Intrinsic value refers to the inherent worth of an asset, independent of its market price or external factors. It is often used in finance and investing to assess a stock or security based on fundamentals such as cash flow, dividends, and growth potential. Explore this article to understand how intrinsic value can guide your investment decisions effectively.
Table of Comparison
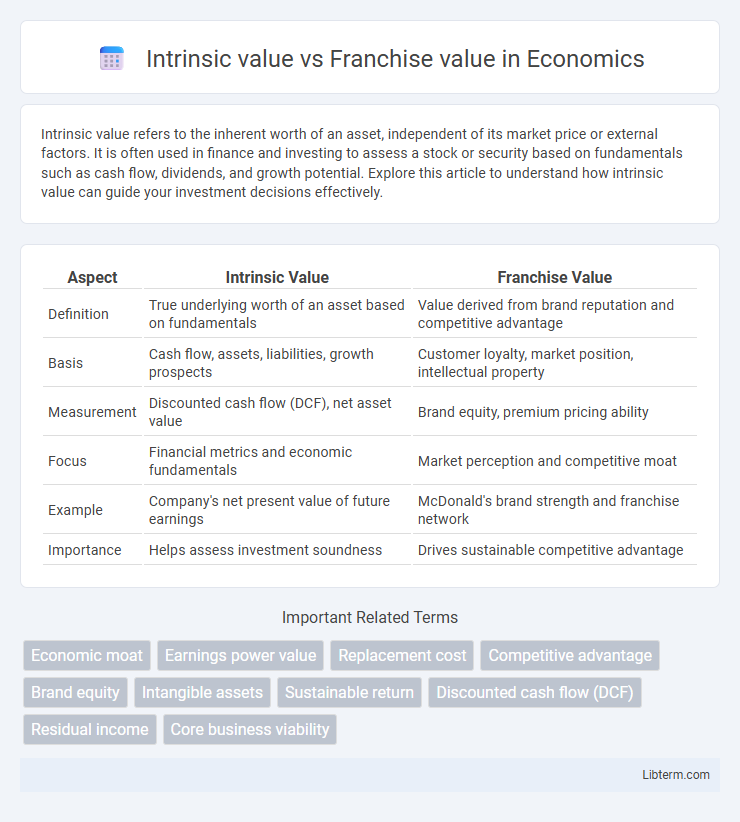
| Aspect | Intrinsic Value | Franchise Value |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | True underlying worth of an asset based on fundamentals | Value derived from brand reputation and competitive advantage |
| Basis | Cash flow, assets, liabilities, growth prospects | Customer loyalty, market position, intellectual property |
| Measurement | Discounted cash flow (DCF), net asset value | Brand equity, premium pricing ability |
| Focus | Financial metrics and economic fundamentals | Market perception and competitive moat |
| Example | Company's net present value of future earnings | McDonald's brand strength and franchise network |
| Importance | Helps assess investment soundness | Drives sustainable competitive advantage |
Introduction to Intrinsic Value and Franchise Value
Intrinsic value represents the fundamental worth of an asset based on its underlying financial metrics such as cash flow, earnings, and growth potential, serving as a critical benchmark in investment analysis. Franchise value, on the other hand, encapsulates the premium derived from a company's brand strength, market positioning, and competitive advantages that enable sustained above-average returns. Understanding the distinction between intrinsic and franchise value is essential for accurately assessing a company's true long-term investment potential.
Defining Intrinsic Value
Intrinsic value represents the fundamental worth of an asset based on its underlying financial metrics, including cash flow, earnings, and tangible assets, independent of market price. It reflects the true economic value derived from an asset's ability to generate future benefits, providing investors with a baseline for valuation. Understanding intrinsic value enables better assessment of whether an investment is undervalued or overvalued relative to its current market trading level.
Understanding Franchise Value
Franchise value represents the intangible competitive advantages a company holds, such as brand reputation, customer loyalty, and market position, which drive sustainable earnings beyond intrinsic asset value. Unlike intrinsic value, which is based on tangible and measurable assets and earnings, franchise value captures the premium investors are willing to pay for these durable economic moats. Analyzing franchise value requires assessing factors like brand strength, recurring revenue streams, and barriers to entry that contribute to long-term profitability and superior returns.
Key Differences Between Intrinsic and Franchise Value
Intrinsic value refers to the fundamental worth of an asset based on its tangible and intangible attributes, such as cash flow, assets, and earnings potential, while franchise value represents the premium a company commands due to its brand strength, customer loyalty, and competitive advantages. Intrinsic value is grounded in quantitative financial metrics and discounted cash flow analysis, whereas franchise value captures qualitative factors like market position and intellectual property that contribute to sustained profitability. Understanding the distinction aids investors in evaluating whether a stock is undervalued based on hard financial data or overvalued due to brand-specific benefits.
Methods for Calculating Intrinsic Value
Intrinsic value is calculated using discounted cash flow (DCF) analysis, which estimates the present value of expected future cash flows generated by the business. Another method involves adjusting the net asset value by considering the company's earnings power and intangible assets like patents or brand loyalty. These approaches contrast with franchise value estimation, which focuses on competitive advantages and sustainable profitability derived from market position.
Evaluating Franchise Value in Business Analysis
Evaluating franchise value in business analysis involves assessing the brand strength, customer loyalty, and competitive advantages that generate sustainable excess returns beyond intrinsic asset values. Franchise value reflects intangible assets such as reputation, unique business models, and market positioning that enable pricing power and high profitability over time. Accurate measurement requires analyzing historical financial performance, market share stability, and the durability of competitive moats to estimate future cash flow premiums attributable to the franchise.
The Role of Competitive Moats in Franchise Value
Competitive moats significantly enhance franchise value by providing durable advantages such as brand strength, customer loyalty, and cost barriers that protect market share from competitors. These moats create a sustainable cash flow stream and justify premium valuations beyond intrinsic value based purely on assets or earnings. Intrinsic value measures a company's fundamental worth, while franchise value captures the long-term benefits derived from these unique competitive positions.
Real-World Examples: Intrinsic vs Franchise Value
Intrinsic value measures a company's fundamental worth based on tangible assets and earnings potential, as seen in utility firms with steady cash flows but limited growth. Franchise value reflects brand strength and competitive advantages, exemplified by companies like Coca-Cola, whose strong brand loyalty and pricing power drive long-term profitability beyond intrinsic asset value. Comparing ExxonMobil's intrinsic value driven by oil reserves to Starbucks' franchise value rooted in customer experience illustrates how investors weigh foundational assets against intangible competitive moats.
Implications for Investors and Analysts
Intrinsic value reflects a company's true worth based on fundamental financial metrics like discounted cash flows, providing investors a baseline for undervaluation or overvaluation. Franchise value captures the competitive advantages and brand strength that enable sustained above-average returns, crucial for analysts assessing long-term growth potential. Understanding both values helps investors allocate capital more efficiently by distinguishing between companies with solid fundamentals and those with durable competitive moats.
Conclusion: Balancing Intrinsic and Franchise Perspectives
Balancing intrinsic value and franchise value requires recognizing intrinsic value as the measure of a company's fundamental worth based on assets, earnings, and cash flow, while franchise value captures the competitive advantages and brand strength that drive long-term growth. Investors should integrate both perspectives to form a comprehensive valuation that reflects not only current financial health but also the sustainable profitability derived from market position. Achieving this balance enhances investment decisions by combining quantitative analysis with strategic insights into firm durability.
Intrinsic value Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com