Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) plays a crucial role in driving economic growth by bringing capital, technology, and expertise into host countries. It helps create jobs, enhance infrastructure, and boost productivity, making it vital for both developing and developed economies. Discover how FDI impacts your economy and the opportunities it can unlock by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
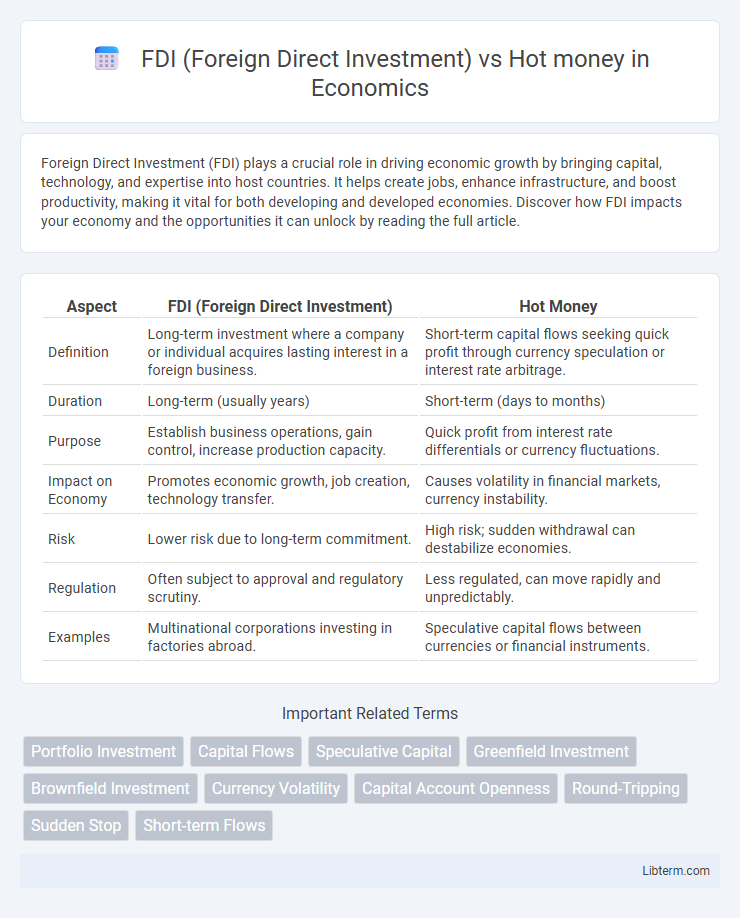
| Aspect | FDI (Foreign Direct Investment) | Hot Money |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Long-term investment where a company or individual acquires lasting interest in a foreign business. | Short-term capital flows seeking quick profit through currency speculation or interest rate arbitrage. |
| Duration | Long-term (usually years) | Short-term (days to months) |
| Purpose | Establish business operations, gain control, increase production capacity. | Quick profit from interest rate differentials or currency fluctuations. |
| Impact on Economy | Promotes economic growth, job creation, technology transfer. | Causes volatility in financial markets, currency instability. |
| Risk | Lower risk due to long-term commitment. | High risk; sudden withdrawal can destabilize economies. |
| Regulation | Often subject to approval and regulatory scrutiny. | Less regulated, can move rapidly and unpredictably. |
| Examples | Multinational corporations investing in factories abroad. | Speculative capital flows between currencies or financial instruments. |
Understanding FDI and Hot Money: Key Definitions
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) involves long-term capital investment by a foreign entity in a country's productive assets, including acquisitions, establishing subsidiaries, or joint ventures, aimed at gaining lasting management control. Hot money refers to short-term capital flows driven by speculative motives, rapidly moving to exploit interest rate differentials or currency fluctuations without establishing a sustained economic presence. Understanding FDI and hot money is crucial for analyzing their distinct impacts on economic stability, growth, and financial markets.
