Gaining a competitive advantage involves leveraging unique strengths to outperform rivals in the marketplace. Focusing on innovation, quality, and customer satisfaction can help your business stand out and sustain long-term success. Discover the key strategies that can elevate your position by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
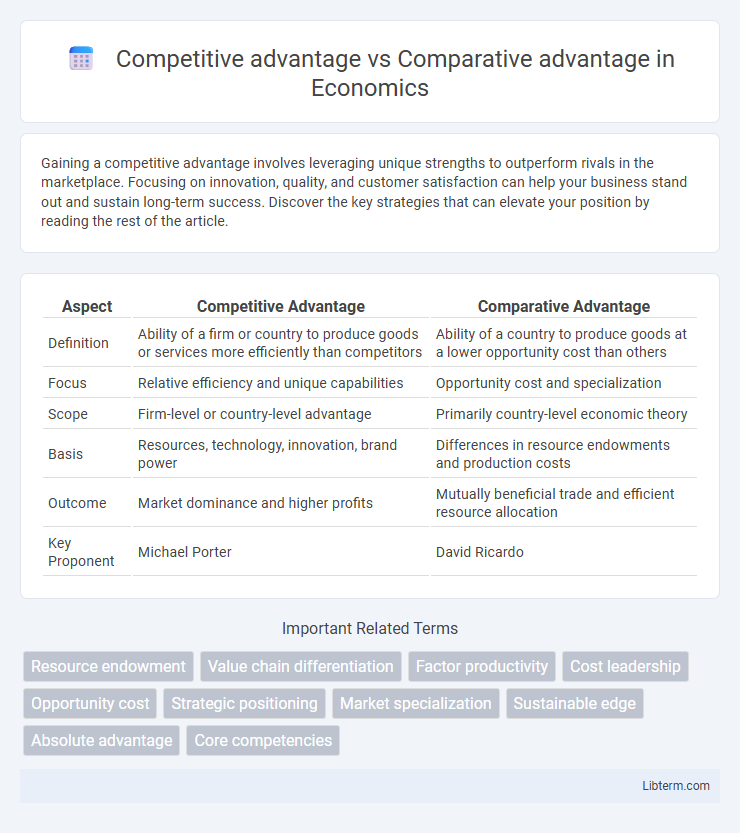
| Aspect | Competitive Advantage | Comparative Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ability of a firm or country to produce goods or services more efficiently than competitors | Ability of a country to produce goods at a lower opportunity cost than others |
| Focus | Relative efficiency and unique capabilities | Opportunity cost and specialization |
| Scope | Firm-level or country-level advantage | Primarily country-level economic theory |
| Basis | Resources, technology, innovation, brand power | Differences in resource endowments and production costs |
| Outcome | Market dominance and higher profits | Mutually beneficial trade and efficient resource allocation |
| Key Proponent | Michael Porter | David Ricardo |
Understanding Competitive Advantage
Competitive advantage refers to a firm's ability to outperform competitors by offering unique value through superior resources, capabilities, or market positioning. It involves leveraging core competencies such as innovation, brand strength, or cost efficiency to achieve sustained profitability. Understanding competitive advantage helps businesses identify strategic strengths that differentiate them in the marketplace and drive long-term success.
Defining Comparative Advantage
Comparative advantage is an economic principle that explains how countries or entities benefit from specializing in producing goods or services for which they have the lowest opportunity cost compared to others. Unlike competitive advantage, which emphasizes superior efficiency or uniqueness in production, comparative advantage centers on relative efficiency and cost differences in resource allocation. This concept, foundational in international trade theory, drives economies to engage in trade that enhances overall productivity and mutual gains.
Key Differences Between Competitive and Comparative Advantage
Competitive advantage refers to a firm's ability to produce goods or services more efficiently or uniquely than its rivals, often through innovation, cost leadership, or brand reputation. Comparative advantage is an economic concept indicating that a country or entity benefits from specializing in producing goods for which it has the lowest opportunity cost, enabling mutually beneficial trade. Key differences include the scale of application--competitive advantage applies to individual businesses while comparative advantage applies to nations--and the basis of advantage, with competitive advantage focusing on superior performance and comparative advantage on opportunity cost efficiency.
Historical Origins of Both Concepts
David Ricardo introduced the concept of comparative advantage in the early 19th century, emphasizing the benefits of specialization and trade based on relative opportunity costs between nations. Adam Smith laid the foundation for competitive advantage in the late 18th century by highlighting the importance of efficiency and productivity improvements within industries. While comparative advantage focuses on international trade efficiency, competitive advantage centers on firm-level strategies that drive market dominance and innovation.
Application in Business Strategy
Competitive advantage refers to a company's ability to outperform rivals by leveraging unique resources, capabilities, or market positioning, leading to sustained superior profitability. Comparative advantage emphasizes specializing in activities where a firm or country has lower opportunity costs, enabling efficient resource allocation and cost leadership. Businesses integrate competitive advantage by differentiating products or innovating, while comparative advantage guides strategic decisions on outsourcing, partnerships, and global supply chain management.
Impact on Global Trade
Competitive advantage drives firms to innovate, increase efficiency, and differentiate products, intensifying global trade competition and expanding market share. Comparative advantage facilitates specialization based on relative production efficiency, promoting international trade by enabling countries to benefit from lower opportunity costs. Together, these concepts shape global trade patterns, influencing resource allocation and economic interdependence among nations.
Role in Economic Growth
Competitive advantage drives economic growth by enabling firms and countries to innovate, increase productivity, and capture larger market shares through unique capabilities or resources, fostering higher value creation and job opportunities. Comparative advantage contributes to economic growth by promoting efficient resource allocation and specialization in producing goods or services at lower opportunity costs, enhancing trade benefits and overall output. Together, these advantages optimize economic performance by balancing innovative differentiation with cost-effective production strategies.
Case Studies: Real-world Examples
Apple Inc. leverages competitive advantage through continuous innovation and brand loyalty, setting itself apart in the global smartphone market. In contrast, Bangladesh exemplifies comparative advantage by focusing on low-cost textile manufacturing to dominate global apparel exports. These distinct strategies highlight how firms and countries create value either by outperforming rivals or specializing in efficient resource allocation.
Developing Sustainable Advantage
Competitive advantage focuses on unique resources and capabilities that allow a firm to outperform rivals, emphasizing innovation, brand strength, and operational efficiency for sustained market leadership. Comparative advantage is rooted in the ability of a country or firm to produce goods at a lower opportunity cost, promoting specialization and trade efficiency. Developing sustainable advantage requires continuous investment in intangible assets like technology, human capital, and adaptive strategies to maintain long-term differentiation and resilience against competitors.
Future Trends and Evolving Theories
Future trends in competitive advantage emphasize innovation, technology adoption, and dynamic capabilities to sustain market leadership amid rapidly changing environments. Evolving theories of comparative advantage incorporate factors like digital globalization, knowledge economies, and artificial intelligence to redefine traditional cost and resource-based distinctions between nations or firms. The convergence of these concepts highlights the growing importance of agility, intellectual capital, and strategic foresight in achieving and maintaining economic success.
Competitive advantage Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com