A short squeeze occurs when a heavily shorted stock's price rapidly rises, forcing short sellers to buy shares to cover their positions, driving the price even higher. This phenomenon can lead to extreme market volatility and significant losses for traders betting against the stock. Discover how a short squeeze unfolds and what strategies you can use to protect your investments in the full article.
Table of Comparison
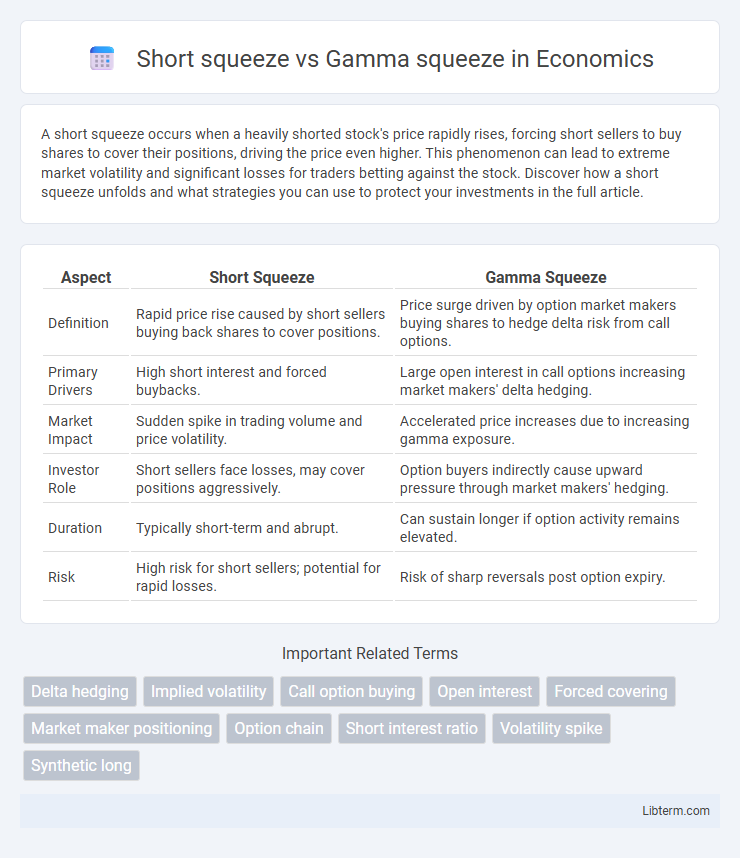
| Aspect | Short Squeeze | Gamma Squeeze |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Rapid price rise caused by short sellers buying back shares to cover positions. | Price surge driven by option market makers buying shares to hedge delta risk from call options. |
| Primary Drivers | High short interest and forced buybacks. | Large open interest in call options increasing market makers' delta hedging. |
| Market Impact | Sudden spike in trading volume and price volatility. | Accelerated price increases due to increasing gamma exposure. |
| Investor Role | Short sellers face losses, may cover positions aggressively. | Option buyers indirectly cause upward pressure through market makers' hedging. |
| Duration | Typically short-term and abrupt. | Can sustain longer if option activity remains elevated. |
| Risk | High risk for short sellers; potential for rapid losses. | Risk of sharp reversals post option expiry. |
Understanding Short Squeeze: Definition and Mechanism
A short squeeze occurs when a heavily shorted stock's price rapidly increases, forcing short sellers to buy shares to cover their positions, which further escalates the price surge. This mechanism intensifies market volatility as the demand for shares outpaces supply due to margin calls and stop-loss triggers. Understanding this dynamic is crucial for investors, as it highlights the risks of short selling in rapidly moving markets.
What is a Gamma Squeeze?
A gamma squeeze occurs when options market makers hedge their positions by buying the underlying stock as its price rises, driven by increasing demand for call options and rising implied volatility. This buying pressure accelerates the stock's price movement, leading to rapid upward momentum beyond fundamental valuation. Unlike a short squeeze, which is fueled by short sellers covering their positions, a gamma squeeze is primarily caused by the dynamic hedging activities related to options trading.
