Productive transformation enhances economic growth by shifting resources toward higher value-added activities, increasing efficiency and innovation. This process drives sustainable development and improves living standards through better job creation and technology adoption. Discover how productive transformation can impact Your industry and stimulate long-term success in the full article.
Table of Comparison
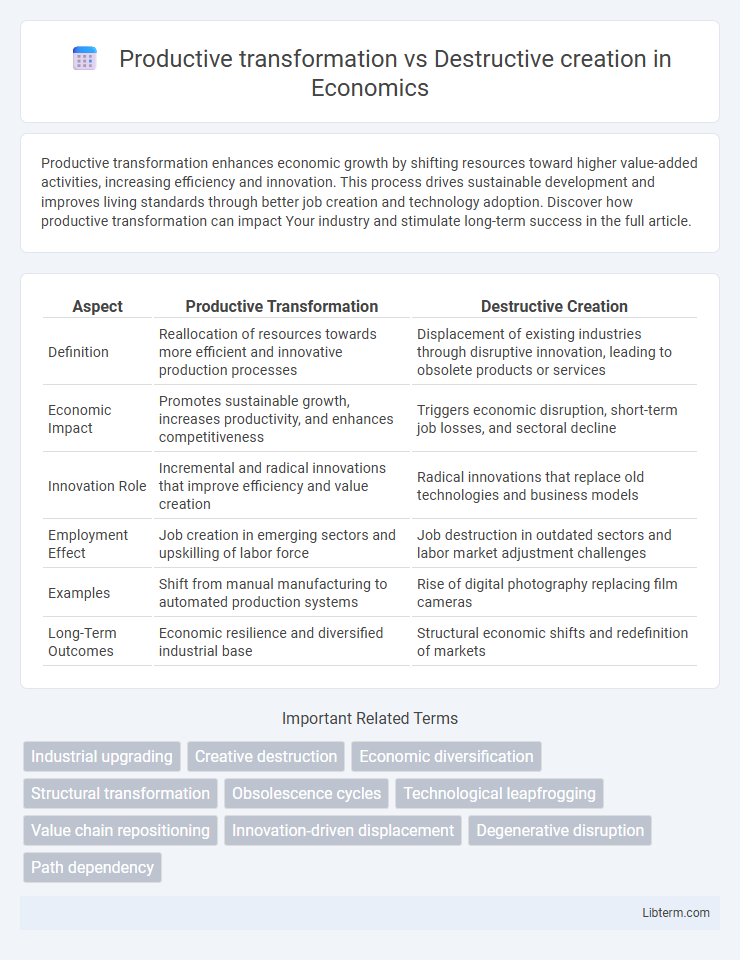
| Aspect | Productive Transformation | Destructive Creation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reallocation of resources towards more efficient and innovative production processes | Displacement of existing industries through disruptive innovation, leading to obsolete products or services |
| Economic Impact | Promotes sustainable growth, increases productivity, and enhances competitiveness | Triggers economic disruption, short-term job losses, and sectoral decline |
| Innovation Role | Incremental and radical innovations that improve efficiency and value creation | Radical innovations that replace old technologies and business models |
| Employment Effect | Job creation in emerging sectors and upskilling of labor force | Job destruction in outdated sectors and labor market adjustment challenges |
| Examples | Shift from manual manufacturing to automated production systems | Rise of digital photography replacing film cameras |
| Long-Term Outcomes | Economic resilience and diversified industrial base | Structural economic shifts and redefinition of markets |
Understanding Productive Transformation
Productive transformation involves improving or repurposing existing resources and processes to create value without depleting assets, emphasizing sustainability and long-term growth. It contrasts with destructive creation, which generates new outputs by consuming or damaging resources, often leading to net losses. Understanding productive transformation is crucial for fostering innovation that enhances efficiency and economic resilience without compromising environmental or social stability.
