Macroprudential regulation strengthens the stability of the financial system by monitoring and addressing systemic risks that could lead to widespread economic disruption. It involves tools such as capital requirements, countercyclical buffers, and stress testing to prevent financial crises and safeguard economic growth. Discover how these regulatory measures impact Your financial environment and the broader economy in the following sections.
Table of Comparison
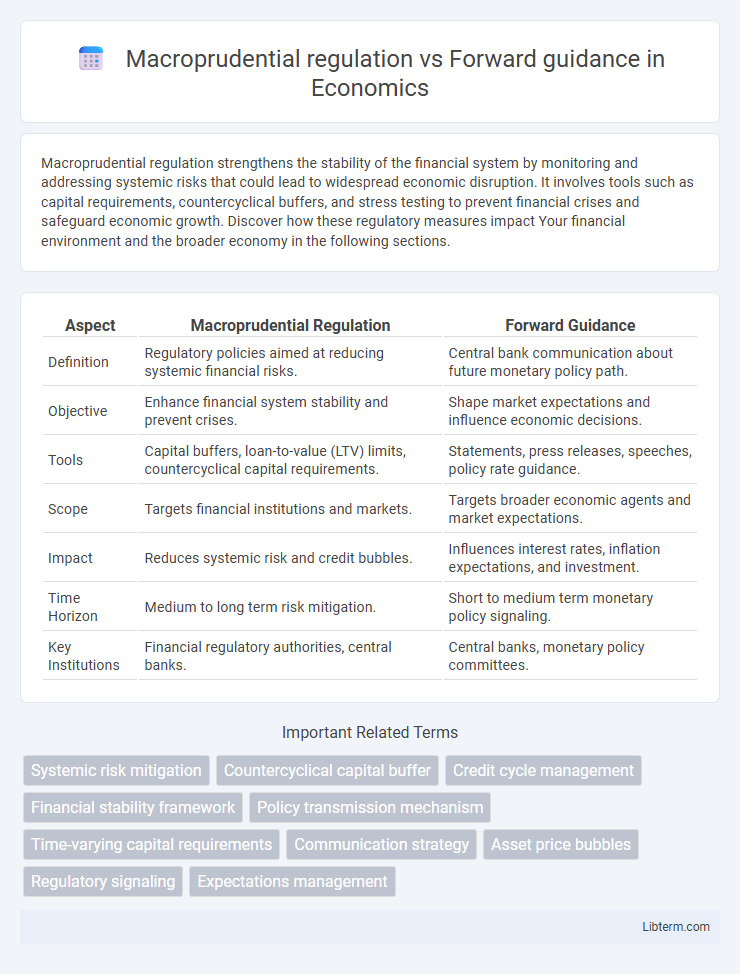
| Aspect | Macroprudential Regulation | Forward Guidance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Regulatory policies aimed at reducing systemic financial risks. | Central bank communication about future monetary policy path. |
| Objective | Enhance financial system stability and prevent crises. | Shape market expectations and influence economic decisions. |
| Tools | Capital buffers, loan-to-value (LTV) limits, countercyclical capital requirements. | Statements, press releases, speeches, policy rate guidance. |
| Scope | Targets financial institutions and markets. | Targets broader economic agents and market expectations. |
| Impact | Reduces systemic risk and credit bubbles. | Influences interest rates, inflation expectations, and investment. |
| Time Horizon | Medium to long term risk mitigation. | Short to medium term monetary policy signaling. |
| Key Institutions | Financial regulatory authorities, central banks. | Central banks, monetary policy committees. |
Introduction to Macroprudential Regulation and Forward Guidance
Macroprudential regulation encompasses policies aimed at safeguarding the financial system's stability by mitigating systemic risks and preventing financial crises through tools such as capital buffers and stress testing. Forward guidance involves central banks communicating anticipated future monetary policy actions to influence market expectations and economic behavior. Both mechanisms play critical roles in enhancing economic resilience, with macroprudential regulation focusing on the structural soundness of financial institutions and forward guidance targeting expectations management and interest rate signaling.
