Fiscal policy involves government decisions on taxation and spending that influence economic activity. By adjusting public revenues and expenditures, it aims to stabilize growth, control inflation, and reduce unemployment. Discover how effective fiscal policy can shape your economy by exploring the details in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
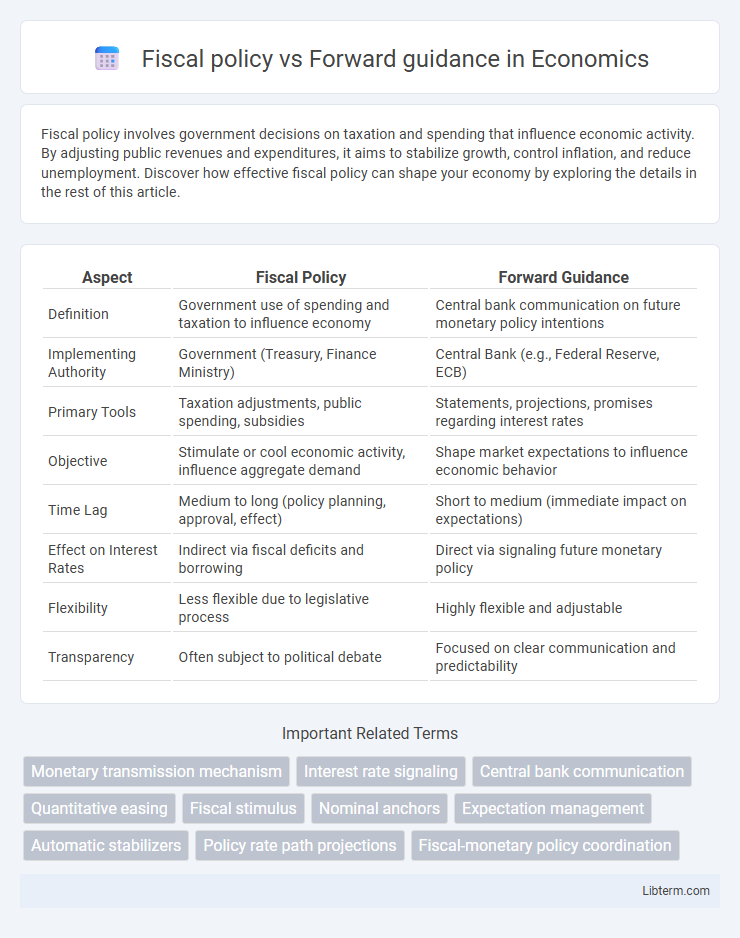
| Aspect | Fiscal Policy | Forward Guidance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Government use of spending and taxation to influence economy | Central bank communication on future monetary policy intentions |
| Implementing Authority | Government (Treasury, Finance Ministry) | Central Bank (e.g., Federal Reserve, ECB) |
| Primary Tools | Taxation adjustments, public spending, subsidies | Statements, projections, promises regarding interest rates |
| Objective | Stimulate or cool economic activity, influence aggregate demand | Shape market expectations to influence economic behavior |
| Time Lag | Medium to long (policy planning, approval, effect) | Short to medium (immediate impact on expectations) |
| Effect on Interest Rates | Indirect via fiscal deficits and borrowing | Direct via signaling future monetary policy |
| Flexibility | Less flexible due to legislative process | Highly flexible and adjustable |
| Transparency | Often subject to political debate | Focused on clear communication and predictability |
Defining Fiscal Policy and Forward Guidance
Fiscal policy involves government decisions on taxation and public spending to influence economic activity, aiming to promote growth, control inflation, and reduce unemployment. Forward guidance refers to central banks' communication strategies that provide expectations about future monetary policy actions to shape market behavior and economic decisions. Both tools serve distinct roles in managing economic stability but operate through different mechanisms and institutional actors.
