Creative destruction drives economic innovation by dismantling outdated industries to make way for new technologies and business models. This cycle fosters long-term growth, boosts productivity, and transforms markets, impacting both companies and consumers alike. Discover how understanding creative destruction can empower your approach to business and investment by exploring the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
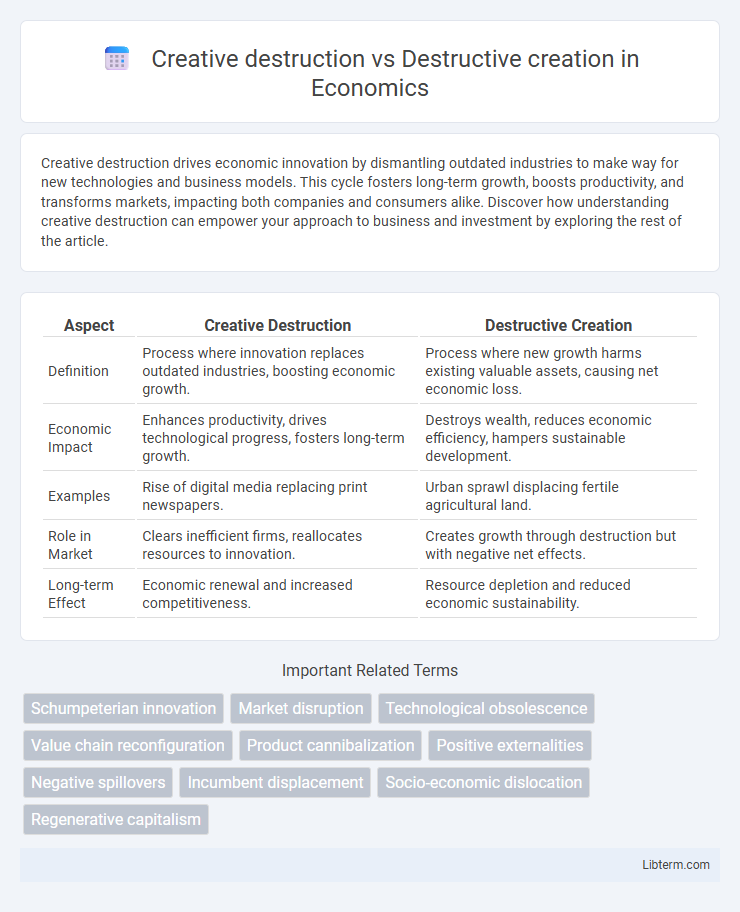
| Aspect | Creative Destruction | Destructive Creation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process where innovation replaces outdated industries, boosting economic growth. | Process where new growth harms existing valuable assets, causing net economic loss. |
| Economic Impact | Enhances productivity, drives technological progress, fosters long-term growth. | Destroys wealth, reduces economic efficiency, hampers sustainable development. |
| Examples | Rise of digital media replacing print newspapers. | Urban sprawl displacing fertile agricultural land. |
| Role in Market | Clears inefficient firms, reallocates resources to innovation. | Creates growth through destruction but with negative net effects. |
| Long-term Effect | Economic renewal and increased competitiveness. | Resource depletion and reduced economic sustainability. |
Understanding Creative Destruction
Creative destruction drives economic growth by replacing outdated industries with innovative technologies, fostering productivity and market efficiency. It involves the systematic dismantling of existing structures to make way for new products, services, and business models that better meet current demands. Understanding creative destruction is crucial for recognizing how innovation disrupts and reshapes economic landscapes, leading to long-term progress despite short-term challenges.
What Is Destructive Creation?
Destructive creation refers to the process where existing economic structures or industries are dismantled not through innovation-driven growth but through harmful or inefficient practices that erode value and stifle progress. Unlike creative destruction, which revitalizes markets by replacing outdated entities with innovative solutions, destructive creation leads to economic stagnation, job losses, and diminished competitiveness. This concept highlights the risks of misguided policies or management decisions that undermine sustainable development and long-term economic health.
Origins and Theoretical Foundations
Creative destruction originates from Joseph Schumpeter's theory describing how innovation-driven economic growth replaces outdated industries with new technologies, fueling capitalism's dynamism. Destructive creation, a less-explored concept, emphasizes the detrimental side of innovation where the process of creating new value simultaneously causes significant harm or collapse to existing structures. Both concepts stem from evolutionary economic theories, highlighting the tension between progress and loss in market transformations.
Key Differences Between the Two Concepts
Creative destruction drives economic growth by replacing outdated technologies and industries with innovative ones, fostering progress and increased productivity. Destructive creation involves the deliberate dismantling of existing systems or structures, often causing social or economic harm without generating substantial new value. Key differences lie in their impact: creative destruction fuels sustainable development and innovation, while destructive creation leads to disruption and loss without corresponding benefits.
Economic Impact: Growth or Collapse?
Creative destruction drives economic growth by replacing outdated industries with innovative technologies, boosting productivity and generating new employment opportunities. Destructive creation, however, risks economic collapse when destructive processes outpace innovation, causing widespread job losses and market instability. The balance between these forces determines whether an economy experiences sustainable expansion or contraction.
Real-World Examples: Innovations and Downfalls
Creative destruction drives economic growth by replacing obsolete technologies with innovative solutions, exemplified by the rise of digital photography overtaking traditional film cameras, leading to new market leaders like Canon and Nikon adopting mirrorless technology. Destructive creation highlights situations where new innovations cause harmful societal impacts, such as the introduction of ride-sharing apps disrupting taxi industries, resulting in job losses and regulatory challenges worldwide. Real-world examples reveal the delicate balance between fostering innovation and managing the negative consequences of industrial transformation.
Societal Consequences and Adaptation
Creative destruction drives economic progress by dismantling outdated industries, fostering innovation and new job opportunities, but it also causes social disruption and employment instability requiring workforce retraining and social safety nets. Destructive creation, often linked to exploitative or environmentally harmful practices, can degrade social cohesion and ecological health, undermining long-term societal resilience. Effective adaptation depends on policy frameworks promoting sustainable innovation, equitable resource distribution, and community engagement to balance growth with societal well-being.
The Role of Technology in Both Phenomena
Technology serves as a catalyst in creative destruction by driving innovation that disrupts existing markets and renders obsolete products or services, thereby fostering economic growth. In destructive creation, technology can lead to the emergence of new industries or innovations at the expense of established systems, often causing unintended negative consequences such as environmental harm or job displacement. Understanding the dual role of technology is crucial for balancing innovation with sustainable development and social welfare.
Policy Implications and Strategic Responses
Creative destruction fosters economic growth by replacing outdated industries with innovative ones, prompting policymakers to support innovation ecosystems and smooth labor market transitions. Destructive creation, which simultaneously generates new opportunities and systemic risks, requires regulations that balance entrepreneurial freedom with financial stability. Strategic responses include adaptive policies promoting reskilling programs, innovation incentives, and robust safety nets to mitigate social disruptions while encouraging dynamic economic renewal.
Future Outlook: Balancing Creation and Destruction
Creative destruction drives innovation by replacing outdated industries with new technologies, fostering economic growth and productivity. Destructive creation emphasizes the environmental and social costs of innovation, urging sustainable practices to minimize harm while advancing progress. Balancing these forces requires policies that promote responsible innovation, investments in green technology, and frameworks supporting workforce adaptation to ensure long-term economic and ecological resilience.
Creative destruction Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com