Defining Macroprudential Regulation
Macroprudential regulation involves policies and frameworks designed to mitigate systemic risks and enhance the stability of the financial system by addressing vulnerabilities that affect the entire economy. It focuses on managing risks related to interconnected financial institutions, market infrastructure, and macroeconomic factors to prevent widespread financial crises. Unlike forward guidance, which provides communication on future monetary policy intentions, macroprudential regulation implements targeted tools such as countercyclical capital buffers and stress testing to safeguard economic resilience.
Understanding Forward Guidance in Monetary Policy
Forward guidance in monetary policy involves central banks communicating future policy intentions to influence market expectations and economic behavior, enhancing transparency and reducing uncertainty. This tool helps manage inflation and stabilize financial markets by signaling the likely path of interest rates, contrasting with macroprudential regulation which focuses on systemic risk and financial stability through capital requirements and leverage limits. Effective forward guidance relies on clear, credible communication to shape investor and consumer decisions, supporting monetary policy transmission.
Objectives of Macroprudential Regulation
Macroprudential regulation aims to enhance the stability of the financial system by addressing systemic risks and preventing financial crises through tools like countercyclical capital buffers and stress testing. It focuses on mitigating risks that arise from interconnectedness in financial institutions and market disruptions, ensuring resilience against shocks. Unlike forward guidance, which provides information on future monetary policy intentions to influence expectations, macroprudential regulation targets the robustness and soundness of the financial sector itself.
Goals of Forward Guidance Strategies
Forward guidance strategies aim to influence market expectations about future monetary policy to stabilize inflation and support economic growth by providing clear and credible signals on the central bank's future interest rate path. These strategies help reduce uncertainty, shape consumption and investment decisions, and enhance the effectiveness of monetary policy, particularly during periods of low interest rates. Forward guidance complements macroprudential regulation by managing expectations and financial conditions without directly imposing constraints on financial institutions or markets.
Key Tools and Instruments of Macroprudential Regulation
Macroprudential regulation employs key tools such as countercyclical capital buffers, loan-to-value (LTV) ratios, and sectoral capital requirements to mitigate systemic financial risks and enhance banking system resilience. Instruments like stress testing, dynamic provisioning, and limits on interconnected exposures help contain systemic vulnerabilities and prevent asset bubbles. Forward guidance, by contrast, primarily influences market expectations and economic behavior through communication strategies rather than direct regulatory measures.
Communication Channels in Forward Guidance
Forward guidance relies heavily on communication channels such as central bank speeches, press releases, and policy statements to shape market expectations and influence economic behavior. These channels ensure transparency and reduce uncertainty by providing explicit information about future monetary policy paths. Effective forward guidance leverages consistent, clear messages disseminated through multiple platforms to anchor inflation expectations and enhance policy credibility.
Comparative Effectiveness: Stability vs Expectations
Macroprudential regulation targets systemic financial stability by imposing capital requirements, leverage limits, and stress testing to mitigate risks across the banking sector. Forward guidance shapes market expectations about future monetary policy by communicating central bank intentions on interest rates and inflation targets, influencing investor behavior and economic forecasts. While macroprudential tools directly strengthen financial system resilience, forward guidance indirectly stabilizes markets by managing expectations and reducing uncertainty, making their comparative effectiveness dependent on whether the goal is robustness or anticipatory market behavior adjustment.
Case Studies: Global Applications and Outcomes
Macroprudential regulation has been effectively implemented in countries like South Korea and New Zealand to mitigate systemic risks by imposing countercyclical capital buffers and loan-to-value ratio restrictions, resulting in enhanced financial stability during economic downturns. Forward guidance, prominently used by the Federal Reserve and the European Central Bank, has improved market predictability and influenced long-term interest rates by clearly communicating future monetary policy intentions. Case studies reveal that combining macroprudential tools with forward guidance can optimize both financial stability and economic growth by addressing credit cycles and managing inflation expectations.
Policy Trade-offs and Future Challenges
Macroprudential regulation aims to safeguard financial stability by addressing systemic risks through tools like capital buffers and loan-to-value ratios, while forward guidance influences market expectations by communicating central banks' future policy intentions. Trade-offs emerge as macroprudential policies may restrict credit growth and economic expansion, whereas forward guidance risks misinterpretation, potentially reducing policy effectiveness during economic shocks. Future challenges include calibrating macroprudential measures without stifling innovation and ensuring forward guidance remains credible in volatile markets amid evolving global financial conditions.
Macroprudential regulation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com