A fiscal surplus occurs when a government's revenue exceeds its expenditures during a specific period, indicating sound financial management and economic stability. Maintaining a fiscal surplus can help reduce national debt and provide funds for future investments or emergencies. Discover how understanding fiscal surplus impacts your economy and financial planning in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
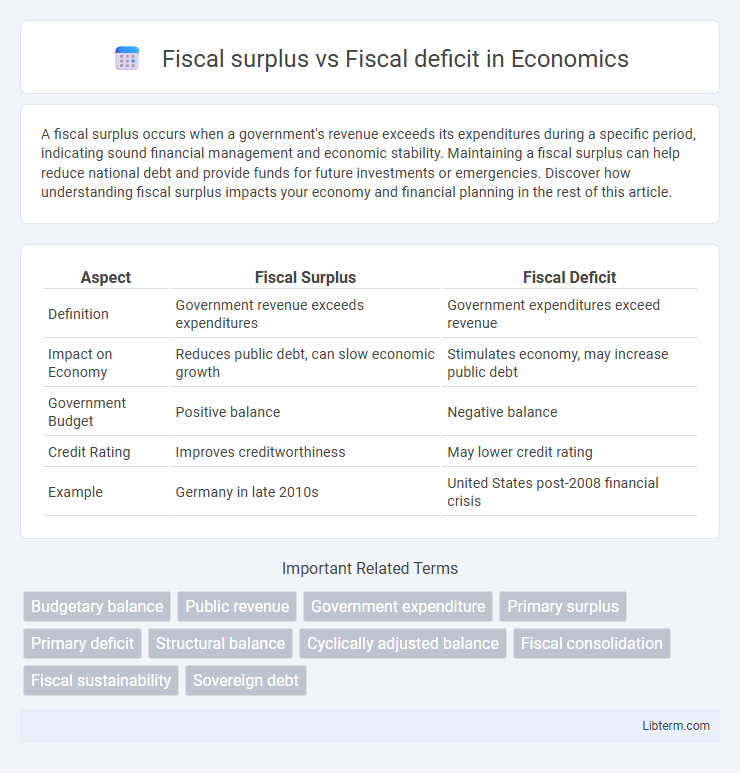
| Aspect | Fiscal Surplus | Fiscal Deficit |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Government revenue exceeds expenditures | Government expenditures exceed revenue |
| Impact on Economy | Reduces public debt, can slow economic growth | Stimulates economy, may increase public debt |
| Government Budget | Positive balance | Negative balance |
| Credit Rating | Improves creditworthiness | May lower credit rating |
| Example | Germany in late 2010s | United States post-2008 financial crisis |
Understanding Fiscal Surplus and Fiscal Deficit
Fiscal surplus occurs when a government's revenue exceeds its expenditures during a specific period, indicating effective fiscal management and potential for debt reduction or increased savings. Fiscal deficit arises when government spending surpasses its revenue, necessitating borrowing to cover the gap, which can lead to increased public debt and inflationary pressures if persistent. Understanding the balance between fiscal surplus and deficit is crucial for assessing a country's economic health and its ability to finance public services without excessive debt.
Key Differences Between Fiscal Surplus and Fiscal Deficit
Fiscal surplus occurs when a government's total revenue exceeds its total expenditures during a fiscal period, indicating a positive budget balance, whereas fiscal deficit happens when expenditures surpass revenues, resulting in a negative budget balance. A fiscal surplus often allows for debt reduction or increased public savings, while a fiscal deficit typically requires borrowing, increasing national debt. Key differences include their impact on economic policy, with surplus promoting fiscal stability and deficits potentially stimulating economic growth or causing inflation.
Causes of Fiscal Surplus
A fiscal surplus occurs when government revenues exceed expenditures, often resulting from increased tax collection, robust economic growth, or significant reductions in public spending. Strong commodity prices or windfall gains, such as from natural resource exports, can also contribute to a fiscal surplus. Efficient fiscal management, including stringent budget controls and debt servicing strategies, supports maintaining a surplus and financial stability.
Reasons Behind Fiscal Deficit
Fiscal deficit occurs when government expenditures exceed its revenues, primarily due to increased public spending on infrastructure, social programs, or defense without corresponding revenue growth. Economic downturns reduce tax collections and increase welfare spending, exacerbating the fiscal deficit. Structural issues such as inefficient tax systems and reliance on borrowing further contribute to persistent fiscal deficits.
Economic Implications of Fiscal Surplus
Fiscal surplus indicates that a government's revenues exceed its expenditures, enabling debt reduction and increased public savings. This excess revenue can stimulate economic stability by lowering interest rates and funding essential infrastructure projects without borrowing. A sustained fiscal surplus often signals sound financial management, which can boost investor confidence and enhance a country's credit rating.
Economic Impact of Fiscal Deficit
A fiscal deficit occurs when government expenditures exceed revenues, leading to increased borrowing and higher public debt levels. This situation can stimulate short-term economic growth by funding infrastructure and social programs, but excessive deficits may crowd out private investment and trigger inflationary pressures. Persistent fiscal deficits undermine fiscal sustainability, reduce investor confidence, and can result in higher interest rates, ultimately slowing down economic growth.
Fiscal Surplus: Benefits and Drawbacks
Fiscal surplus occurs when a government's revenue exceeds its expenditures, allowing for debt reduction and increased savings that can stabilize the economy during downturns. It provides opportunities for investment in infrastructure, public services, and fostering long-term economic growth while enhancing creditworthiness. However, prolonged fiscal surplus may indicate underinvestment in essential public services, potentially slowing economic growth and reducing social welfare.
Fiscal Deficit: Pros and Cons
Fiscal deficit occurs when government expenditures exceed revenues, fueling economic growth by enabling increased public investment in infrastructure and social programs. However, persistent fiscal deficits can lead to higher public debt, rising interest rates, and inflationary pressures that may undermine economic stability. Balancing short-term economic stimulus against long-term fiscal sustainability remains crucial in managing the pros and cons of fiscal deficits.
Fiscal Policy Strategies for Managing Surplus and Deficit
Fiscal policy strategies for managing a fiscal surplus include increasing public investment, reducing tax rates, and paying down public debt to stimulate economic growth. In contrast, strategies for addressing a fiscal deficit involve cutting government spending, raising taxes, and implementing structural reforms to restore fiscal balance. Effective fiscal management requires timely adjustments to budgetary policies to stabilize the economy and support long-term fiscal sustainability.
Case Studies: Countries with Fiscal Surplus vs Deficit
Countries such as Norway and Singapore exemplify fiscal surplus through prudent management of natural resources and strong sovereign wealth funds, enabling robust economic stability and investment capacity. In contrast, nations like Greece and Argentina have struggled with persistent fiscal deficits driven by high public debt and inefficient government spending, leading to economic crises and reliance on external bailouts. These case studies highlight the critical impact of fiscal discipline and strategic resource allocation on national economic health and sustainability.
Fiscal surplus Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com