Effective competition policy ensures fair market practices, prevents monopolies, and fosters innovation, leading to better products and services for consumers. By regulating mergers and curbing anti-competitive behavior, such policies protect Your interests and promote economic growth. Explore the rest of this article to understand how competition policy impacts industries and benefits society.
Table of Comparison
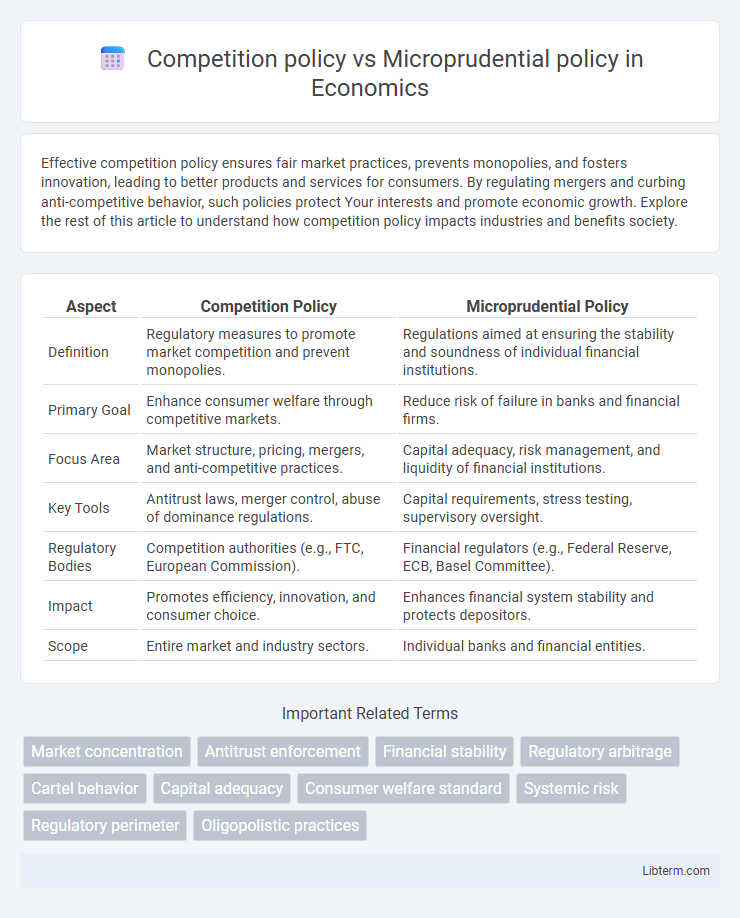
| Aspect | Competition Policy | Microprudential Policy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Regulatory measures to promote market competition and prevent monopolies. | Regulations aimed at ensuring the stability and soundness of individual financial institutions. |
| Primary Goal | Enhance consumer welfare through competitive markets. | Reduce risk of failure in banks and financial firms. |
| Focus Area | Market structure, pricing, mergers, and anti-competitive practices. | Capital adequacy, risk management, and liquidity of financial institutions. |
| Key Tools | Antitrust laws, merger control, abuse of dominance regulations. | Capital requirements, stress testing, supervisory oversight. |
| Regulatory Bodies | Competition authorities (e.g., FTC, European Commission). | Financial regulators (e.g., Federal Reserve, ECB, Basel Committee). |
| Impact | Promotes efficiency, innovation, and consumer choice. | Enhances financial system stability and protects depositors. |
| Scope | Entire market and industry sectors. | Individual banks and financial entities. |
Introduction to Competition Policy and Microprudential Policy
Competition policy promotes market efficiency by preventing monopolies, encouraging innovation, and ensuring fair pricing to protect consumers and businesses. Microprudential policy focuses on the stability of individual financial institutions through regulations that mitigate risks like insolvency and excessive leverage. Together, these policies enhance economic resilience by balancing market competitiveness with the soundness of financial entities.