Core Objectives: Stabilizing the Economy
Fiscal policy aims to stabilize the economy by adjusting government spending and taxation to influence aggregate demand, directly impacting employment and inflation levels. Forward guidance, employed by central banks, focuses on shaping market expectations about future monetary policy to manage inflation and economic growth indirectly. Both tools target economic stabilization but operate through different mechanisms: fiscal policy alters real resources, while forward guidance influences interest rates and investor behavior.
Tools and Mechanisms: Direct vs Indirect Approaches
Fiscal policy utilizes direct tools such as government spending and taxation to influence economic activity by adjusting aggregate demand. Forward guidance employs indirect mechanisms through central bank communications to shape market expectations and influence interest rates and financial conditions. The direct approach in fiscal policy impacts the economy by altering disposable income and investment, while forward guidance steers behavior by managing anticipations about future monetary policy actions.
Impact on Inflation and Economic Growth
Fiscal policy directly influences inflation and economic growth through government spending and taxation, stimulating demand or curbing overheating in the economy. Forward guidance shapes expectations by signaling future monetary policy actions, thereby indirectly affecting inflation and investment decisions. Combining fiscal policy's immediate demand management with forward guidance's role in anchoring inflation expectations can enhance overall economic stability.
Effectiveness During Economic Crises
Fiscal policy directly influences economic recovery during crises through government spending and tax adjustments, providing immediate demand stimulation. Forward guidance, a monetary policy tool, shapes market expectations by communicating future interest rate paths, influencing longer-term investment decisions. Fiscal measures tend to have faster and more tangible impacts on output, while forward guidance supports stability by managing inflation expectations and financial conditions over time.
Time Lags and Implementation Speed
Fiscal policy experiences significant time lags due to legislative approval, budget allocation, and project execution, making its effects slower and less predictable. Forward guidance, as a monetary tool, achieves implementation speed rapidly through central bank announcements, influencing market expectations almost immediately. The disparity in responsiveness highlights forward guidance's advantage in shaping economic behavior promptly, while fiscal policy exerts longer-term structural impacts.
Communication Strategies and Market Expectations
Fiscal policy relies on government announcements about spending and taxation to influence economic activity, but its communication impact is often indirect and delayed due to legislative processes. Forward guidance by central banks uses explicit statements about future monetary policy to shape market expectations and reduce uncertainty, providing a direct and timely signal to investors and consumers. Effective communication strategies in forward guidance enhance credibility and transparency, which are crucial for anchoring market expectations and achieving desired economic outcomes.
Limitations and Risks of Each Approach
Fiscal policy faces limitations such as implementation delays, political constraints, and increased public debt risks, which can reduce its effectiveness in stabilizing the economy. Forward guidance, while useful for shaping market expectations, risks credibility loss if economic conditions change unexpectedly or if central banks are perceived to lack commitment. Both approaches can contribute to financial market volatility if miscommunicated or poorly timed, potentially undermining economic stability.
Case Studies: Historical Applications
The 2009 U.S. fiscal stimulus, the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act, demonstrated how fiscal policy can jumpstart economic growth during recessions, contrasting with the Federal Reserve's forward guidance, which influenced market expectations without immediate spending. Japan's experience in the 1990s exemplifies forward guidance's limits when faced with a liquidity trap, where fiscal policy measures like public works spending were necessary to boost demand. The European Central Bank's use of forward guidance post-2010 sovereign debt crisis highlights how clear communication helped stabilize markets while fiscal austerity constrained economic recovery in several member states.
Policy Synergies: Combining Fiscal Policy and Forward Guidance
Combining fiscal policy and forward guidance creates powerful policy synergies that enhance economic stability and growth. Coordinated fiscal stimulus, such as government spending or tax cuts, paired with central bank forward guidance shapes expectations about future monetary conditions, amplifying the impact on investment and consumption. This integrated approach reduces uncertainty, supports demand, and promotes a more effective transmission of economic policy to achieve targets like inflation control and employment growth.
Fiscal policy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com