Key Differences Between Short Squeeze and Gamma Squeeze
Short squeeze occurs when heavily shorted stocks experience rapid price increases due to short sellers buying shares to cover their positions, forcing more buying pressure. Gamma squeeze involves options market makers buying the underlying stock to hedge their positions as option prices move, amplifying upward momentum. Key differences include the primary drivers: short sellers covering positions in short squeezes versus options hedging by market makers in gamma squeezes.
How Short Squeezes Impact Stock Prices
Short squeezes occur when heavily shorted stocks experience a rapid price increase as short sellers buy shares to cover their positions, driving demand and pushing prices higher. This surge often triggers a cascading effect, forcing more shorts to cover, amplifying the price spike. Gamma squeezes, influenced by options market dynamics, also escalate stock prices by causing market makers to buy shares to hedge their positions, but the impact of short squeezes is primarily rooted in the rush among short sellers to exit losing trades.
The Role of Options in Gamma Squeezes
Options play a crucial role in gamma squeezes by forcing market makers to buy underlying shares as the stock price nears the option's strike price, causing rapid price increases. This occurs because market makers hedge their exposure by purchasing shares to maintain delta neutrality, intensifying upward momentum. Gamma squeezes differ from short squeezes since they stem primarily from options activity rather than excessive short selling.
Signs and Indicators of an Approaching Short Squeeze
Rapid increases in stock price accompanied by unusually high trading volumes often signal an approaching short squeeze as short sellers rush to cover positions to minimize losses. A surge in the short interest ratio, showing a substantial percentage of shares sold short relative to average daily volume, indicates vulnerability to a short squeeze. Monitor for sharp upticks in call option buying, which may suggest a gamma squeeze amplifying upward price pressure, often preempting or coinciding with a short squeeze event.
Gamma Exposure: Why It Matters for Traders
Gamma exposure reflects the sensitivity of option delta to underlying price changes, critically influencing market volatility and price dynamics during short squeezes and gamma squeezes. Traders monitor gamma exposure to anticipate rapid shifts in option hedging demands, which can exacerbate price movements and fuel extreme squeezes. Understanding gamma exposure enables traders to manage risk effectively and capitalize on potential short-term volatility spikes driven by complex options activity.
Famous Examples of Short and Gamma Squeezes
The GameStop (GME) short squeeze in early 2021 highlighted a massive surge in stock price as retail investors targeted heavily shorted shares, forcing short sellers to cover positions and amplifying the rally. In contrast, the Tesla (TSLA) gamma squeeze in 2020 demonstrated how options market makers hedging their positions drove the underlying stock price higher when call option volumes surged, creating feedback loops in price movements. Both events underscore distinctive market mechanics: short squeezes rely on forced buybacks from short sellers, while gamma squeezes stem from options hedging dynamics influencing equity price volatility.
Risks and Rewards: Trading Squeezes
Short squeezes involve a rapid price increase triggered when short sellers rush to cover positions, risking significant losses if unprepared but providing high rewards for early buyers. Gamma squeezes occur when options market makers hedge their positions, driving up stock prices and creating volatility that can lead to swift gains or sharp declines. Both trading squeezes carry elevated risks due to unpredictable price spikes and require careful risk management to capitalize on potential rewards.
Strategies to Navigate Short and Gamma Squeezy Markets
Short squeeze strategies focus on identifying heavily shorted stocks with rising buy volume to capitalize on rapid price surges, employing tight stop-losses to manage risk during volatile rebounds. Gamma squeeze tactics revolve around tracking options market activity, especially large call option buying that forces market makers to hedge by purchasing shares, amplifying upward price pressure. Combining real-time options data analysis with short interest metrics enables traders to navigate both short and gamma squeezes effectively, optimizing entry and exit points while minimizing downside exposure.
Short squeeze Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com