Defining Competition Policy: Objectives and Scope
Competition policy aims to promote market efficiency, prevent monopolistic practices, and enhance consumer welfare by ensuring fair competition across industries. It encompasses regulatory measures such as antitrust laws, merger control, and cartel prohibition to maintain competitive market structures. The scope of competition policy extends to sectors including telecommunications, energy, and finance, targeting practices that distort market dynamics or create barriers to entry.
Understanding Microprudential Policy: Purpose and Function
Microprudential policy aims to ensure the stability and soundness of individual financial institutions by monitoring risks like credit, market, and operational exposures. It enforces regulatory standards such as capital adequacy, liquidity requirements, and risk management practices to prevent institution-specific failures. This approach contrasts with competition policy, which focuses on promoting market efficiency and consumer welfare by preventing anti-competitive behaviors.
Key Differences Between Competition and Microprudential Policies
Competition policy promotes market efficiency and consumer welfare by encouraging fair rivalry and preventing monopolistic practices, while microprudential policy focuses on the stability of individual financial institutions to mitigate risks such as insolvency. Competition policy targets market structures and behavior to enhance choice and innovation, whereas microprudential regulation emphasizes capital adequacy, liquidity, and risk management within banks. The key difference lies in their objectives: competition policy aims at optimizing market outcomes, whereas microprudential policy ensures the soundness and resilience of the financial system at the firm level.
Overlapping Areas: Where Competition and Microprudential Policies Intersect
Competition policy and microprudential policy intersect in regulating financial institutions to ensure market stability and efficiency. Both policies address risk management, where competition influences banks' risk-taking behaviors and microprudential regulations enforce capital adequacy and liquidity standards to prevent insolvency. Overlapping areas include monitoring market concentration, mitigating systemic risks, and promoting transparency to safeguard consumer interests while maintaining competitive markets.
Impact on Market Structure and Financial Stability
Competition policy promotes market efficiency by preventing monopolies and encouraging diverse market participants, which enhances consumer choice and innovation. Microprudential policy focuses on the soundness of individual financial institutions, reducing risks of insolvency that can trigger systemic crises. Together, these policies influence market structure by balancing competitive dynamics with institutional stability, ultimately supporting a resilient financial system.
Case Studies: Real-World Applications and Outcomes
Competition policy fosters market efficiency and consumer welfare by preventing monopolies and promoting fair business practices, as seen in the European Union's antitrust actions against tech giants like Google. Microprudential policy ensures individual financial institution stability, exemplified by the Federal Reserve's stringent supervisory measures post-2008 financial crisis that mitigated bank failures. Case studies reveal these policies often interact, with competition policy encouraging innovation while microprudential policy safeguards systemic resilience, balancing market dynamism and financial stability.
Challenges in Harmonizing Competition and Microprudential Approaches
Harmonizing competition policy with microprudential policy presents challenges due to their differing objectives: competition policy promotes market efficiency and consumer welfare, while microprudential policy focuses on financial stability and risk management within individual institutions. Regulatory frameworks often struggle to balance the promotion of competitive markets with the need for stringent oversight, as increased competition may lead to risk-taking behaviors that threaten systemic stability. Effective policy integration requires dynamic coordination mechanisms and tailored regulatory tools to mitigate conflicts between fostering innovation and maintaining robust financial safety nets.
Policy Implications for Regulators and Market Participants
Competition policy promotes market efficiency by preventing monopolies and encouraging innovation, which benefits consumers and enhances overall economic welfare. Microprudential policy focuses on the stability of individual financial institutions to prevent systemic risks and protect depositors. Regulators must balance these policies by ensuring competitive markets do not compromise financial stability, while market participants need clear guidelines to navigate compliance without stifling growth or innovation.
Future Trends in Competition and Microprudential Policy Integration
Future trends in competition and microprudential policy integration emphasize enhanced data sharing and real-time monitoring to identify systemic risks while preserving market competition. Regulatory frameworks increasingly incorporate advanced analytics and artificial intelligence to balance financial stability with competitive dynamics. Collaboration between competition authorities and prudential regulators drives more holistic oversight, ensuring resilient yet innovative financial markets.
Competition policy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com