Book value represents the net asset value of a company calculated by subtracting total liabilities from total assets, reflecting its intrinsic worth on the balance sheet. It serves as a key indicator for investors to assess whether a stock is undervalued or overvalued compared to its market price. Explore the full article to understand how book value impacts your investment decisions and financial analysis.
Table of Comparison
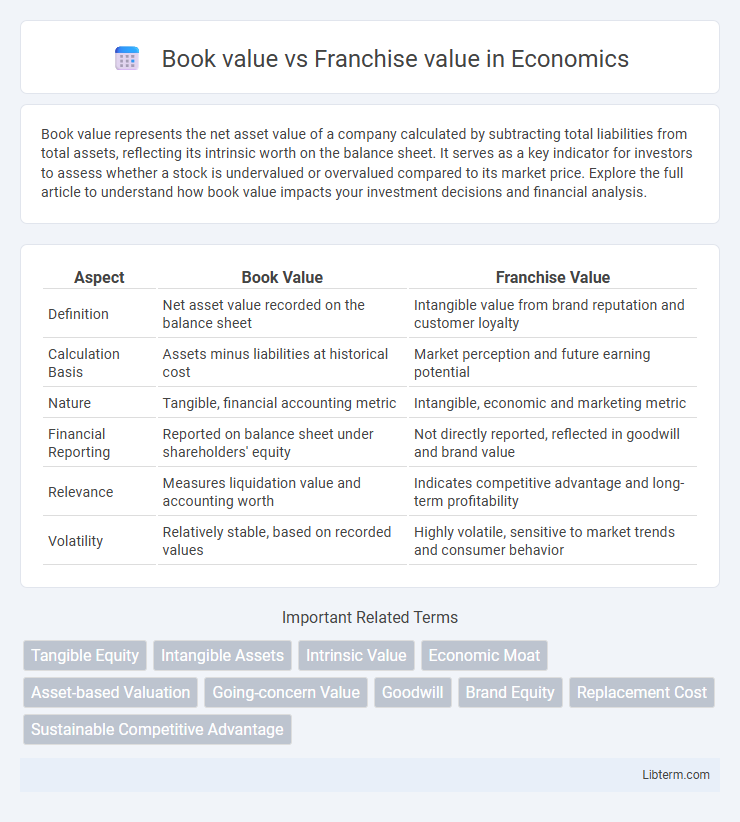
| Aspect | Book Value | Franchise Value |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Net asset value recorded on the balance sheet | Intangible value from brand reputation and customer loyalty |
| Calculation Basis | Assets minus liabilities at historical cost | Market perception and future earning potential |
| Nature | Tangible, financial accounting metric | Intangible, economic and marketing metric |
| Financial Reporting | Reported on balance sheet under shareholders' equity | Not directly reported, reflected in goodwill and brand value |
| Relevance | Measures liquidation value and accounting worth | Indicates competitive advantage and long-term profitability |
| Volatility | Relatively stable, based on recorded values | Highly volatile, sensitive to market trends and consumer behavior |
Understanding Book Value: Definition and Calculation
Book value represents a company's net asset value, calculated by subtracting total liabilities from total assets as recorded on the balance sheet. This accounting metric reflects the historical cost of assets minus depreciation and is critical for evaluating a firm's intrinsic worth. Investors use book value to compare against market value, assessing whether a stock is undervalued or overvalued based on tangible asset strength.
Decoding Franchise Value: Meaning and Significance
Franchise value represents the added worth a business gains from its established brand recognition, customer loyalty, and market position beyond its book value, which reflects the net asset value recorded on the balance sheet. Decoding franchise value involves analyzing intangible assets such as brand equity, intellectual property, and customer relationships that contribute to long-term profitability and competitive advantage. Understanding franchise value is crucial for investors and management in assessing a company's true economic potential and strategic growth opportunities.
Key Differences Between Book Value and Franchise Value
Book value represents a company's net asset value calculated as total assets minus total liabilities, reflecting tangible financial worth on the balance sheet. Franchise value, however, is an intangible asset encompassing the brand reputation, customer loyalty, and proprietary advantages that contribute to earning potential beyond physical assets. The key difference lies in book value's focus on measurable, historical cost-based figures, whereas franchise value captures future-oriented, non-physical benefits driving competitive advantage and profitability.
Importance of Book Value in Financial Analysis
Book value represents a company's net asset value, essential for assessing its financial health and stability by reflecting tangible assets minus liabilities. In financial analysis, book value serves as a critical benchmark to evaluate whether a firm's stock is undervalued or overvalued relative to its actual worth. Franchise value, often linked to intangible assets and brand strength, complements but does not replace the concrete assessment provided by book value in fundamental analysis.
The Role of Franchise Value in Business Valuation
Franchise value represents the premium a business commands beyond its book value, reflecting intangible assets such as brand reputation, customer loyalty, and market position. This value plays a critical role in business valuation by capturing future earning potential not evident on balance sheets. Investors and analysts prioritize franchise value to assess competitive advantages and sustainable profitability in the marketplace.
Book Value vs Franchise Value: Which Matters to Investors?
Book value represents a company's net asset value calculated by subtracting liabilities from total assets, providing a tangible baseline for assessing financial health. Franchise value captures intangible assets such as brand reputation, customer loyalty, and market position, often driving premium valuation beyond book value. Investors prioritize franchise value when assessing long-term growth potential and competitive advantage, while book value remains critical for evaluating liquidation scenarios and accounting stability.
Impact of Intangible Assets on Franchise Value
Intangible assets such as brand reputation, customer loyalty, and intellectual property significantly enhance franchise value beyond the tangible book value of physical assets and liabilities. These intangible factors contribute to sustained competitive advantage and future earning potential, resulting in a franchise value often exceeding reported book value. Accurate valuation of intangible assets is essential for investors to gauge the true economic worth and growth prospects of franchise businesses.
Factors Influencing Changes in Book and Franchise Values
Book value changes primarily due to asset depreciation, capital expenditures, and retained earnings adjustments, reflecting a company's net asset worth on the balance sheet. Franchise value fluctuates based on brand strength, customer loyalty, market position, and future earning potential, influenced by competitive dynamics and consumer perception. Both values are impacted by economic conditions, management decisions, and industry trends that affect asset performance and intangible asset valuation.
Real-World Examples: Book Value vs Franchise Value
Book value represents a company's net asset value as recorded on the balance sheet, often used in capital-intensive industries like manufacturing, where physical assets dominate valuation. Franchise value reflects the premium derived from brand strength and customer loyalty, exemplified by companies such as McDonald's, whose intangible assets far exceed their book value. Real-world examples show Walmart's book value aligns closely with its physical inventory and property, whereas its franchise value arises from its extensive distribution network and brand reputation.
How to Incorporate Both Values in Investment Decisions
Incorporating book value and franchise value in investment decisions requires evaluating tangible assets alongside intangible competitive advantages. Book value provides a baseline of a company's net asset worth, while franchise value captures brand strength, customer loyalty, and future earning potential. Balancing these metrics allows investors to assess both the liquidation value and long-term profitability prospects, optimizing portfolio returns.
Book value Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com