Layoffs can significantly impact employee morale and company productivity, often resulting from economic downturns or organizational restructuring. Understanding the causes and strategies for managing layoffs helps businesses minimize negative effects and support affected workers effectively. Explore the rest of the article to learn how your organization can navigate layoffs with compassion and efficiency.
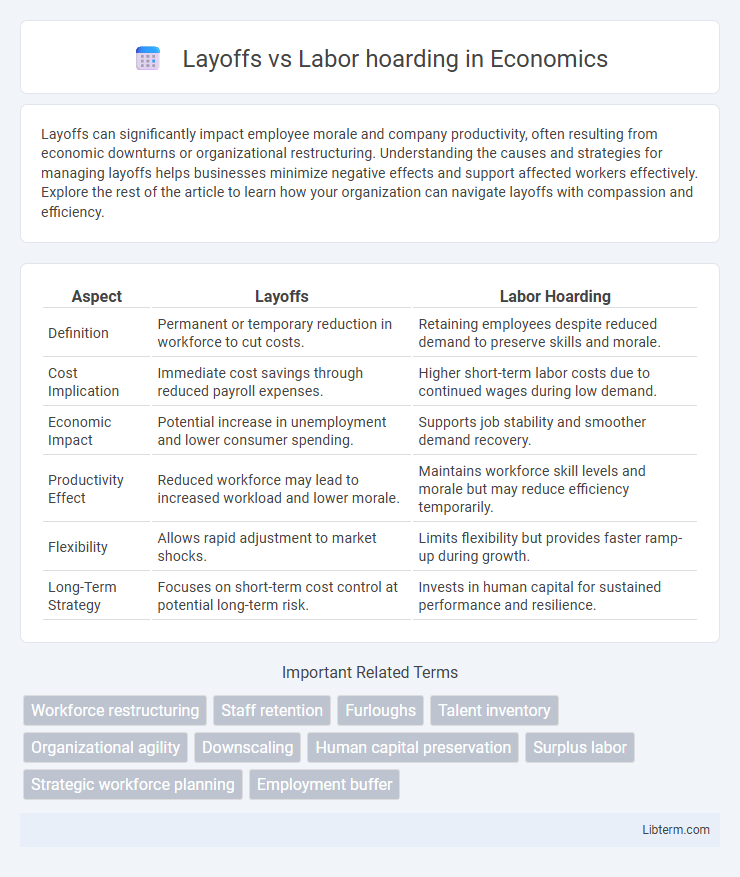
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Layoffs | Labor Hoarding |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Permanent or temporary reduction in workforce to cut costs. | Retaining employees despite reduced demand to preserve skills and morale. |
| Cost Implication | Immediate cost savings through reduced payroll expenses. | Higher short-term labor costs due to continued wages during low demand. |
| Economic Impact | Potential increase in unemployment and lower consumer spending. | Supports job stability and smoother demand recovery. |
| Productivity Effect | Reduced workforce may lead to increased workload and lower morale. | Maintains workforce skill levels and morale but may reduce efficiency temporarily. |
| Flexibility | Allows rapid adjustment to market shocks. | Limits flexibility but provides faster ramp-up during growth. |
| Long-Term Strategy | Focuses on short-term cost control at potential long-term risk. | Invests in human capital for sustained performance and resilience. |
Understanding Layoffs: Definition and Key Drivers
Layoffs refer to the temporary or permanent termination of employees by an organization, typically driven by economic downturns, technological changes, or shifts in market demand. Key drivers include cost reduction objectives, restructuring efforts, and the need to improve operational efficiency during periods of financial uncertainty. Understanding these factors helps businesses balance workforce optimization while managing long-term talent retention.
What is Labor Hoarding? An Overview
Labor hoarding is the practice where companies retain more employees than necessary during economic downturns or periods of reduced demand to avoid future hiring and training costs. This strategy helps preserve organizational knowledge and maintain workforce morale while ensuring readiness for demand recovery. Unlike layoffs, labor hoarding can increase short-term labor costs but potentially improves long-term productivity and stability.
