Extrinsic value refers to the external worth of an object or asset based on factors such as market demand, utility, or cultural significance rather than its inherent properties. It plays a crucial role in economics, investing, and decision-making by influencing how much people are willing to pay or trade for something. Explore the rest of this article to understand how extrinsic value impacts your financial and personal choices.
Table of Comparison
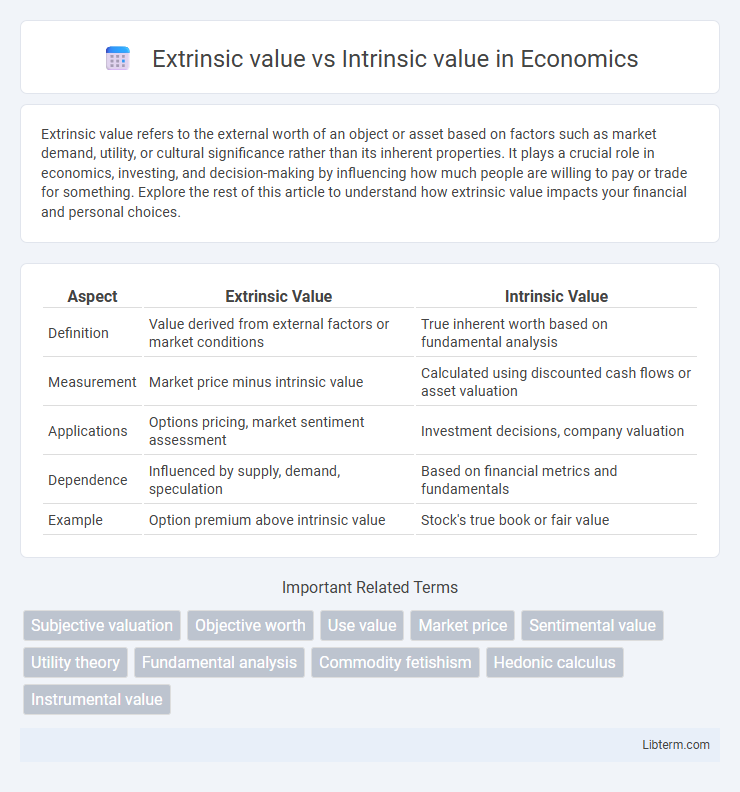
| Aspect | Extrinsic Value | Intrinsic Value |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Value derived from external factors or market conditions | True inherent worth based on fundamental analysis |
| Measurement | Market price minus intrinsic value | Calculated using discounted cash flows or asset valuation |
| Applications | Options pricing, market sentiment assessment | Investment decisions, company valuation |
| Dependence | Influenced by supply, demand, speculation | Based on financial metrics and fundamentals |
| Example | Option premium above intrinsic value | Stock's true book or fair value |
Introduction to Value Theory
Extrinsic value refers to the worth an object or action has due to external factors or its usefulness in achieving a desired outcome, while intrinsic value denotes the inherent worth something possesses independently of external benefits or consequences. Value theory explores the distinctions between these types of values to understand how individuals and societies prioritize moral, aesthetic, and practical judgments. Recognizing the interplay between extrinsic and intrinsic values is essential for analyzing ethical decisions, economic evaluations, and cultural significance.
Defining Intrinsic Value
Intrinsic value represents the inherent worth of an asset, independent of market conditions or external factors, often reflecting its fundamental characteristics or utility. It is commonly used in finance to evaluate stocks or options based on tangible elements such as earnings, dividends, or the actual exercise value of options. Understanding intrinsic value helps investors make decisions grounded in an asset's true economic benefit rather than speculative market prices.
Understanding Extrinsic Value
Extrinsic value refers to the value assigned to an asset or option based on external factors such as market demand, time remaining until expiration, and volatility, rather than the asset's inherent worth. In finance, extrinsic value is commonly associated with options pricing, representing the premium paid above the intrinsic value, reflecting the potential for future profit. Understanding extrinsic value is crucial for traders to assess the risk and reward of options beyond their immediate exercise value.
Key Differences Between Intrinsic and Extrinsic Value
Intrinsic value refers to the inherent worth of an asset, object, or concept based on its fundamental qualities, such as utility, rarity, or essential nature, independent of external factors. Extrinsic value depends on external influences like market demand, investor sentiment, or perceived future benefit, often fluctuating with economic conditions and speculation. The key differences lie in intrinsic value being objective and stable, while extrinsic value is subjective and volatile.
Examples of Intrinsic Value in Real Life
Intrinsic value in real life is often seen in natural resources such as clean air and fresh water, which hold importance independent of economic benefits. Artworks like the Mona Lisa possess intrinsic value due to their cultural and historical significance beyond monetary price. Personal relationships and happiness also exemplify intrinsic value, reflecting importance rooted in emotional fulfillment rather than external rewards.
Examples of Extrinsic Value in Real Life
Extrinsic value is the worth assigned to an object or action based on external factors such as utility or market demand, unlike intrinsic value, which is inherent and independent of external context. Examples of extrinsic value in real life include currency, whose value is determined by governmental backing and societal trust, branded products whose price reflects consumer perception and marketing, and collectibles like rare coins or trading cards valued for rarity and demand rather than physical properties. Stock options also hold extrinsic value depending on market conditions and time until expiration.
Role of Intrinsic Value in Philosophy
Intrinsic value in philosophy signifies the inherent worth of an object or action, independent of external factors or consequences. Unlike extrinsic value, which depends on external benefits or outcomes, intrinsic value reflects the fundamental importance ascribed to things for their own sake. This concept plays a crucial role in ethical theories, underpinning moral judgments and guiding principles about what is genuinely valuable in human life.
Extrinsic Value in Economics and Ethics
Extrinsic value in economics refers to the worth of an asset or good based on external factors such as market demand, price, and utility derived from trade, contrasting with intrinsic value which is inherent and independent of external influence. In ethics, extrinsic value is attributed to objects or actions due to their consequences or usefulness in achieving desired outcomes, differing from intrinsic value that is deemed valuable in itself. Understanding extrinsic value is crucial for economic decision-making and ethical evaluations where context and external benefits dictate value judgments.
Debates and Criticisms on Value Theory
Debates on extrinsic value versus intrinsic value center on whether value resides in an object's inherent properties or in its relationships and consequences. Critics argue that focusing solely on intrinsic value neglects the practical significance of external factors and contextual dependencies, while defenders of intrinsic value maintain that it provides a more stable ethical foundation. This tension influences contemporary value theory by challenging frameworks in ethics, economics, and environmental philosophy, where the balance between inherent worth and instrumental usefulness remains contested.
Practical Implications of Value Distinctions
Extrinsic value reflects an asset's worth based on external factors such as market demand or time until expiration, significantly impacting trading strategies and risk management decisions. Intrinsic value measures the fundamental, inherent worth derived from the actual properties or utility of the asset, guiding long-term investment and valuation models. Understanding the distinction between extrinsic and intrinsic value aids investors in option pricing, portfolio diversification, and assessing potential returns relative to underlying asset performance.
Extrinsic value Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com