The private sector drives economic growth by fostering innovation, creating jobs, and generating wealth through privately owned businesses and enterprises. Efficient market dynamics and competition within this sector contribute to improved products and services that meet consumer needs. Explore the full article to understand how your engagement with the private sector shapes the broader economy.
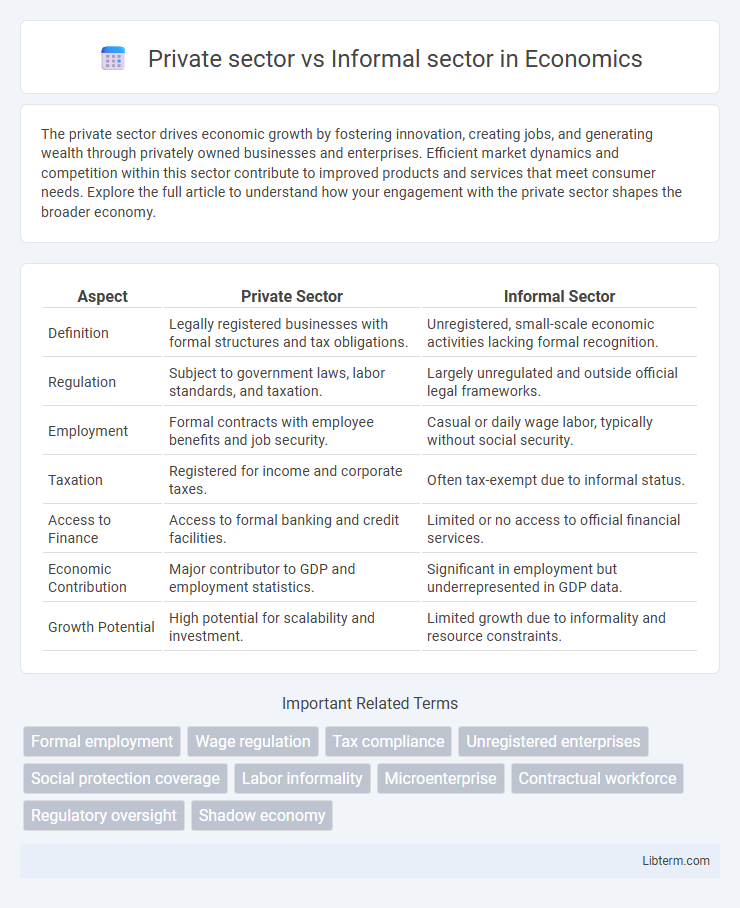
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Private Sector | Informal Sector |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legally registered businesses with formal structures and tax obligations. | Unregistered, small-scale economic activities lacking formal recognition. |
| Regulation | Subject to government laws, labor standards, and taxation. | Largely unregulated and outside official legal frameworks. |
| Employment | Formal contracts with employee benefits and job security. | Casual or daily wage labor, typically without social security. |
| Taxation | Registered for income and corporate taxes. | Often tax-exempt due to informal status. |
| Access to Finance | Access to formal banking and credit facilities. | Limited or no access to official financial services. |
| Economic Contribution | Major contributor to GDP and employment statistics. | Significant in employment but underrepresented in GDP data. |
| Growth Potential | High potential for scalability and investment. | Limited growth due to informality and resource constraints. |
Definition of Private Sector and Informal Sector
The private sector comprises registered businesses and organizations that operate for profit, adhering to government regulations and formal economic frameworks. In contrast, the informal sector includes unregistered, small-scale activities that often evade formal taxation and regulatory oversight, contributing significantly to employment and local economies. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for economic policy development targeting growth, labor markets, and social protection.
Key Characteristics of the Private Sector
The private sector comprises formally registered businesses that operate for profit, adhere to government regulations, and contribute to tax revenues, contrasting with the informal sector's unregistered and often untaxed activities. Key characteristics of the private sector include structured organizational frameworks, access to formal credit and financial services, and established labor practices with employee protections. Its economic impact is significant due to sustained investment, innovation, and scalability, driving gross domestic product (GDP) growth and employment.
Distinct Features of the Informal Sector
The informal sector is characterized by unregistered enterprises that lack formal contracts, social security, and regulatory oversight, distinguishing it from the private sector's structured and legally recognized businesses. It features flexible, small-scale operations often reliant on family labor and cash transactions, with limited access to credit and formal markets. This sector plays a crucial role in employment generation, especially in developing economies, despite its vulnerability to economic fluctuations and absence of worker protections.
Employment Patterns in Both Sectors
The private sector typically offers formal employment with structured contracts, social security benefits, and regulated working hours, fostering job stability and career growth. In contrast, the informal sector is characterized by irregular employment patterns, lack of formal agreements, and absence of social protections, often driven by temporary or seasonal work. Employment in the informal sector predominantly includes self-employed individuals, family labor, and unregistered workers, impacting income security and labor rights enforcement.
Economic Contributions: Private vs Informal Sector
The private sector, comprising registered businesses and corporations, significantly contributes to GDP through formalized production, taxation, and employment generation, fostering economic stability and growth. In contrast, the informal sector operates outside regulatory frameworks, offering flexible employment and filling gaps in the labor market but often lacks access to credit, social protections, and formal infrastructure, limiting its scalability and tax contributions. Together, these sectors drive economic activity, with the private sector providing formal economic structure and the informal sector sustaining livelihoods and local economies.
Legal and Regulatory Frameworks
The private sector operates within formal legal and regulatory frameworks, complying with business registration, taxation, labor laws, and environmental standards enforced by government authorities. In contrast, the informal sector typically functions outside these formal regulations, lacking official registration and often avoiding tax obligations, which limits access to legal protections and financial services. This regulatory disparity affects the growth potential, worker rights, and economic contributions of informal sector activities compared to those in the formal private sector.
Wage Structures and Social Benefits
The private sector typically offers structured wage systems with regular salary payments, performance bonuses, and formal employment contracts ensuring predictable income. In contrast, the informal sector often features irregular wages, lack of standardized pay scales, and no formal employment agreements, resulting in income instability. Social benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, and paid leave are standard in the private sector but are mostly absent in the informal sector, leading to limited social security coverage for informal workers.
Challenges Faced by Private and Informal Sectors
The private sector faces challenges including regulatory compliance, access to finance, and intense market competition that hinder growth and innovation. The informal sector struggles with limited legal recognition, lack of social protections, and difficulty accessing formal credit, which restricts scaling opportunities and financial stability. Both sectors also encounter workforce skill gaps and inadequate infrastructure, exacerbating operational inefficiencies and economic vulnerability.
Impact on National Economic Growth
The private sector significantly drives national economic growth by contributing to GDP, generating employment, and fostering innovation through formal business activities. The informal sector, while less visible in official statistics, plays a crucial role by providing livelihoods and supporting local economies, especially in developing countries. However, its limited access to capital and regulatory frameworks can constrain productivity and tax revenue, affecting overall economic development.
Future Trends and Potential Integration Paths
The private sector is increasingly adopting digital technologies and formalized financial tools, driving efficiency and scalability in emerging markets, while the informal sector remains reliant on cash-based transactions and localized networks. Future trends indicate a convergence where mobile banking, blockchain, and regulatory reforms can facilitate the gradual integration of informal businesses into the formal economy. Strategic partnerships, inclusive policy frameworks, and innovative fintech solutions offer viable paths for bridging gaps between private enterprises and informal actors, enhancing economic resilience and broadening market access.
Private sector Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com