Economic Conditions Influencing Workforce Decisions
Economic downturns often prompt layoffs as companies reduce costs to maintain financial stability, while labor hoarding occurs when firms retain employees despite decreased demand to preserve skills and avoid future rehiring expenses. During recessions, layoffs provide immediate budget relief but risk long-term productivity losses, whereas labor hoarding supports smoother recovery in improving economic conditions. Business decisions between layoffs and labor hoarding hinge on factors such as cash flow, industry volatility, and projections of market demand.
Short-Term vs Long-Term Impacts on Companies
Layoffs provide immediate cost savings by reducing payroll expenses, improving short-term financial stability for companies facing economic downturns. Labor hoarding, maintaining workforce levels despite lower demand, supports long-term employee retention, skill preservation, and faster recovery when market conditions improve. Companies that prioritize labor hoarding often benefit from sustained productivity and reduced rehiring costs, while those relying on layoffs risk losing institutional knowledge and incurring higher future recruitment expenses.
Employee Morale: Layoffs vs Labor Hoarding
Employee morale often declines sharply after layoffs due to increased job insecurity and workload pressures on remaining staff. Labor hoarding, by contrast, helps maintain workforce stability and can boost morale by preserving job security and demonstrating organizational commitment to employees. Companies practicing labor hoarding tend to foster higher engagement, reducing turnover risks and enhancing overall productivity.
Financial Implications for Businesses
Layoffs reduce immediate labor costs, improving short-term cash flow but can lead to increased rehiring and training expenses when demand rebounds. Labor hoarding maintains workforce stability, preserving institutional knowledge and minimizing turnover costs, but raises ongoing payroll expenses during downturns. Balancing these strategies impacts profitability, with layoffs offering quick financial relief and labor hoarding supporting long-term operational resilience.
Productivity and Skill Retention Considerations
Layoffs can boost short-term productivity by reducing labor costs but often lead to the loss of critical skills and institutional knowledge, which hampers long-term innovation and efficiency. Labor hoarding preserves employee skills and organizational expertise, enabling quicker recovery and sustained productivity when demand rebounds. Maintaining a skilled workforce through labor hoarding supports knowledge retention and continuous improvement, crucial for competitive advantage in fluctuating markets.
Strategic Decision-Making: When to Lay Off or Hoard Labor
Strategic decision-making around layoffs versus labor hoarding hinges on forecasting demand volatility and financial resilience; firms experiencing short-term demand drops may choose labor hoarding to preserve skilled workers and avoid rehiring costs. Conversely, organizations facing prolonged market downturns might opt for layoffs to reduce fixed labor costs and maintain cash flow flexibility. Data-driven analysis of labor market conditions, cost implications, and recovery timelines informs whether retaining employees or downsizing aligns with long-term competitive advantage.
Industry-Specific Trends in Workforce Management
Manufacturing industries often lean towards labor hoarding during economic downturns to preserve skilled labor and reduce rehiring costs, whereas tech sectors may opt for layoffs to quickly adjust to market demands and technological shifts. Retail and hospitality industries show a higher tendency for layoffs due to fluctuating consumer demand and seasonal variability. Understanding these industry-specific trends is crucial for workforce management strategies aimed at balancing cost control and employee retention.
Future Outlook: Balancing Workforce Stability and Cost Control
Forecasting future workforce strategies highlights a shift toward labor hoarding as companies aim to maintain employee skills and morale in volatile markets, reducing rehiring costs and preserving institutional knowledge. Economic uncertainty and technological advancements drive businesses to balance layoffs with labor hoarding to optimize operational flexibility while controlling expenses. Data from McKinsey reveals organizations practicing strategic labor hoarding experience higher long-term productivity and cost-efficiency compared to those relying heavily on layoffs.
Layoffs Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com