Resource blessing offers abundant opportunities for sustainable growth by effectively utilizing natural and human assets. Maximizing these blessings can boost economic development, improve living standards, and ensure environmental balance. Explore the rest of the article to discover how your region can harness resource blessings for lasting success.
Table of Comparison
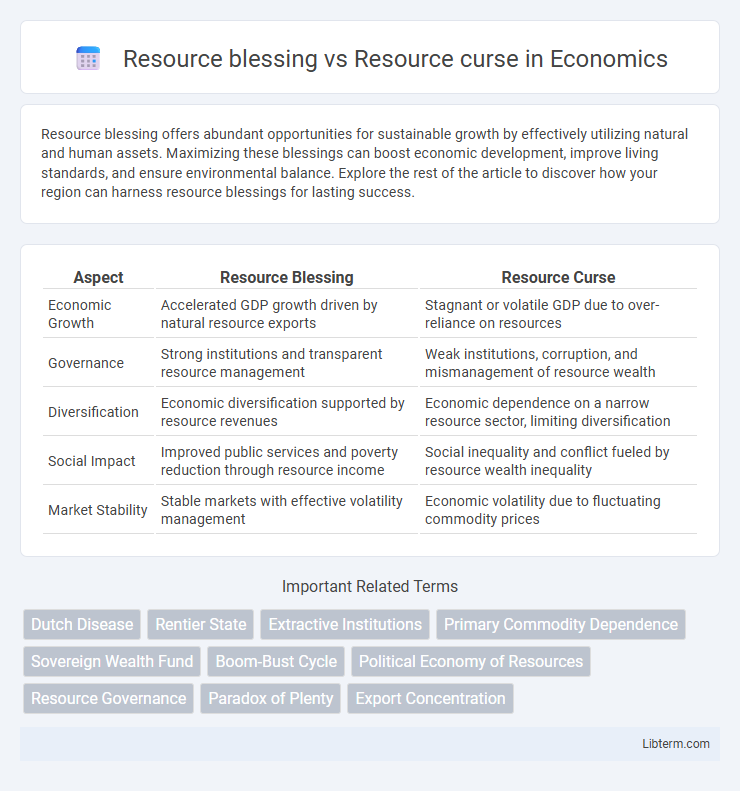
| Aspect | Resource Blessing | Resource Curse |
|---|---|---|
| Economic Growth | Accelerated GDP growth driven by natural resource exports | Stagnant or volatile GDP due to over-reliance on resources |
| Governance | Strong institutions and transparent resource management | Weak institutions, corruption, and mismanagement of resource wealth |
| Diversification | Economic diversification supported by resource revenues | Economic dependence on a narrow resource sector, limiting diversification |
| Social Impact | Improved public services and poverty reduction through resource income | Social inequality and conflict fueled by resource wealth inequality |
| Market Stability | Stable markets with effective volatility management | Economic volatility due to fluctuating commodity prices |
Understanding Resource Blessing and Resource Curse
Resource blessing occurs when abundant natural resources stimulate economic growth, enhance governance, and improve living standards through effective management and diversification. Resource curse, conversely, emerges when reliance on resource wealth causes economic volatility, corruption, and underdevelopment by crowding out other sectors and fostering rent-seeking behavior. Understanding these concepts hinges on recognizing how institutional quality, policy decisions, and global market dynamics influence the divergent outcomes of resource abundance.
Historical Context of Resource Wealth
Resource wealth has historically shaped the economic trajectories of nations, with some countries leveraging natural riches to fuel industrial growth and infrastructure development. Conversely, others have suffered from the resource curse, where abundant minerals or oil led to economic dependency, corruption, and conflict, undermining sustainable development. Empirical evidence from regions like sub-Saharan Africa and the Middle East illustrates how governance and institutional quality critically mediate the outcomes of resource abundance.
Economic Impacts of Resource Abundance
Resource abundance can drive robust economic growth through increased government revenues, foreign investments, and infrastructure development, particularly when managed with sound fiscal policies. However, resource-rich countries often face the resource curse, characterized by economic volatility, over-reliance on commodity exports, and underdevelopment of other sectors, leading to slower overall growth and higher inequality. Effective governance, diversification strategies, and transparent institutions are critical to converting natural wealth into sustainable economic benefits.
Political Stability and Governance Challenges
Resource blessing often fosters political stability by providing governments with revenues to strengthen institutions and invest in public services, enhancing governance effectiveness. In contrast, the resource curse can trigger governance challenges such as corruption, rent-seeking, and weakened democratic accountability, leading to political instability and conflict. Countries like Norway exemplify resource blessing with stable governance, while nations like Nigeria illustrate resource curse dynamics with persistent political turmoil and governance deficits.
Social Outcomes in Resource-Rich Countries
Resource-rich countries often experience varied social outcomes influenced by the management of natural wealth. Effective governance and equitable resource distribution can lead to improved public services, poverty reduction, and enhanced social cohesion, representing the resource blessing. Conversely, mismanagement, corruption, and unequal wealth allocation frequently result in social inequality, conflict, and weakened institutions, exemplifying the resource curse in these nations.
Environmental Consequences of Resource Exploitation
Resource exploitation often leads to severe environmental degradation, including deforestation, soil erosion, and pollution, which exacerbate the negative impacts associated with the resource curse. Countries experiencing the resource blessing may benefit economically but frequently struggle with habitat destruction and biodiversity loss due to intensive mining and fossil fuel extraction. Sustainable resource management practices and environmental regulations are critical to mitigating ecological damage and transforming natural wealth into long-term developmental advantages.
Factors Influencing Resource Outcomes
Resource outcomes depend heavily on governance quality, institutional strength, and economic diversification. Countries with transparent legal frameworks and robust institutions tend to harness natural resources for sustainable development, avoiding the pitfalls of corruption and rent-seeking behaviors. Conversely, weak governance and over-reliance on resource exports often lead to economic volatility and the resource curse.
Global Examples: Success Stories vs. Failures
Norway exemplifies the resource blessing through its effective management of oil wealth, establishing the Government Pension Fund Global to ensure long-term economic stability and social welfare. In contrast, Nigeria illustrates the resource curse, where abundant oil resources have fueled corruption, economic volatility, and social unrest, hindering sustainable development. Botswana showcases a success story in diamond resource management, combining prudent governance with investment in public infrastructure, while Venezuela represents a failure due to mismanagement of oil revenues leading to economic collapse and hyperinflation.
Policy Strategies to Avoid the Resource Curse
Effective policy strategies to avoid the resource curse include establishing transparent governance frameworks, investing resource revenues in diversified economic sectors, and creating sovereign wealth funds to stabilize fiscal spending. Implementing strong legal institutions and anti-corruption measures ensures that resource wealth benefits broad societal development rather than fueling rent-seeking behaviors. Countries like Norway demonstrate success by prioritizing accountability, long-term planning, and fiscal prudence to transform natural resource abundance into sustainable economic growth.
Future Prospects and Sustainable Resource Management
Effective sustainable resource management can transform the resource curse into a resource blessing by promoting long-term economic stability, environmental preservation, and social equity. Future prospects depend on adopting transparent governance frameworks, investing in renewable resource technologies, and enhancing local capacity for resource stewardship. Countries embracing innovation and diversification in resource-based economies increase resilience against market volatility and contribute to sustainable development goals.
Resource blessing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com