Operating profit measures a company's earnings from core business activities before deducting interest and taxes, reflecting true operational efficiency. Maintaining a strong operating profit margin indicates effective cost management and revenue generation. Discover how optimizing your operating profit can drive business growth by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
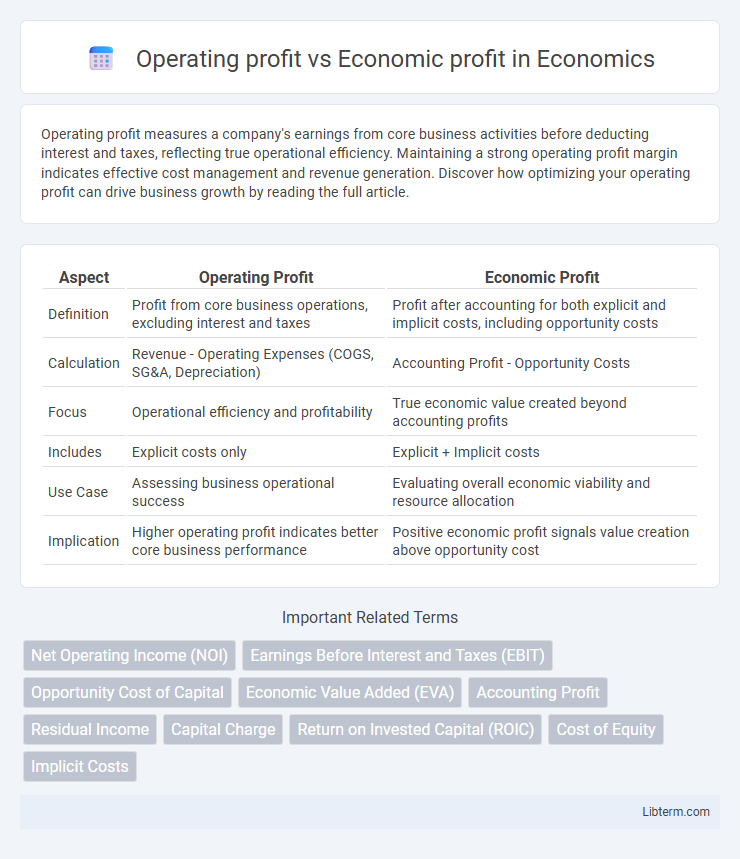
| Aspect | Operating Profit | Economic Profit |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Profit from core business operations, excluding interest and taxes | Profit after accounting for both explicit and implicit costs, including opportunity costs |
| Calculation | Revenue - Operating Expenses (COGS, SG&A, Depreciation) | Accounting Profit - Opportunity Costs |
| Focus | Operational efficiency and profitability | True economic value created beyond accounting profits |
| Includes | Explicit costs only | Explicit + Implicit costs |
| Use Case | Assessing business operational success | Evaluating overall economic viability and resource allocation |
| Implication | Higher operating profit indicates better core business performance | Positive economic profit signals value creation above opportunity cost |
Introduction to Operating Profit and Economic Profit
Operating profit, also known as operating income, measures a company's profitability from core business operations, excluding interest and taxes. Economic profit calculates the true profitability by subtracting both explicit costs and implicit costs, including opportunity costs, from total revenue. Understanding the distinction highlights operating profit's focus on operational efficiency versus economic profit's comprehensive assessment of value creation.
Defining Operating Profit
Operating profit, also known as operating income, measures a company's profitability from core business operations before interest and taxes, calculated as gross profit minus operating expenses such as selling, general, and administrative costs. This metric reflects the efficiency of a company's primary activities by excluding non-operating revenues and expenses, providing insight into operational performance. Understanding operating profit is crucial for assessing how well a business generates earnings from its core functions independently of financial and tax-related factors.
What is Economic Profit?
Economic profit measures a company's true profitability by subtracting both explicit costs and implicit opportunity costs from total revenue, unlike operating profit which only deducts operating expenses. This metric reflects the value created beyond the minimum return required by investors, incorporating alternative investment opportunities. Businesses use economic profit to assess long-term sustainability and efficient resource allocation.
Key Differences Between Operating Profit and Economic Profit
Operating profit measures a company's profitability from core business operations, excluding interest and taxes, while economic profit accounts for both explicit and implicit costs, including opportunity costs. Operating profit focuses on revenue minus operating expenses, providing insight into operational efficiency, whereas economic profit evaluates true profitability by subtracting total costs, including the cost of capital. Economic profit is often used to assess long-term value creation, contrasting with operating profit's emphasis on short-term operational performance.
How to Calculate Operating Profit
Operating profit is calculated by subtracting operating expenses, such as cost of goods sold, wages, and depreciation, from total revenue, reflecting the company's core business profitability before interest and taxes. It excludes non-operating income and expenses, offering a clear view of operational efficiency. This metric differs from economic profit, which considers opportunity costs, providing a broader assessment of value creation beyond accounting profits.
Calculating Economic Profit: A Step-by-Step Guide
Economic profit is calculated by subtracting both explicit costs and implicit costs, including opportunity costs, from total revenue, providing a comprehensive measure of profitability beyond operating profit. The first step is to determine accounting profit by deducting explicit expenses such as wages and materials from total revenue. Next, quantify implicit costs, such as the opportunity cost of invested capital or forgone income, and subtract these from accounting profit to arrive at economic profit.
Importance of Operating Profit in Financial Analysis
Operating profit is crucial in financial analysis as it reflects a company's core profitability from its primary business operations, excluding non-operating income and expenses. It provides a clear measure of operational efficiency and management effectiveness before the impact of financing and tax strategies. Analysts rely on operating profit to assess a firm's ability to generate sustainable earnings and to compare performance within industries.
The Role of Economic Profit in Strategic Decision Making
Economic profit plays a critical role in strategic decision making by providing a comprehensive measure of a firm's true profitability, considering both explicit and implicit costs, including opportunity costs. Unlike operating profit, which accounts only for revenues minus operating expenses, economic profit evaluates whether the company's returns exceed the cost of capital, guiding management in resource allocation and long-term investment decisions. This metric helps identify value-creating opportunities and avoid investments that may generate accounting profit but destroy economic value.
Real-world Examples: Operating Profit vs Economic Profit
Operating profit measures a company's earnings from core business operations, excluding interest and taxes, while economic profit accounts for both explicit costs and opportunity costs, providing a broader assessment of value creation. For example, Apple's high operating profit reflects efficient production and sales, but when factoring in economic profit, the cost of capital investments and lost alternative returns may reduce its net gain. In contrast, a startup might show low or negative operating profit but positive economic profit if the opportunity costs are minimal, illustrating the importance of evaluating both metrics for comprehensive financial analysis.
Which Metric Should Businesses Prioritize?
Operating profit measures a company's earnings from core business operations, excluding interest and taxes, providing insight into operational efficiency and profitability. Economic profit accounts for opportunity costs, subtracting both explicit and implicit costs, making it a more comprehensive indicator of true value creation. Businesses should prioritize economic profit to assess long-term sustainability and resource allocation effectiveness beyond short-term operational success.
Operating profit Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com