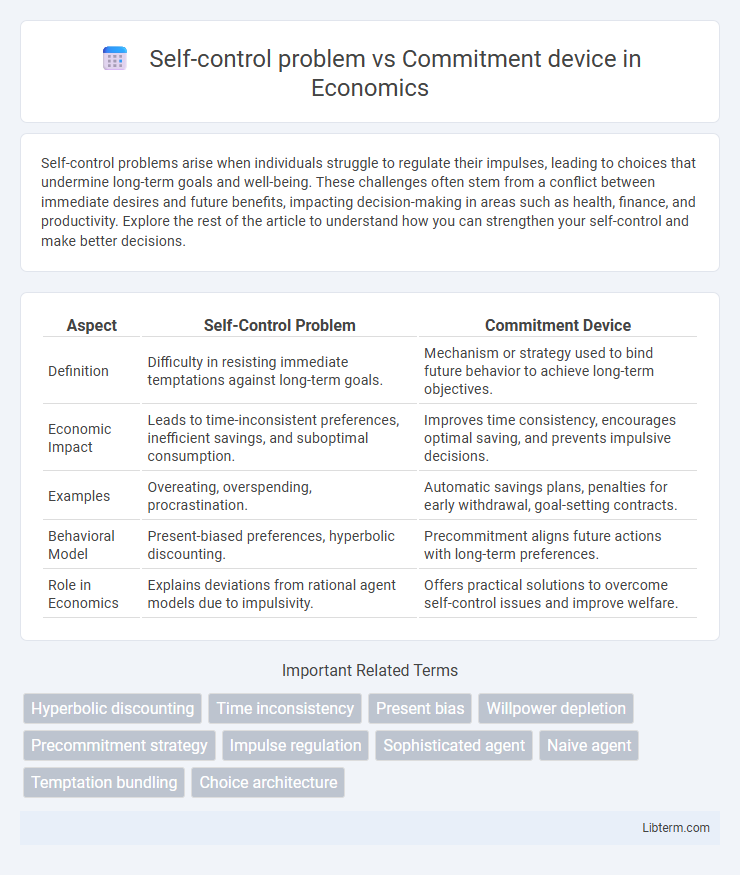
| Aspect | Self-Control Problem | Commitment Device |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Difficulty in resisting immediate temptations against long-term goals. | Mechanism or strategy used to bind future behavior to achieve long-term objectives. |
| Economic Impact | Leads to time-inconsistent preferences, inefficient savings, and suboptimal consumption. | Improves time consistency, encourages optimal saving, and prevents impulsive decisions. |
| Examples | Overeating, overspending, procrastination. | Automatic savings plans, penalties for early withdrawal, goal-setting contracts. |
| Behavioral Model | Present-biased preferences, hyperbolic discounting. | Precommitment aligns future actions with long-term preferences. |
| Role in Economics | Explains deviations from rational agent models due to impulsivity. | Offers practical solutions to overcome self-control issues and improve welfare. |
Understanding Self-Control Problems
Self-control problems arise when individuals struggle to align short-term desires with long-term goals, often leading to impulsive decisions that undermine future well-being. Commitment devices serve as strategic tools or mechanisms designed to restrict future choices, thereby helping individuals stick to their intended plans and mitigate the effects of self-control failures. Understanding self-control problems is essential for developing effective commitment devices that enhance decision-making and promote sustained goal achievement.
The Psychology Behind Impulse and Willpower
The psychology behind impulse and willpower reveals that self-control problems arise when immediate desires conflict with long-term goals, often caused by the brain's reward system prioritizing instant gratification. Commitment devices act as practical tools or strategies that help individuals curb impulsive behaviors by pre-emptively limiting choices or increasing the cost of giving in to temptation. These mechanisms leverage cognitive biases and enhance motivation, reinforcing discipline and aligning actions with intended outcomes.
What Is a Commitment Device?
A commitment device is a strategic tool or mechanism designed to help individuals overcome self-control problems by binding their future actions to predetermined choices that align with long-term goals. These devices work by creating costs or barriers to undesirable behaviors, such as financial penalties for missing a deadline or automated savings plans that restrict access to funds. By limiting impulsive decisions and reinforcing consistent discipline, commitment devices enhance goal adherence and improve overall self-regulation.
Types of Commitment Devices
Types of commitment devices include pre-commitment strategies like financial deposits, automatic savings plans, and social contracts that restrict future choices to enhance self-control. Behavioral tools such as time-bound goals, implementation intentions, and reminder systems function to reduce temptation and improve adherence to long-term objectives. Technological commitment devices leverage apps and digital locks to create barriers against impulsive decisions, providing scalable solutions for managing self-control problems.
How Commitment Devices Address Self-Control Issues
Commitment devices effectively address self-control problems by binding individuals to pre-committed actions, reducing the temptation to deviate from long-term goals. These mechanisms, such as automatic savings plans or password-protected restrictions, leverage behavioral economics principles to minimize impulsive decisions. Evidence from studies in psychology and economics demonstrates that employing commitment devices significantly enhances goal adherence and mitigates self-control failures.
The Science of Delayed Gratification
Self-control problems arise when immediate temptations undermine long-term goals, a challenge extensively studied in the science of delayed gratification. Commitment devices serve as tools or strategies that individuals use to bind themselves, effectively reducing the impact of impulsive choices by limiting future options. Research in behavioral economics and psychology demonstrates that well-designed commitment devices enhance self-regulation by reinforcing patience and promoting goal-consistent behaviors.
Real-Life Examples of Self-Control Failures
Self-control failures often manifest in real life through behaviors like overspending, unhealthy eating, or procrastination, which occur due to immediate temptations overriding long-term goals. Commitment devices, such as automatic savings plans, gym memberships with penalties for cancellation, or software that blocks distracting websites, help individuals overcome these lapses by restricting choices and reinforcing discipline. These strategies effectively convert abstract intentions into concrete actions, reducing the impact of self-control problems in daily decision-making.
Success Stories Using Commitment Devices
Commitment devices have been proven effective in overcoming self-control problems by locking in future behaviors to align with long-term goals, as demonstrated by success stories from behavioral economics and psychology. For instance, individuals using apps like StickK have increased savings or weight loss rates by creating financial stakes that activate accountability. Companies and personal coaches endorse commitment devices for achieving goals ranging from quitting smoking to improving exercise routines, highlighting measurable improvements in adherence and outcomes.
Choosing the Right Commitment Device for You
Choosing the right commitment device depends on understanding your self-control problem's specific nature, such as procrastination or impulsive spending. Options like time-lock apps, financial penalties, or social accountability tools target distinct behaviors to increase success rates. Matching the commitment device to personal triggers and goals maximizes its effectiveness in overcoming self-control challenges.
Building Lasting Habits Through Commitment
Self-control problems often undermine efforts to build lasting habits due to a lack of immediate motivation and susceptibility to temptation. Commitment devices act as proactive tools that lock in future behavior, ensuring consistency by restricting choices that lead to short-term gratification but long-term harm. Utilizing commitment devices like automatic savings plans or pre-committed workout schedules leverages behavioral economics to strengthen habit formation and sustain positive change over time.
Self-control problem Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com