Main Characteristics of FDI
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) involves long-term capital inflows committed to acquiring lasting interest and control in foreign enterprises, promoting stable economic growth and technology transfer. Unlike hot money, which is short-term, speculative, and highly volatile, FDI emphasizes strategic investment with greater risk tolerance and regulatory compliance. Key characteristics include direct managerial influence, sustained impact on the host country's economy, and contribution to employment and infrastructure development.
Main Characteristics of Hot Money
Hot money refers to short-term capital flows that rapidly move in and out of financial markets seeking quick profits from interest rate differentials or currency speculation, unlike Foreign Direct Investment (FDI), which involves long-term commitments in physical assets or business operations. Characterized by high volatility and sensitivity to market conditions, hot money can cause sudden exchange rate fluctuations and financial instability in recipient countries. Its main attributes include liquidity, short investment horizons, and susceptibility to rapid withdrawal during economic uncertainty.
Sources of FDI and Hot Money
Sources of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) primarily include multinational corporations investing in physical assets such as factories, infrastructure, and technology in the host country, driven by strategic long-term business interests. Hot money, by contrast, originates from institutional investors and speculators seeking short-term financial gains through rapid inflows and outflows in foreign exchange markets, bonds, and equities. FDI flows tend to come from developed economies with strong industrial bases, while hot money often originates from international hedge funds, banks, and portfolio investors looking for quick returns.
Economic Impact: FDI vs Hot Money
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) provides stable capital inflows that promote long-term economic growth by enhancing infrastructure, technology transfer, and employment opportunities. Hot money, characterized by short-term speculative capital movements, often leads to financial market volatility and currency instability, undermining sustainable economic development. Unlike FDI, hot money does not contribute significantly to productive capacity or enduring economic advances.
Advantages and Disadvantages of FDI
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) provides long-term capital inflow, technology transfer, and job creation, fostering sustainable economic growth. Its advantages include stable investment, local infrastructure development, and improved balance of payments, while disadvantages encompass foreign control over domestic enterprises and potential profit repatriation causing economic dependency. Unlike hot money, which is short-term and speculative capital causing market volatility, FDI offers more predictable and strategic economic benefits.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Hot Money
Hot money involves short-term capital flows seeking quick profits through interest rate differentials or currency speculation, providing liquidity and potentially boosting asset prices in host countries. However, its volatility can lead to sudden capital flight, causing exchange rate instability and undermining economic growth. Unlike FDI, which brings long-term investment and technology transfer, hot money lacks sustainable development benefits and may exacerbate financial crises.
Risk Factors Associated with Hot Money Inflows
Hot money inflows, characterized by short-term, speculative capital movements, pose significant financial risks compared to stable Foreign Direct Investment (FDI). These inflows can lead to heightened market volatility, sudden capital flight, currency instability, and overheating of asset prices, undermining economic stability. Unlike FDI, which typically involves long-term investment and technology transfer, hot money's unpredictability can disrupt monetary policy and complicate economic planning.
Policy Approaches to Regulate FDI and Hot Money
Policy approaches to regulate Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) typically emphasize long-term economic benefits by implementing screening mechanisms, local content requirements, and sector-specific caps to ensure sustainable development and technology transfer. In contrast, hot money, characterized by short-term speculative capital flows, requires tighter capital controls, transaction taxes, and macroprudential regulations to prevent financial volatility and sudden currency fluctuations. Coordinated global and domestic regulatory frameworks balance attracting stable FDI while mitigating risks associated with volatile hot money inflows.
Case Studies: FDI and Hot Money in Emerging Markets
Emerging markets like India and Brazil demonstrate that Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) provides long-term capital, technology transfer, and employment opportunities, fostering sustainable economic growth. In contrast, hot money flows, exemplified by rapid capital movements in countries like Thailand during the 1997 Asian Financial Crisis, contribute to market volatility and financial instability due to their speculative and short-term nature. Case studies reveal that while FDI stabilizes economic development, reliance on hot money exposes emerging markets to sudden capital flight and currency crises.
FDI (Foreign Direct Investment) Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com