Defining Destructive Creation
Destructive creation refers to innovation or development processes that replace existing technologies, industries, or products in ways that cause significant disruption or loss of established jobs and economic structures. Unlike productive transformation, which enhances efficiency and growth by building upon existing assets, destructive creation often leads to short-term economic dislocation and social challenges. Understanding destructive creation is crucial for policymakers to manage transitions and mitigate negative impacts on affected workers and communities.
Key Differences Between Productive and Destructive Change
Productive transformation fosters innovation by improving processes, creating value, and enhancing efficiency, driving sustainable economic growth and long-term benefits. Destructive creation involves the dismantling of existing structures or systems, often causing short-term disruption and loss before new developments emerge. The key differences lie in their impacts: productive change builds on existing foundations constructively, while destructive change breaks down old models to enable new possibilities but with greater initial uncertainty.
Drivers of Productive Transformation
Drivers of productive transformation include technological innovation, investment in human capital, and institutional reforms that foster efficient resource allocation and market competitiveness. These factors lead to sustainable economic growth by enhancing productivity, upgrading industry capabilities, and enabling structural shifts toward higher value-added sectors. Unlike destructive creation, productive transformation builds on existing assets and capabilities to generate lasting improvements in output and employment quality.
Causes of Destructive Creation
Destructive creation stems from factors such as monopolistic practices that stifle competition, regulatory failures that allow harmful market behaviors, and disruptive technological shifts that render existing industries obsolete without adequate transition support. Economic policies favoring short-term gains over sustainable growth can intensify destructive creation by undermining productive investments. Furthermore, excessive reliance on rent-seeking activities diverts resources away from innovation, accelerating the decline of productive sectors.
Economic Impact: Growth vs. Decline
Productive transformation drives economic growth by reallocating resources to more efficient and innovative sectors, increasing output and enhancing competitiveness. Destructive creation, while fostering innovation, often results in the displacement of existing industries and job losses, causing short-term economic decline and social disruption. Sustainable economic development depends on balancing productive transformation to maximize growth while mitigating the adverse impacts of destructive creative shifts.
Case Studies: Success in Productive Transformation
Case studies on productive transformation highlight how firms shift resources to create new value without reducing existing assets, leading to sustainable economic growth and innovation. Examples include Toyota's transition to hybrid technology, which enhanced eco-friendly vehicle production and expanded market share without cannibalizing its existing products. Contrastly, destructive creation, as seen in industries disrupted by digital platforms, often eliminates old market segments but may undermine long-term ecosystem stability.
Case Studies: Failures from Destructive Creation
Case studies of failures from destructive creation highlight projects where innovation led to net economic losses due to resource misallocation and market disruption. Notable examples include Kodak's decline after digital photography innovations disrupted its core film business and Blockbuster's collapse following the rise of streaming services like Netflix, demonstrating failure to adapt productively. These cases illustrate the risks of destructive creation when technological change damages existing productive structures without fostering sustained value or growth.
Strategic Approaches for Sustainable Change
Productive transformation emphasizes leveraging existing resources and capabilities to generate sustainable growth by optimizing processes, innovation, and value addition, while destructive creation disrupts current systems through radical change often causing short-term losses. Strategic approaches for sustainable change prioritize inclusive stakeholder engagement, adaptive policy frameworks, and continuous feedback mechanisms to balance economic growth with social and environmental responsibility. Emphasizing resilience and long-term impact ensures the transition fosters equitable development without compromising future resource availability.
Future Trends in Transformation and Creation
Productive transformation drives sustainable growth by innovating existing resources and enhancing efficiency, while destructive creation disrupts markets by replacing outdated systems through radical innovation. Future trends emphasize leveraging artificial intelligence and blockchain technologies to enable seamless, adaptive productive transformations that minimize waste and environmental impact. Embracing circular economy principles and advanced automation will further distinguish productive transformation, fostering long-term value over the short-term gains associated with destructive creation.
Productive transformation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com